Heat-accumulation temperature-regulation fiber and preparation method thereof
A technology of heat storage and temperature regulation and fiber, which is applied in fiber processing, conjugated synthetic polymer artificial filament, filament/thread forming, etc. Low enthalpy and other issues, to achieve good heat storage and temperature adjustment performance, good electrical conductivity, and good thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] The present invention also designs the preparation method of the fiber, the preparation method is suitable for the fiber described in the present invention, and adopts the fusion composite spinning method. Specifically, according to the composition and structural design of the fiber of the present invention, the following steps are mainly adopted:
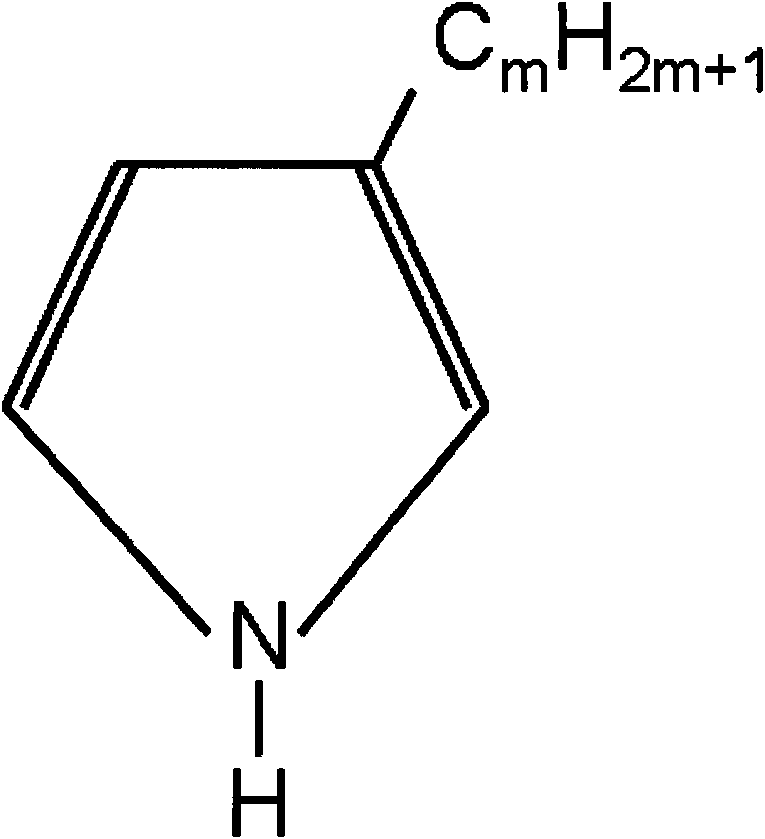
[0024] (1) The homopolymer or copolymer of the comb-shaped polymer phase change material 3-alkylpyrrole, or the homopolymer blend with a mass ratio of 30 to 70:70 to 30, which is the comb-shaped polymer phase change material of the A component, is dried , remove the moisture in it, so that the moisture content reaches 50-150ppm;
[0025] (2) Transport the homopolymer, copolymer or homopolymer blend of the poly-3-alkylpyrrole to the A component metering pump of the fiber after melting by known technology, and control the mass fraction of the fiber A component to be 20 ~60%;
[0026] (3) Using known technology to dry the fib...
Embodiment 1
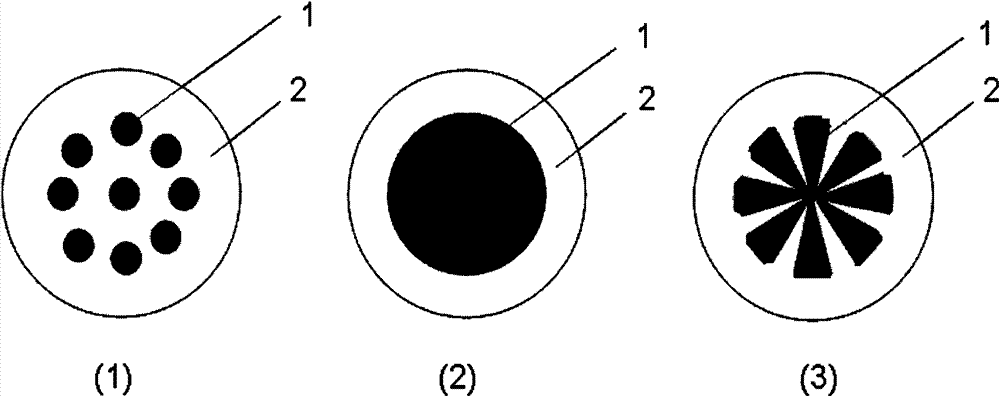
[0037] Poly 3-octadecylpyrrole with a degree of polymerization of 35 is used as the A component of the fiber, and poly 4-methylpentene-1 (number average molecular weight 280,000) is used as the B component of the fiber, and both components are dried to the moisture content When it is lower than 100ppm, the mass ratio of A and B is controlled to be 40:60, melted and composite spun at 250°C to make island-in-the-sea spun yarn, and then processed into stretch yarn after further drawing and twisting.
[0038] After inspection, the fineness of the finished fiber is 112dtex / 78f, the tensile breaking strength is 3.1cN / dtex, and the elongation at break is 30%. 23.1°C, heat release is 25J / g; 5% thermal weight loss temperature is 295°C; fiber surface specific resistance is 41Ω / cm; after using cyclohexane as solvent Soxhlet extractor, the mass loss rate of fiber is 3 %.
Embodiment 2
[0040] A random copolymer of 3-hexadecylpyrrole and 3-octadecylpyrrole (average degree of polymerization 85) with a molar ratio of 70:30 is used as the A component of the fiber, and polypropylene (melt index 35g / 10min) is The B component of the fiber, after both components are dried until the moisture content is lower than 100ppm, the mass ratio of A and B is controlled to be 40:60, melted and composite spun at 250°C to make concentric as-spun yarn, further drafted and twisted After processing into stretch yarn.
[0041] After inspection, the fineness of the finished fiber is 83dtex / 48f, the tensile breaking strength is 2.9cN / dtex, and the elongation at break is 23%. 19.1°C, the heat release is 22J / g; the temperature of 5% thermal weight loss is 245°C; the surface specific resistance of the fiber is 151Ω / cm; after using cyclohexane as the solvent Soxhlet extractor, the mass loss rate of the fiber is 5 %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| endothermic temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| exothermic temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com