Method for manufacturing high-silica glass emitting white light
A high-silica glass, a manufacturing method technology, applied in the field of luminescent glass manufacturing, can solve the problem that the high-silica glass can only be excited by ultraviolet light below 300nm, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
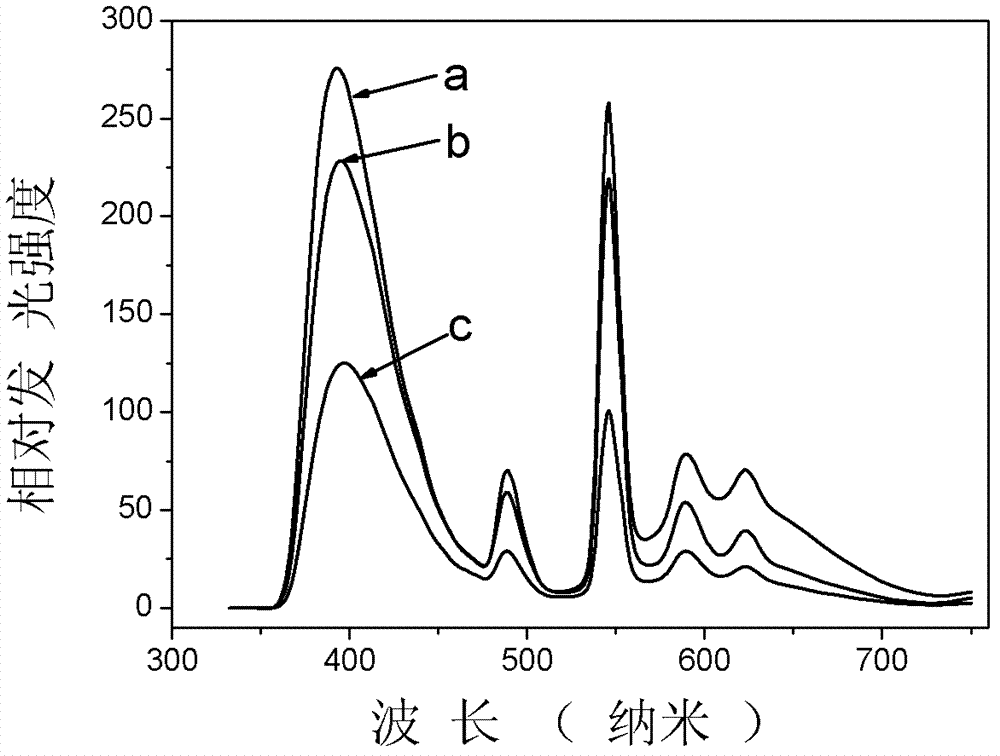
[0030] 6.24g of cerium nitrate, 14.36g of terbium nitrate, 5.03g of manganese chloride and 67.5g of aluminum nitrate are dissolved in 100ml of 3N dilute nitric acid solution. In this mixed solution, the concentration of cerium ions is 0.15mol / L and the concentration of terbium ions 0.33mol / L, manganese ion concentration 0.4mol / L, aluminum ion concentration 1.8mol / L. A porous glass having a size of 10 mm×10 mm×1.5 mm, a pore size of 5 nm to 10 nm, and a silica content of 94% by weight was immersed in the mixed solution for 2 hours.
[0031] The glass was then removed from the solution and allowed to air dry naturally.
[0032] After the glass is completely dry, place it in a sintering furnace covered with carbon powder, and then heat up according to the following temperature regime:
[0033] 90 minutes from room temperature to 100 degrees Celsius, and then 120 minutes at 100 degrees Celsius. The temperature is raised from 100 degrees Celsius to 600 degrees Celsius in 150 minu...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 6.24g of cerium nitrate, 14.36g of terbium nitrate, 5.03g of manganese chloride and 37.5g of aluminum nitrate are dissolved in 100ml of 3N dilute sulfuric acid solution. In this mixed solution, the concentration of cerium ions is 0.15mol / L and the concentration of terbium ions 0.33mol / L, manganese ion concentration 0.4mol / L, aluminum ion concentration 1.0mol / L. A porous glass having a size of 10 mm x 10 mm x 1.5 mm, a pore size of 1 nm to 8 nm, and a silica content of 96% by weight was immersed in the solution for 2 hours.
[0037]The glass was then removed from the solution to air dry naturally.
[0038] After the glass is completely dry, it is placed in a sintering furnace filled with argon, and then the temperature is raised according to the following temperature regime:
[0039] 175 minutes from room temperature to 200 degrees Celsius, then 120 minutes at 200 degrees Celsius. The temperature is raised from 200 degrees Celsius to 750 degrees Celsius in 160 minutes,...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 6.24g of cerium nitrate, 14.36g of terbium nitrate, 5.03g of manganese chloride, 41.5g of lanthanum nitrate, 7.02g of barium nitrate and 48.75g of aluminum nitrate are dissolved in 100ml of 3N dilute hydrochloric acid solution. In this mixed solution, cerium ions Concentration is 0.15mol / L, terbium ion concentration is 0.33mol / L, manganese ion concentration is 0.4mol / L, lanthanum ion concentration is 1.0mol / L, barium ion concentration is 0.2mol / L, aluminum ion concentration is 1.3mol / L L. A porous glass having a size of 10 mm×10 mm×1.5 mm, a pore size of 4 nm to 20 nm, and a silica content of 98% by weight was immersed in the solution for 2 hours.
[0042] The glass was then removed from the solution to air dry naturally.
[0043] After the glass is completely dry, place it in a sintering furnace filled with nitrogen, and then heat up according to the following temperature regime:
[0044] 175 minutes from room temperature to 200 degrees Celsius, then 120 minutes at 2...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com