Method for preparing aluminum gadolinium samarium intermediate alloy from gadolinium carbonate and samaric carbonate through molten salt electrolysis
A technology of molten salt electrolysis and intermediate alloy, applied in the field of rare earth aluminum alloy preparation, can solve the problems of long production process, easy segregation of alloy components and high production cost, and achieve the effects of changing creep performance, realizing experimental conditions and simplifying production process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
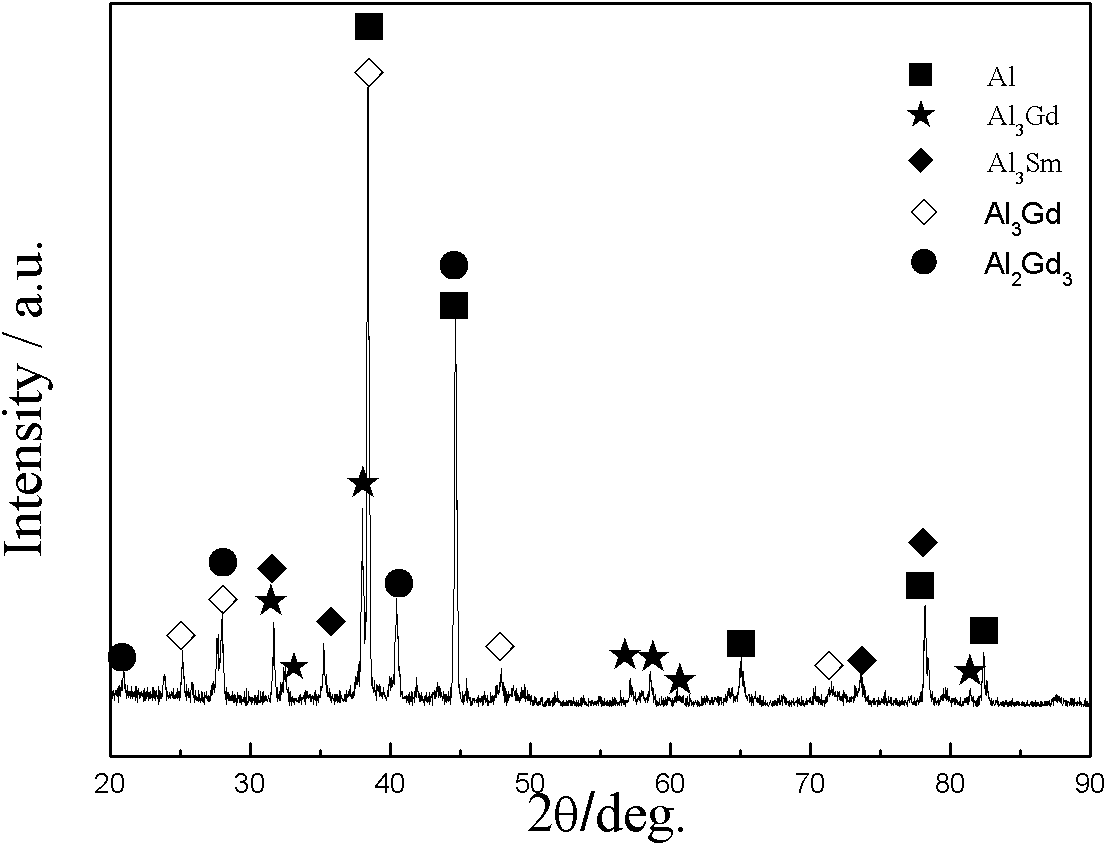
[0020] Embodiment 1: with AlF 3 -NaCl-KCl is the electrolyte system, and the mass percentages of each component are 11.1%, 38.9%, and 50%, respectively, and then press AlF 3 20% by weight added to mix Gd 2 (CO 3 ) 3 、Sm 2 (CO 3 ) 3 Powder, electrolysis temperature is 750℃, cathode current density is 6.2A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 4.5-5.1V, after 2 hours of electrolysis, Al-Gd-Sm alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of aluminum, gadolinium and samarium are respectively: 73%, 22.8%, 4.2%, The current efficiency was 27.2%.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Embodiment 2: with AlF 3 -NaCl-KCl is the electrolyte system, and the mass percentages of each component are 11.1%, 38.9%, and 50%, respectively, and then press AlF 3 20% by weight added to mix Gd 2 (CO 3 ) 3 、Sm 2 (CO 3 ) 3 Powder, electrolysis temperature is 800℃, cathode current density is 7.8A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 4.8-5.4V, after 2 hours of electrolysis, Al-Gd-Sm alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of aluminum, gadolinium and samarium are respectively: 76.2%, 17.7%, 6.1%, The current efficiency is 35.7%.
Embodiment 3
[0022] Embodiment 3: with AlF 3 -NaCl-KCl is the electrolyte system, and the mass percentages of each component are 11.1%, 38.9%, and 50%, respectively, and then press AlF 3 20% by weight added to mix Gd 2 (CO 3 ) 3 、Sm 2 (CO 3 ) 3 Powder, electrolysis temperature 840 ℃, cathode current density 7.8A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 5.7~6.4V, after 3 hours of electrolysis, Al-Gd-Sm alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of aluminum, gadolinium and samarium are respectively: 69.9%, 22.9%, 7.2%, The current efficiency is 37.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com