Synthetic method of tin dioxide nanomaterials
A technology of nanomaterials and tin dioxide, which is applied in the field of preparation of tin dioxide nanomaterials, can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, low product purity, large particle radius, etc., and achieve good repeatability, high product yield, and particle size small effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The preparation process and steps in this embodiment are as follows:
[0020] 1. Measure 10 mL of absolute ethanol (CH 3 CH 2 OH) and 90 mL of deionized water were poured into a beaker and mixed evenly;
[0021] 2. Weigh 1.0738 g (5 mmol) of stannous sulfate (SnSO 4 ) and 4.4115 g (15 mmol) of trisodium citrate dihydrate (Na 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 2H 2 O);
[0022] 3. Put the weighed SnSO 4 and Na 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 2H 2 O was added to the above solution together, and stirred rapidly by magnetic force for 1 hour;
[0023] 4. Put the above mixed solution into a high-pressure reactor and react in an oven at 160°C for 12 hours;
[0024] 5. After the reaction product was cooled, it was washed three times with deionized water and absolute ethanol, and then dried at 80° C. for 12 hours to obtain tin dioxide nanomaterials.
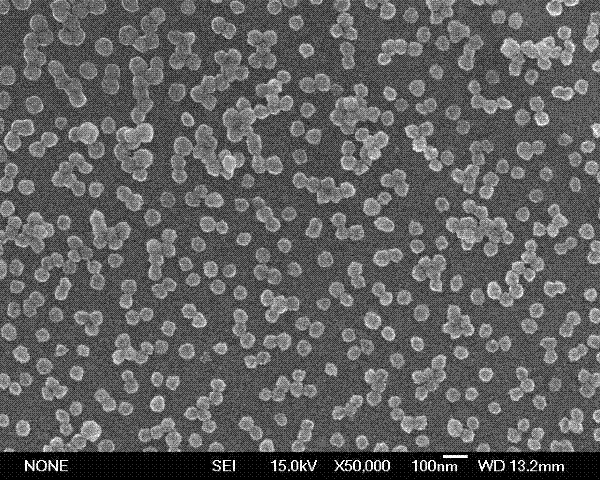
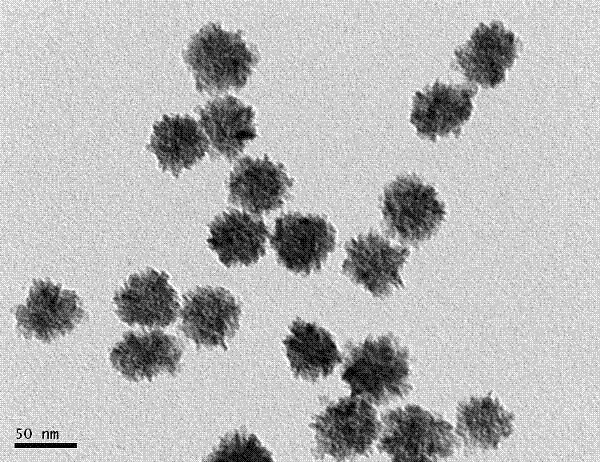
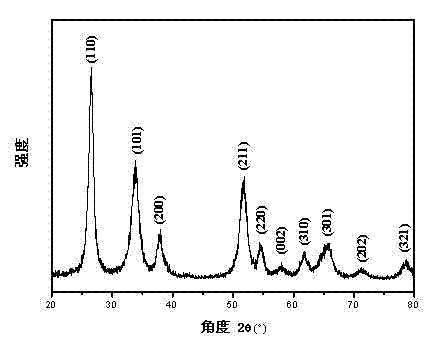
[0025] The particle size of the obtained tin dioxide nanomaterials is in the range of 40-60 nm, and the monodispersity is good.
Embodiment 2
[0027] Implementation process is except following difference, and other is all identical with embodiment 1
[0028] 1. Measure 20 mL of absolute ethanol (CH 3 CH 2 OH) and 80 mL of deionized water were poured into a beaker and mixed evenly;
[0029] 4. Put the above mixed solution into a high-pressure reactor and react in an oven at 120°C for 36 hours;
[0030] The particle size of the obtained tin dioxide nanomaterials is in the range of 40-200 nm.
[0031]
Embodiment 3
[0033] Implementation process is except following difference, and other is all identical with embodiment 1
[0034] 2. Weigh 1.0738 g (5 mmol) of stannous sulfate (SnSO 4 ) and 0.7353 (2.5 mmol) of trisodium citrate dihydrate (Na 3 C 6 h 5 o 7 2H 2 O);
[0035] 4. Put the above mixed solution into a high-pressure reactor and react in an oven at 140°C for 24 hours;
[0036] The particle size of the obtained tin dioxide nanomaterials is in the range of 40–100 nm, but there are a large number of bulk SnO 2 generate.
[0037]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| band gap | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com