Method for removing pollutants in water through stepwise catalytic oxidation-biological activated carbon-ultraviolet (UV) combination
A biological activated carbon and catalytic oxidation technology, which is applied in the direction of oxidized water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems such as difficult to eliminate inorganic salts, and improve the utilization efficiency and removal efficiency of ozone , Reduce the effect of destroying the structure of natural organic matter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
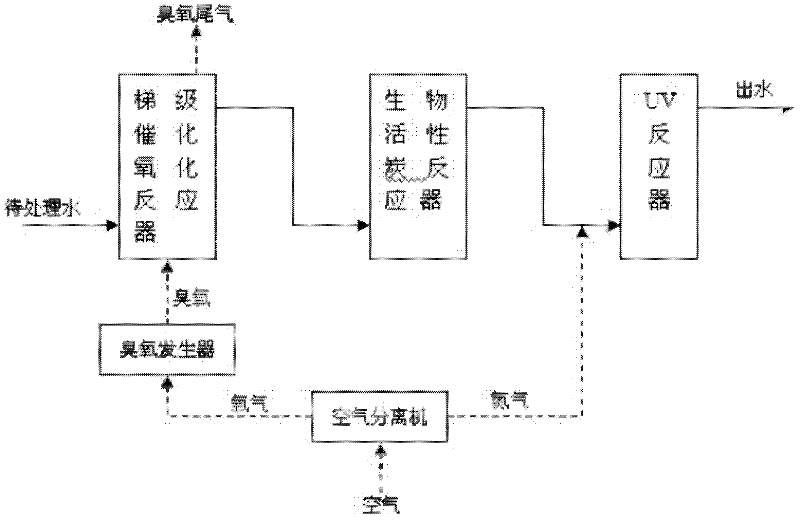
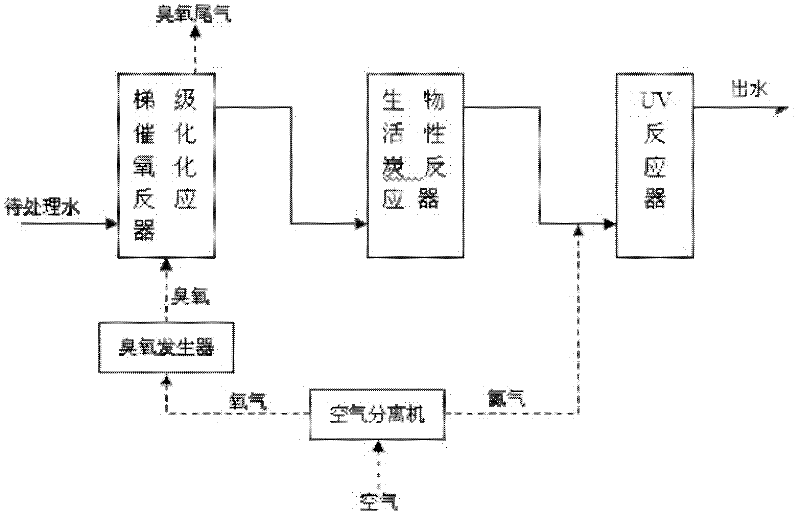
[0014] Specific embodiment one: the method for the combined use of cascade catalytic oxidation-bioactivated carbon-UV in this embodiment to remove pollutants in water is carried out according to the following steps: 1. Make the water to be treated flow into the cascade catalytic oxidation reactor to carry out cascade catalytic oxidation, water flow The speed is 1~20m·h -1 ; Two, water flows out from the cascade catalytic oxidation reactor, and then flows into the biological activated carbon reactor, and the residence time in the biological activated carbon reactor is 5 to 240min; Three, the water flows out from the biological activated carbon reactor, and nitrogen is introduced into the water, and then Make water flow into the UV reactor and irradiate with ultraviolet light for 1 to 60 minutes to complete the cascade catalytic oxidation-biological activated carbon-UV combination to remove pollutants in water.
[0015] The schematic flow chart of the method of this embodiment i...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0017] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the process of stepwise catalytic oxidation described in step one is: a, when the content of bromide ion in the water to be treated is no more than 0.2mg / L, divide into two processes The first process is to inject ozone into the water to be treated and treat it with catalyst A for 5-10 minutes. The second process is to inject ozone into the water treated in the first process and add catalyst B to react for 5-10 minutes; The mass ratio of catalyst A to catalyst B is 1:0.2-5, and the total dosage of ozone is 0.1-30mg L -1 , the ratio of the total moles of catalyst A and catalyst B to the moles of ozone is 1:0.001~1; b, when the bromide ion content in the water to be treated exceeds 0.2mg / L, it is carried out in three processes, the first process It is to pass ozone into the water to be treated and add catalyst A for 5-8 minutes. The second process is to pass ozone into the trea...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the gas source of the ozone generator in step one adopts the oxygen separated by the air separator. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com