Process for producing sintered ore and sintering machine
A manufacturing method and technology of sintered ore, applied to furnaces, lighting and heating equipment, furnace types, etc., can solve the problems of prolonged high temperature retention time, reduced ventilation of combustion air, and inability to obtain mixed gas, etc., to achieve high cold strength, The effect of stable operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
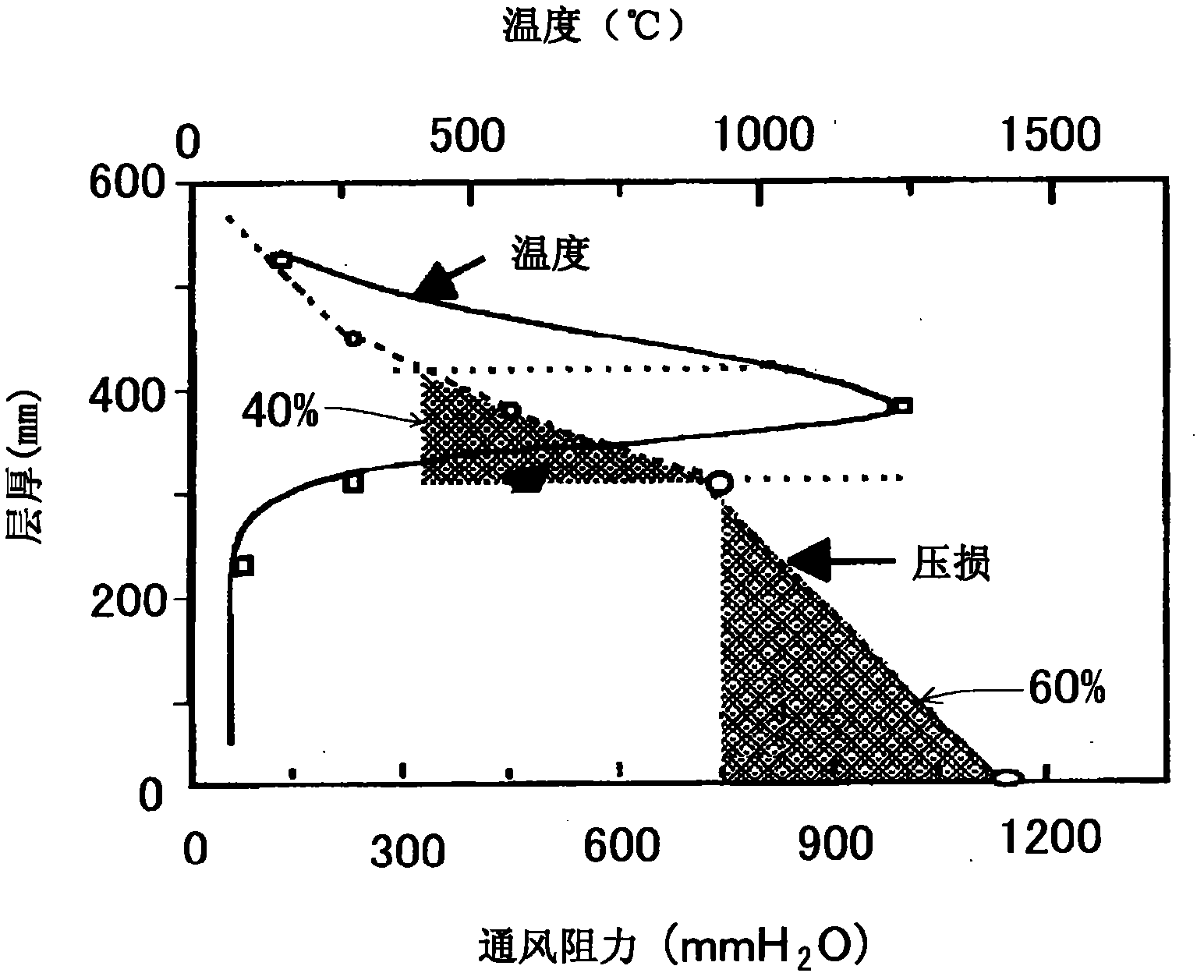
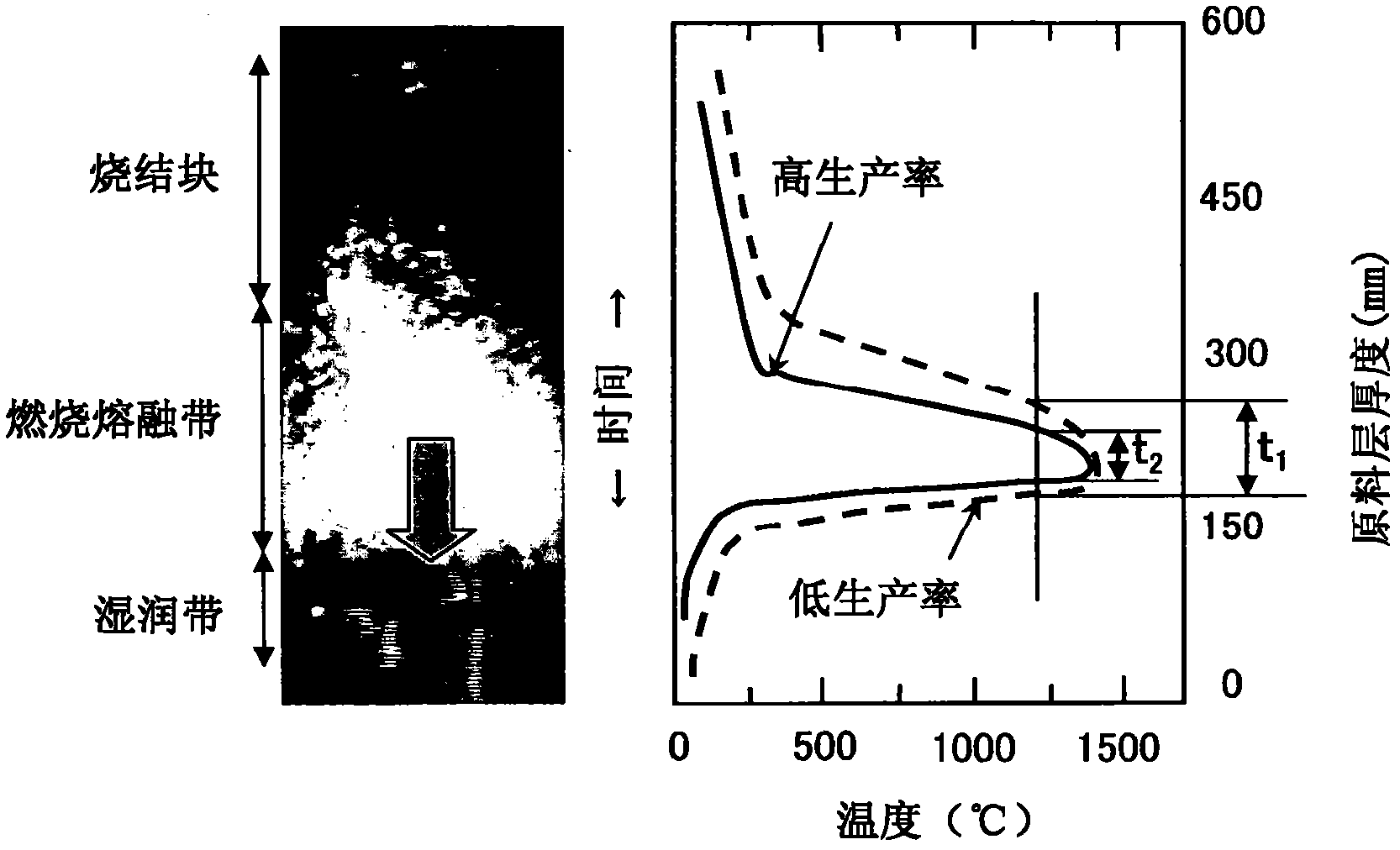
[0316] use Figure 28In the test panel shown, coke oven gas (C gas) diluted to 1 to 2.5% by volume was used as the gas fuel, and the other conditions were the same as the above-mentioned experimental conditions (paragraph 0099), and a carbon material (coke) containing 5% by mass was carried out. The sintered disk test of the sintered raw material. The result is shown in Figure 51 . As shown in the figure, when using C gas diluted according to the method of the present invention, once the concentration of C gas is increased, the width (thickness) of the combustion zone is significantly expanded, and while the yield and productivity are improved, the low-temperature strength (SI) can also be improved.
[0317] Example 1
[0318] Using propane diluted to 0.02% by volume to 0.5% by volume as the diluted gaseous fuel, the other conditions were the same as in Example 1, and a sintering pan test was performed on a sintering raw material containing 5% by mass of carbon material (...
Embodiment 3
[0320] use Figure 28 As shown in Table 14, the test disk shown in Table 14 was discharged from the top of the disk through cooling, and was charged into the charging layer composed of sintering raw materials whose coke powder content (outer number) varied in two levels: 4.9% by mass and 4.8% by mass. , Blow in coke oven gas (C gas) diluted to 1.0 volume % and 2.0 volume % (relative to air) two water concentration, and carry out sintering disc test (No.2~7). In addition, as a comparative example, the same sintering disk test was performed on an example (No. 1) in which the coke fines content (outer number) was 5.0% by mass and no diluent gas was injected. In addition, in this example, the total thickness of the sintered raw materials loaded in the test pan was 600 mm, and the sintered raw materials containing the above-mentioned coke powder were laminated in the upper 400 mm, and the return ore was laminated in the lower 200 mm.
[0321] In addition, when the position of the ...
Embodiment 4
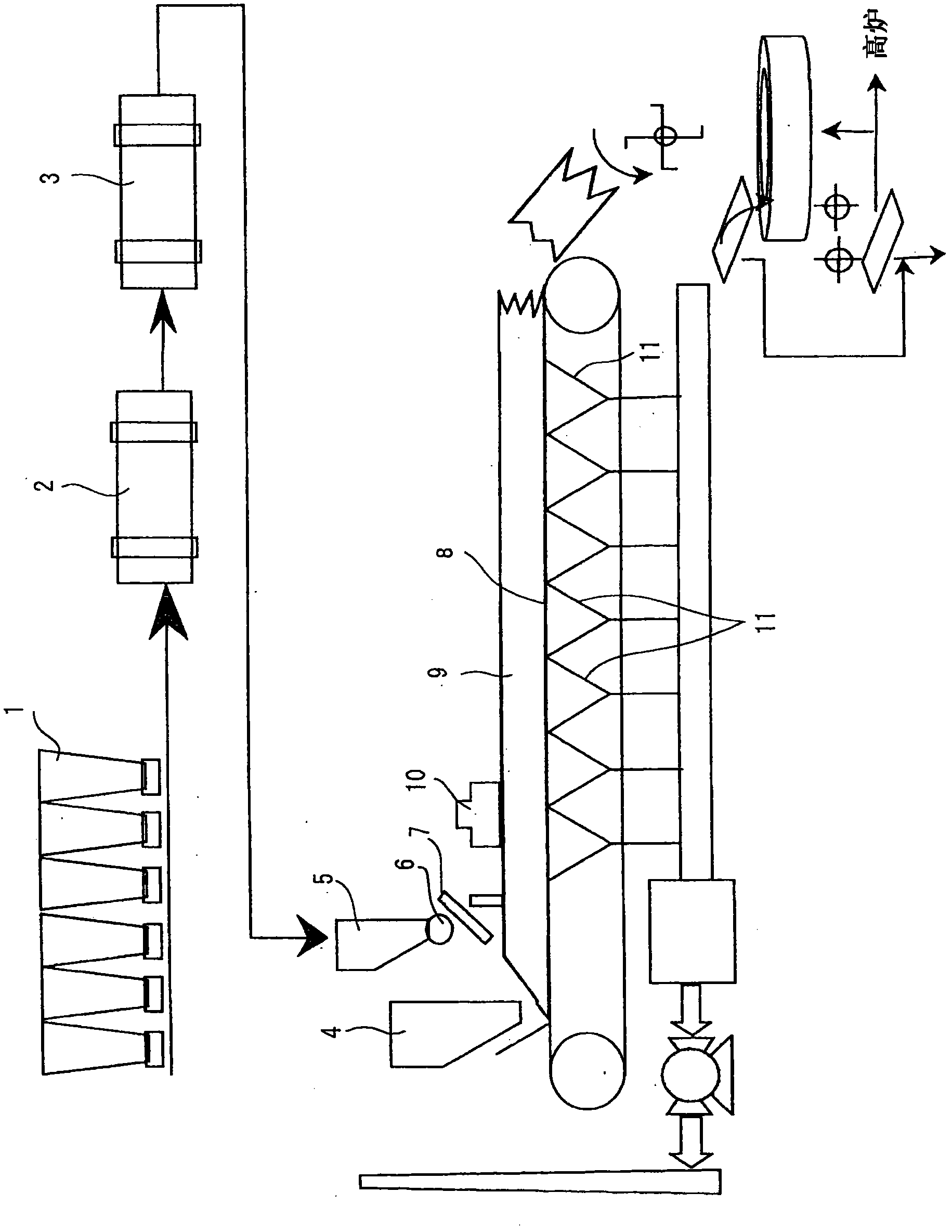
[0331] The method for producing sintered ore according to the present invention is suitable for a DL-type sintering machine with a daily output of 20,000 tons. The length of the DL sintering machine used is 90m from the ignition furnace to the ore discharge part. At a position about 30m behind the ignition furnace of the sintering machine and a height of 500mm above the filling layer, a gas fuel supply device with the following structure is installed: Nine gaseous fuel supply pipes with a length of 15 m (the advancing direction of the table machine) are arranged in parallel in the advancing direction of the table machine, and 149 nozzles (a total of 1341 pieces) that eject gaseous fuel downwards are installed on each pipe at an interval of 100 mm. The nozzle ejects city gas as gas fuel into the air at high speed, and supplies diluted gas fuel with a city gas concentration of 0.8% by volume to the packed layer. In addition, the total thickness of the packed layer was laminated ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com