High-molecular material containing cholic acid and liver-targeting drug delivery nanoparticle modified by same
A drug-loaded nano- and amphiphilic polymer technology, which is applied in the field of liver-targeted drug delivery nanoparticles, can solve the problems of unstable liposome properties, affecting drug bioavailability, and difficult control of modification operating conditions. Simple operation, good biocompatibility effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Embodiment 1: Amphiphilic polymer material containing cholic acid of the present invention and its synthesis
[0050] 1) Dissolve 4-vinylbenzoic acid (2.0mmol) in 10mL of dichloromethane, add SOCl 2 (2.6mmol) and 1 drop of DMF, reacted at room temperature for 4h, evaporated under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, then added 2-3mL chloroform to dissolve, sealed and stored at low temperature (in a refrigerator at -20°C). Unreacted reactants and catalysts do not need to be separated, and will be removed during the recrystallization of the product in step 2).
[0051] 2) Dissolve methyl cholate (3.0mmol) in 15mL of chloroform, add triethylamine (4.8mmol), slowly drop into 4.5mmol of 4-vinylbenzoyl chloride solution (dissolved in a very small amount of In chloroform, there is about 1 mL of chloroform in actual operation), after reacting for 2 hours, slowly warming up to room temperature and continuing to react for 24 hours, distilling off the solvent under reduced pre...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2: Amphiphilic polymer material containing cholic acid of the present invention and its synthesis
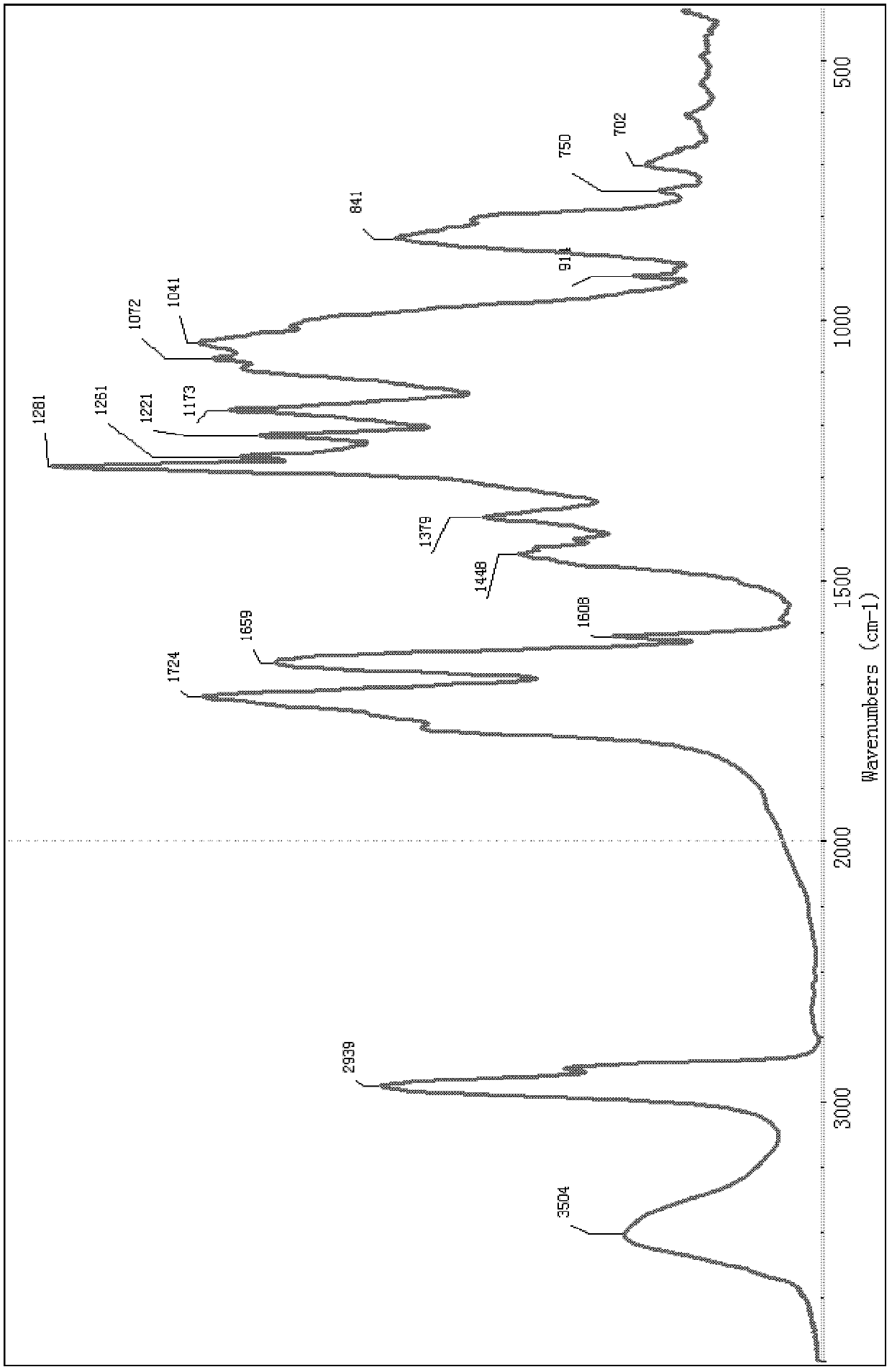
[0057] The synthesis of the monomer was the same as in Example 1. The polymer monomer (0.55 g) and 4.9 mg of AIBN were dissolved in 15 ml of chloroform, and the temperature was slowly raised to 68° C. under the protection of nitrogen, and the reaction was continued for 20 hours with stirring. After the reaction, the solvent was removed, and the polymer was precipitated with methanol, filtered, washed with methanol three times, and dried. The polymerization product is a white solid with a conversion rate of 80.7%, a weight average molecular weight of 15700 (n=28), and m.p.=106.5-114.9°C. 1H-NMR and Fourier transform infrared spectrograms are the same as in Example 1.
[0058] Dissolve the polymer (formula II) (0.3g, containing 0.54mmol of methyl cholate structure) in 10ml of tetrahydrofuran, add 3ml of NaOH aqueous solution (concentration: 2mol / L), heat and ref...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3: the hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties of the cholic acid polymer material PVBCA of the present invention
[0060] The cholic acid-containing polymer material PVBCA was prepared according to Example 1. Configure the CH of PVBCA at a concentration of 1.0 mg / mL 2 Cl 2 The solution was spread evenly on the glass slide, and the PVBCA material film was formed after the solvent volatilized, and the contact angle of the material was measured with a contact angle meter. The average contact angle was 35.8°, which indicated that the material had good hydrophilicity.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Weight average relative molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com