Fluorescence labeled detection kit for simultaneously analyzing 17 gene loci of canine genomic DNA, detection method and application thereof
A detection kit and fluorescent labeling technology, applied in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problem of low genetic polymorphism of locus, large differences between different dog groups, and unsatisfactory use. requirements and other issues to achieve accurate and effective identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
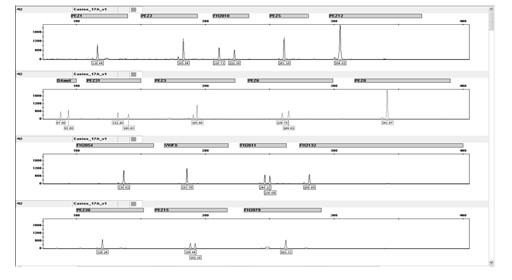
[0063] Example 1 Multiplex amplification and fluorescence detection of the fluorescently labeled multiplexed amplification detection kit for 17 loci
[0064] 1. Sample source
[0065] Canine whole blood samples from 2 unrelated individuals provided by the Nanchang Police Dog Base of the Ministry of Public Security
[0066] 2. DNA extraction (for the extraction of genomic DNA, refer to "GA / T 383-2002 Forensic Science DNA Laboratory Inspection Specification")
[0067] Genomic DNA was extracted from two whole blood samples by Chelex-100 method:
[0068] Take 0.5-5μl whole blood and place it in a sterilized 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add sdH 2 Put O1ml in the tube, shake for a few seconds; place at room temperature for 10 minutes, shake for a few seconds, centrifuge at 12,000rpm for 3 minutes, discard the supernatant, keep enough supernatant to cover the precipitate, do not stir the precipitate; add 200μl 5% Chelex- 100, shake for a few seconds; keep warm at 56°C for 30 minutes,...
Embodiment 2
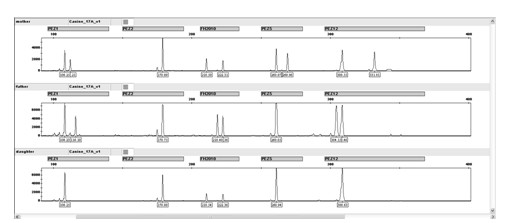
[0086] Example 2 The samples are: the male parent and the offspring ( Provided by the Nanchang Police Dog Base of the Ministry of Public Security) DNA extraction, PCR amplification, and genetic analyzer detection were performed according to Example 1, and the typing results were finally obtained.
[0087] Results and conclusions
[0088] The basic principle of paternity testing is: According to Mendel's law of inheritance, the genotype of the parent determines the genotype of the offspring. Under the premise of no gene mutation and typing error: ① A child’s pair of alleles must be one from the father and one from the mother; ② It is impossible for the child to have an allele that neither parent has.
[0089] The results of this example are shown in the attached Figure 3-6 and Schedule 1, at Figure 3-6 The corresponding test results of the female dog, father dog and young dog are listed in order.
[0090] Table 1:
[0091]
[0092] PI is the paternity index, also kn...
Embodiment 3
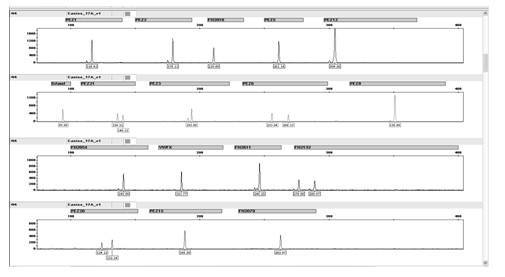
[0100] Example 3 Individual identification of dogs using a fluorescently labeled multiplex amplification detection kit with 17 loci
[0101] 1. The unknown individual identification samples in this experiment are blood spot and semen spot samples, provided by the Nanchang Police Dog Base of the Ministry of Public Security.
[0102] 2. Genomic DNA was extracted with reference to "GA / T 383-2002 Forensic Science DNA Laboratory Inspection Specification".
[0103] 3. Amplification detection
[0104] Perform PCR amplification and genetic analyzer detection according to Example 1, and finally obtain the typing result.
[0105] 4. Results and conclusions
[0106] Since the appearance of dogs of the same breed is not much different, although there are dog ear marks to distinguish them, the ear tags of breed dogs are prone to blurring, loss, and defect during the process of breeding and genetic breeding, making it difficult to identify individual breed dogs, resulting in Huge eco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com