Microbial degrading agent for decomposing cassava stalks and preparation method
A technology for microbial degradation and cassava stalks, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of degrading cassava stalks, achieve rapid degradation, low cost of use, and improve the effect of soil structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Purchased from the China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Center (CICC): Phanerochaete chrysosporium (No. 40719), white rot fungus (No. 40299), Puccinia tufts (No. 40259), Aspergillus fumigatus (No. 2434) ), Bacillus liquefaction (No. 20651), Trichoderma reesei (No. 41492), Aspergillus fig (No. 2420).
[0016] After the above strains were expanded and cultivated respectively, the fungi (filaments) were collected, and combined according to the following proportions based on the biomass of the bacteria: 10% of Phanerochaete chrysosporium, 20% of white rot fungus, and Mold 10%, Aspergillus fumigatus 15%, Bacillus thermophiles liquefaction 20%, Trichoderma reesei 15%, Aspergillus fig 10%. Using wheat bran as the bacterial adsorbent, mix evenly according to the ratio (weight of bacteria: weight of wheat bran=1:10) to prepare microbial degradation bacterial agent.
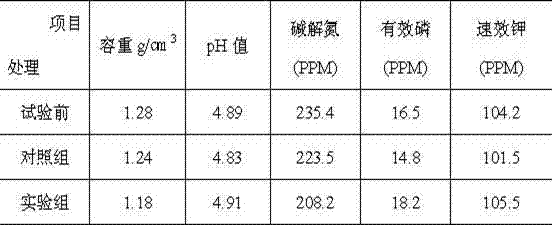
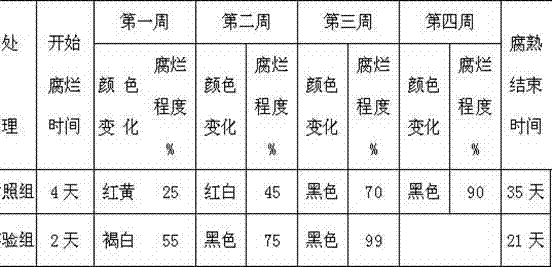
[0017] The cassava stalks were pulverized, and two groups were set up to carry out the experiment: t...
Embodiment 2
[0021] The cassava rod-degrading bacteria were isolated from the cassava planting soil and cassava rod rotting piles. After separation, purification and identification, the lignin-degrading bacteria were: Aspergillus flavus ( Aspergillus flavus ) and Bacillus licheniformis ( Bacillus licheniformis ); the hemicellulose-degrading bacteria are: Bacillus subtilis ( Bacillus subtilis ) and Aspergillus niger ( Aspergillus niger ); Cellulose-degrading bacteria: Penicillium decumbens ( Penicillium decumbens ), Trichoderma viride ( Trichoderma viride ), Trichoderma korningii ( Trichoderma koningii ).
[0022] After the above strains were expanded and cultivated respectively, the fungi (filaments) were collected and combined in the following proportions based on the biomass of the bacteria: Aspergillus flavus 15%, Bacillus licheniformis 20%, Bacillus subtilis 10%, Aspergillus niger 15%, Penicillium recumbens 10%, Trichoderma viride 20%, Trichoderma korningen 10%. Wheat bran...
Embodiment 3
[0028] The lignin-degrading bacterium White-rot fungus; the hemicellulose-degrading bacterium Bacillus liquefier; and the cellulose-degrading bacterium Trichoderma reesei were purchased from China Agricultural Microorganism Culture Collection Center (ACCC). The lignin-degrading bacteria Aspergillus flavus, the hemicellulose-degrading bacteria Bacillus subtilis and the cellulose-degrading bacteria Trichoderma viride were isolated and screened from the rotten pile of cassava stalks.
[0029] After the above-mentioned strains were expanded and cultivated respectively, the fungi (filaments) were collected, and combined in the following proportions based on the biomass of the bacteria: 10% of white rot fungus, 20% of Aspergillus flavus, 20% of thermophilic bacillus liquefaction, Bacillus subtilis 10%, Trichoderma reesei 15%, Trichoderma viride 25%. Wheat bran was used as the bacterial adsorbent and mixed evenly according to the ratio (cell weight: wheat bran weight = 1:10) to prepa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com