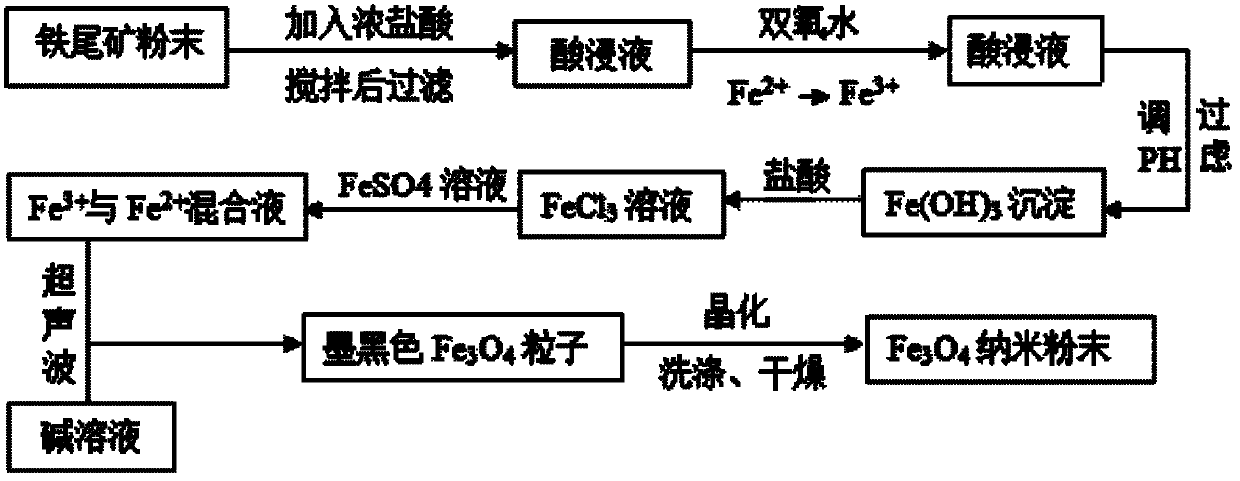
Method for preparing paramagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles by using iron tailings
A superparamagnetic and nanoparticle technology, which is applied in nanotechnology, ferrous oxides, solid waste removal, etc., can solve the problems of particle instability and easy agglomeration, and achieve simple equipment, no agglomeration, and reproducible good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Step 1: Mix 100 g of iron tailings with 37.5 wt% concentrated hydrochloric acid, stir mechanically for 2-4 hours at a stirring rate of 150-250 r / min, and filter out the pickling solution. Add appropriate amount of hydrogen peroxide in the filtrate, so that all the iron elements are replaced by Fe 3+ The form exists, heat the filtrate to 60 ℃, then add an appropriate amount of concentrated ammonia water, adjust the pH value to 3.2, and only make the iron element in the filtrate as Fe 3 Precipitation in the form of iron, so as to realize the separation of iron from tailings.
[0025] Take a certain amount of Fe 3 The precipitate was washed with deionized water several times and then calcined to obtain Fe 2 o 3 , weighed, and elemental analysis was performed to obtain the percentage content of iron element, which provided a basis for subsequent preparation work. Table 1 is the elemental analysis table of the calcined product. Pure Fe 2 o 3 The percentage composi...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Step 1: Same as Step 1 in Example 1, realize the separation of iron in iron tailings.
[0034] Step 2: Fe obtained by separating iron 3 The precipitate was washed with deionized water several times and then dissolved in hydrochloric acid to obtain FeCl 3 of aqueous solution. Add metered FeSO 4 ·7H 2 0, so that Fe in solution 3+ and Fe 2+ The molar ratio is 1.5:1, and a certain amount of 1 mol / L NaOH aqueous solution is prepared simultaneously as a precipitating agent. in Fe 3+ and Fe 2+ Add surfactant sodium lauryl sulfate (C 12 h 25 OSO 3 Na), Fe 3+ The molar ratio to sodium lauryl sulfate is 10:1. Under the action of ultrasonic waves with a power of 200 W and a frequency of 100 kHz, Fe 3+ and Fe 2+ The mixed solution is slowly dropped into NaOH lye, OH - The molar mass of Fe 3+ and Fe 2+ Fe in the mixed solution 3+ The molar ratio is 4.5:1.
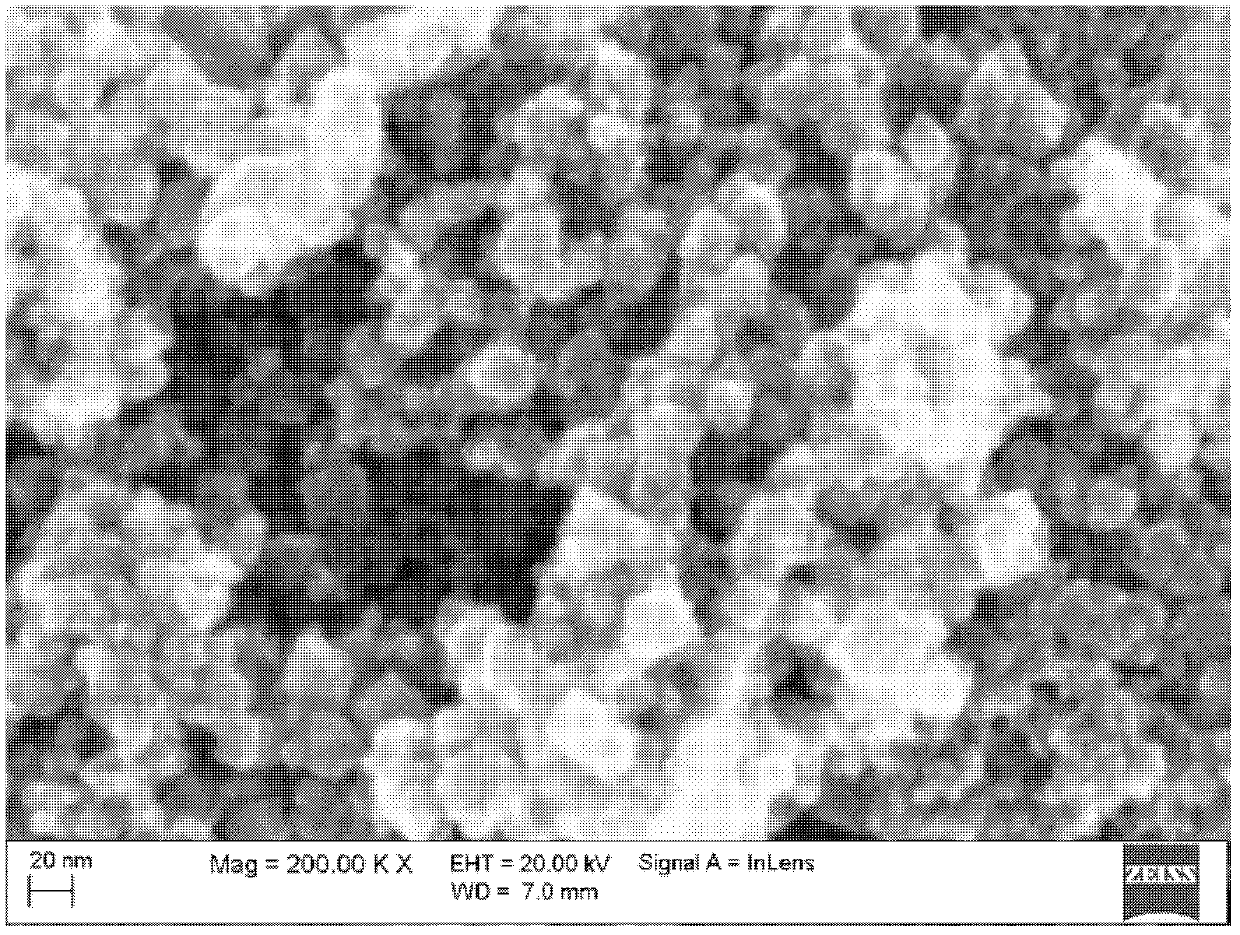
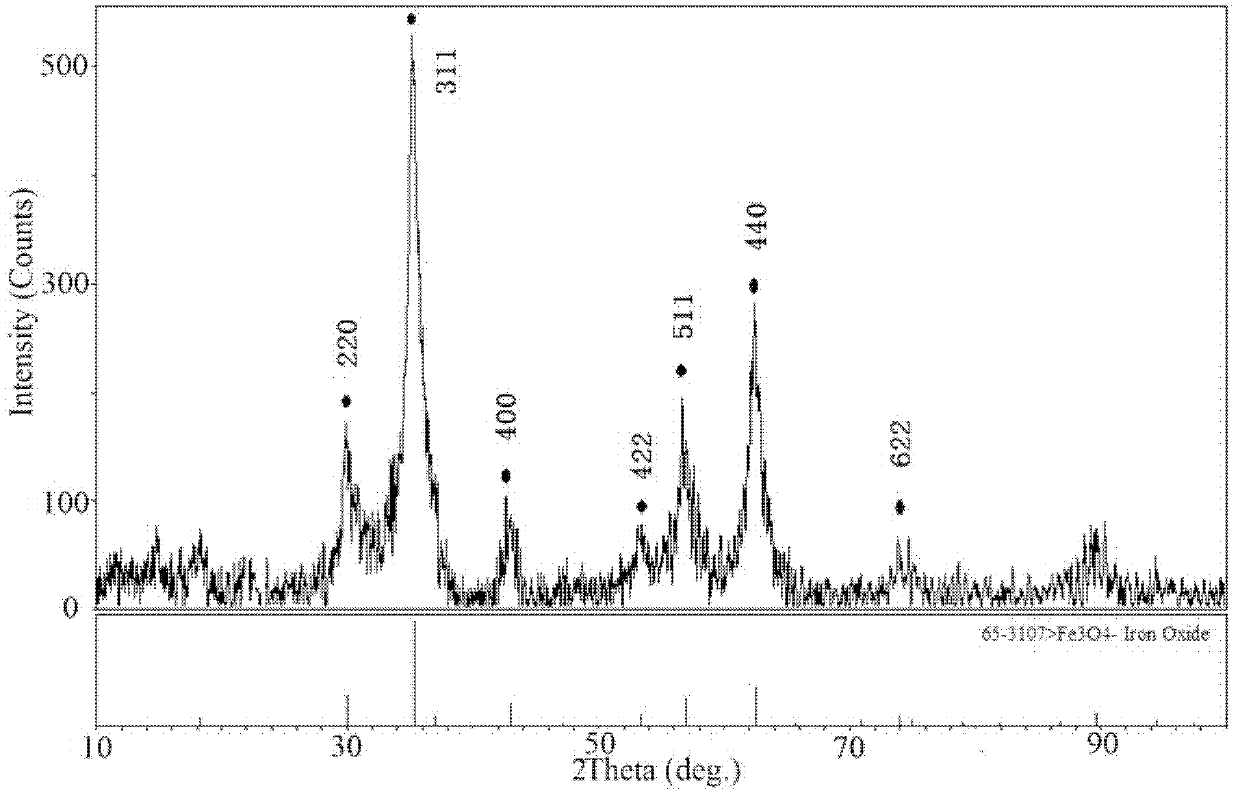
[0035] Step 3: with step 3 in embodiment 1, make Fe 3 0 4 magnetic powder. Field emission scanning elec...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Step 1: Same as Step 1 in Example 1, realize the separation of iron in iron tailings.
[0038] Step 2: with the step 2 in the embodiment 1, the Fe in the solution 3+ and Fe 2+ The mol ratio is 1.75:1, and surfactant is the mixture of sodium lauryl sulfate and polyethylene glycol, and Fe in the solution 3+的 The molar ratio is 0.125:1, and the alkaline precipitant is ammonia water, OH - The molar mass of Fe 3+ and Fe 2+ Fe in the mixed solution 3+ The molar ratio is 4.25:1 under the action of ultrasonic waves with a power of 125 W and a frequency of 70 kHz.
[0039] Step 3: Wait for a large amount of black Fe 3 0 4 After the particles were formed, they were heated in a water bath to 75 °C, crystallized for 90 min, and then centrifuged. The precipitate was washed with deionized water for several times, and then placed in a drying oven at 70 °C for 2 h at constant temperature to obtain Fe 3 0 4 magnetic powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com