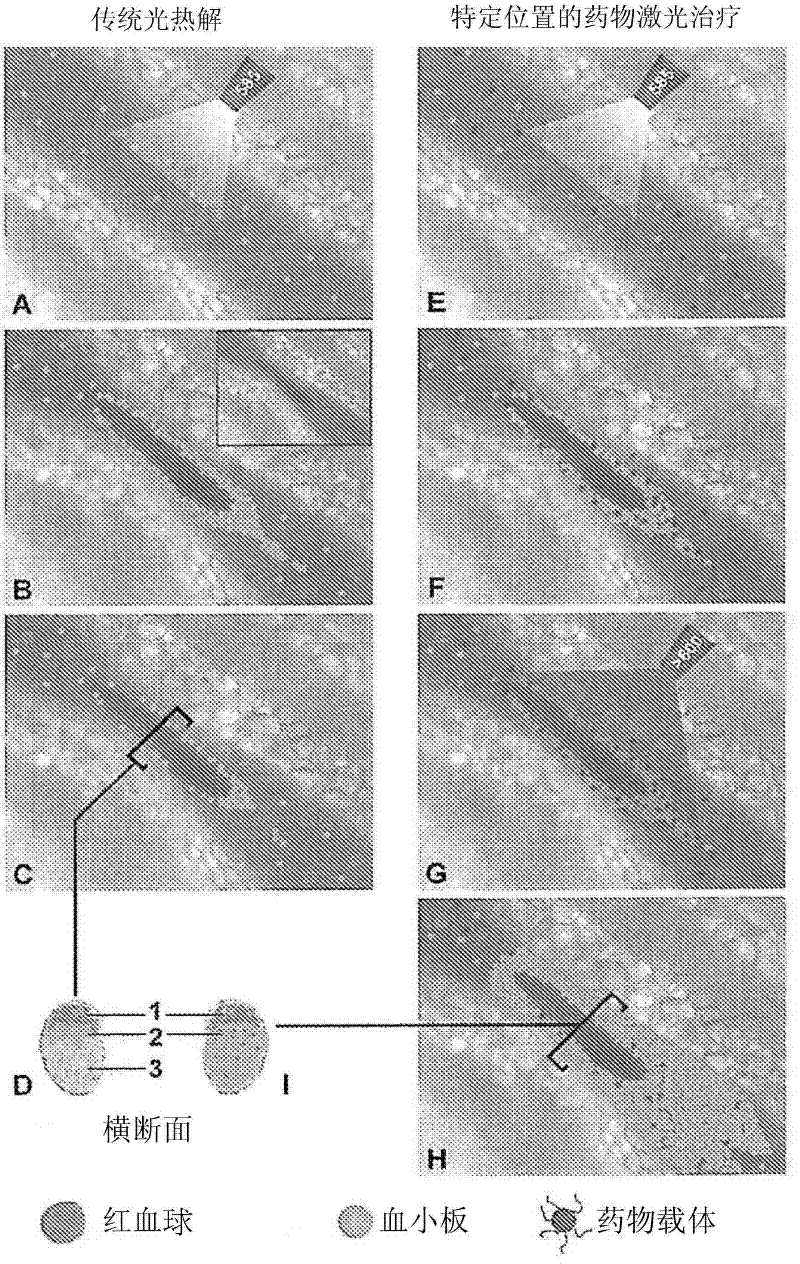
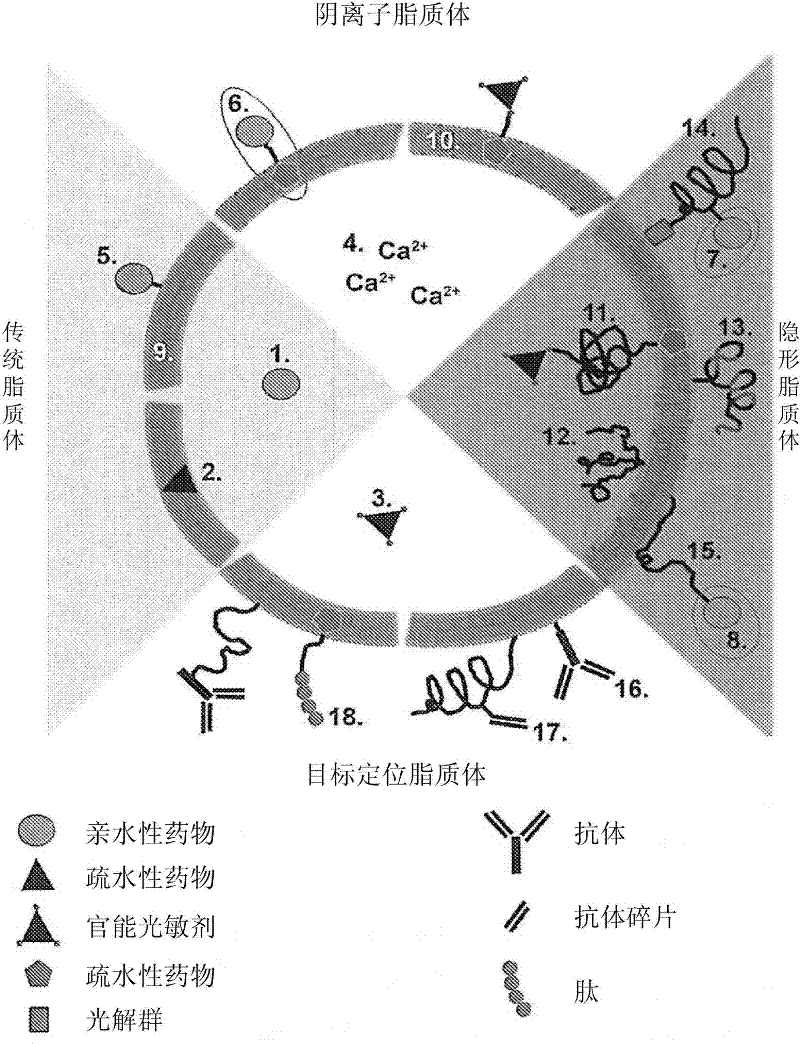
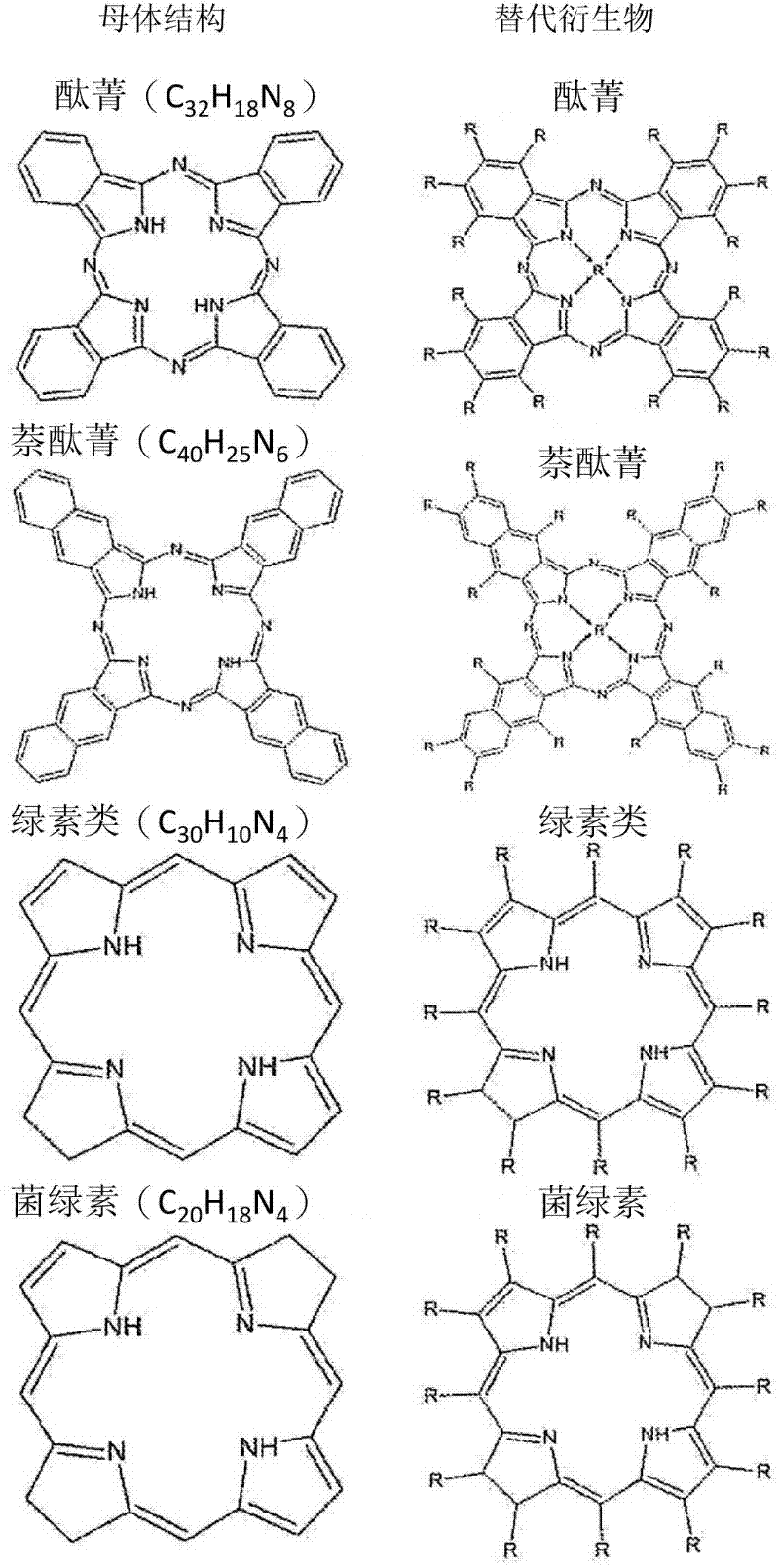
Drug delivery system for the treatment of vascular diseases
A drug delivery system and technology for vascular diseases, applied in the field of drug delivery systems for treating vascular diseases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0163] Preparation of the drug delivery system of the present invention.
[0164] Several possible combinations of drug delivery systems that can be used in SSPLT are in Figure 4 are displayed in . The formulation of the different liposomal delivery systems is described below.
[0165] 1. A heat-sensitive liposome encapsulating an antifibrinolytic agent (tranexamic acid).
[0166] 1,2-Dipalmitoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) and 1-palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine (MPPC) are both derived from Avanti polar Butter (Alabaster, Alabama). The sodium salt of HEPES [4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid] was from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Tranexamic acid (4-(aminomethyl)cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid, TA) was purchased from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland). All other reagents were of analytical grade.
[0167] The large single-layer blastocyst prepared by extrusion technology was prepared from DPPC:MPPC at a molar ratio of 90:10. DPPC was ...
Embodiment 2
[0188] Features of the drug delivery system of the present invention
[0189] 1. Determination of the physicochemical characteristics of the drug delivery system
[0190] Physicochemical characterization of liposome size and polydispersity (measurement of particle size distribution) of liposome delivery systems was performed in equilibration buffer (10 mM HEPES, 0.88% (w / v) NaCl, pH=7.4, 0.291 kilograms of osmol / kg) after diluting, obtain with measurement photon correlation spectrum using single peak analysis (British Malvern instrument, Malvern laser particle size analyzer 3000) at 90 ° angle. The results for several alternative formulations are shown in Figure 8 .
[0191] The phase transition temperature of liposomes was measured by differential scanning calorimetry (MICROCAL, Northampton, MA) after diluting liposomes with equilibration buffer to a final lipid concentration of 3 mM. Equilibration buffer is used as a reference. The results for the two candidate formul...
Embodiment 3
[0217] Drug release of drug delivery system of the present invention
[0218] 1. Heat-induced release of tranexamic acid from polyethylene glycol thermosensitive liposomes
[0219] Quantification of the heat-induced release of tranexamic acid released from heat-sensitive large unilamellar blastocysts (LUVETs) prepared by the extrusion technique was determined by the formula DPPC:DSPE-PEG (96:4 molar ratio) and DPPC:MPPC:DSPE- PEG (86:10:4 molar ratio) was prepared.
[0220] Prior to heat treatment, gel-filtered LUVET suspensions were diluted ten-fold with equilibration buffer kept at 4 °C. 20 μL of gel-filtered LUVET suspension was diluted 50 times (n=3 per experiment) and the total intravascular TA concentration was measured by fluorescence spectroscopy (final dilution was 1250 times). The average overall TA concentration was used to calculate the percentage of TA molecules released.
[0221] After equilibrating for 5 minutes at 4°C, and before heat-induced drug release,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com