Rhodotorula glutinis acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene and clone and function verification method and application thereof
A technology of Rhodotorula viscosus and acetyl coenzyme, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of less final product, affecting sensitivity, short detection cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of overcoming many steps and overcoming environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1 Cloning of Rhodotorula glutinosa acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene
[0053] (1) Genomic DNA was extracted from Rhodotorula glutinis as the experimental material.
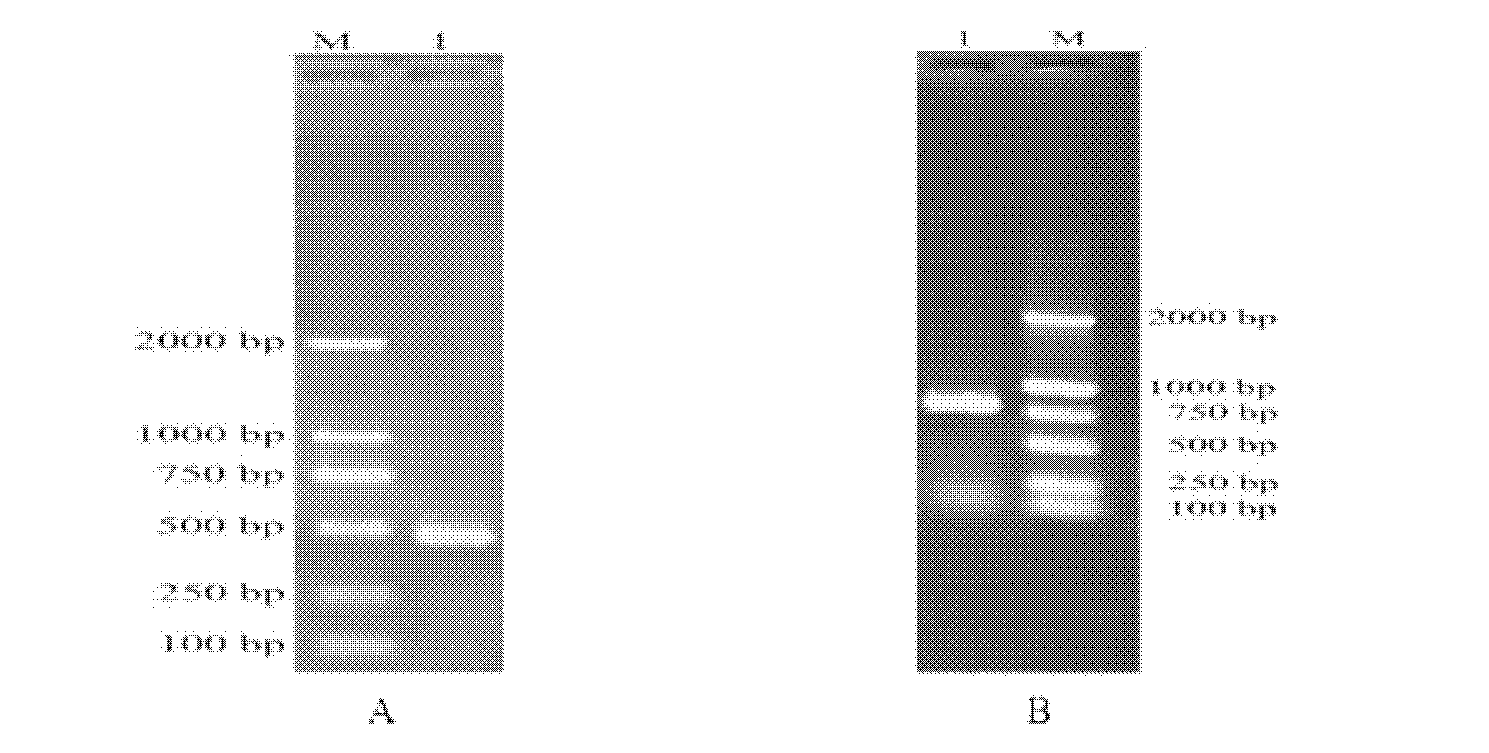
[0054] (2) if figure 1 As shown, the amino acid sequences of acetyl-CoA carboxylases of different species of yeast and filamentous fungi were downloaded from the KEGG database, and after using the software Clustal X1.83 for multiple sequence alignment, three conserved regions IANNGA, QKIIEEA, WGYFSV designed two pairs of degenerate primers IN-F / FY-R, QK-F / WG-R for PCR amplification. Primers are as follows:
[0055] QK-F CAGAAGATYATYGAGGAGGC
[0056] WG-R ACVGAGAAGTAACCCCA
[0057] IN-F ATYGCBAACAACGGNATYGC
[0058] FY-R GAGCCTCCTCRATRATCTTCTG
[0059] The PCR system is as follows (50uL): 10×buffer 5uL, 2.5mM dNTPs 4uL, upstream and downstream primers 1uL, E×Taq enzyme 0.5uL (5U / uL), dd H2O 37.5uL. Drop-down PCR program: 94°C pre-denaturation for 5 minutes; then 94°C for 1min, 51°C for 1min, the tem...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2 Cloning and co-expression of the three functional domains of Rhodotorula viscosus acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene
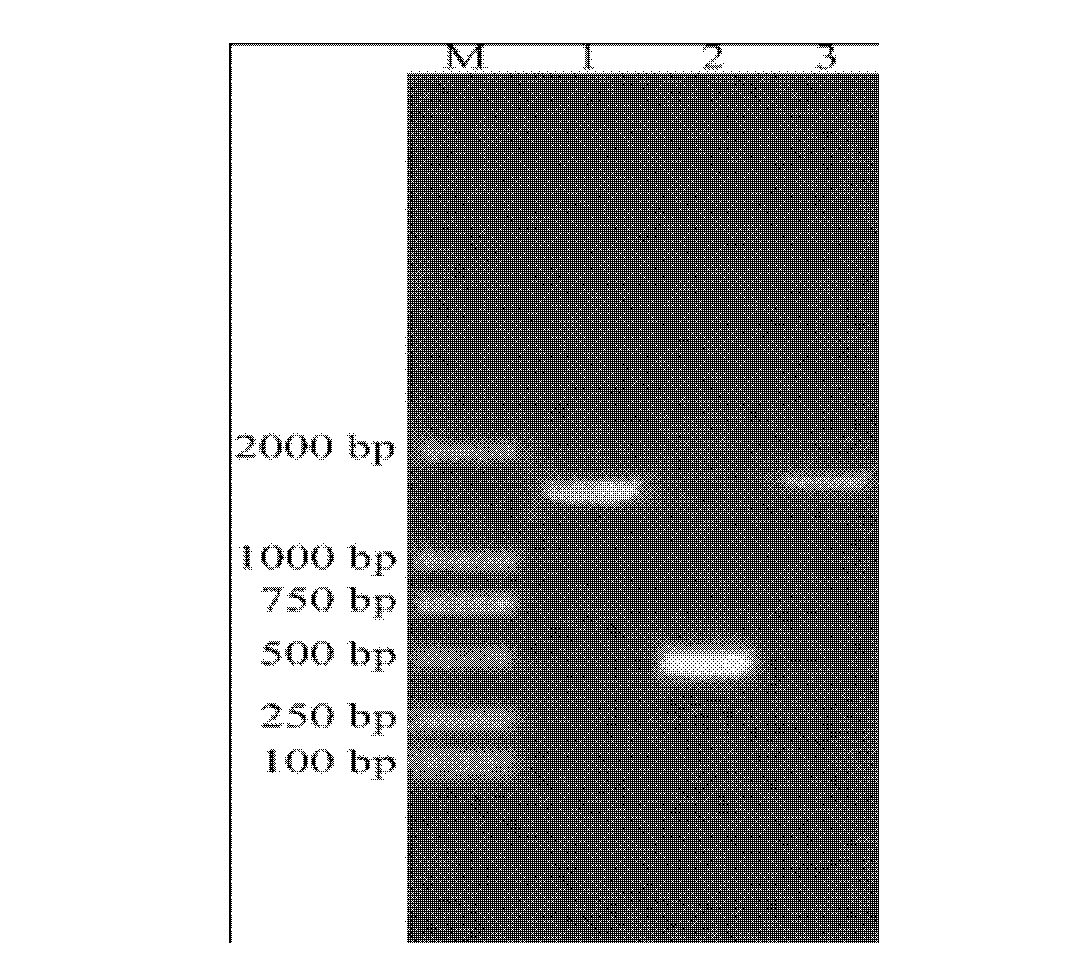
[0075] (1) if figure 2 As shown, use E.Z.N.A. TM Yeast RNA Kit was used to extract total RNA from Rhodotorula viscosus.
[0076] (2) Refer to RevertAid TM First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit instructions first digest total RNA with DNase I, the system is as follows: RNA 1ug, 10×DNase I reaction buffer with MgCl2 1uL, DEPC Water added to 9uL, DNase I 1uL. Total volume 10 uL. Incubate at 37°C for 30min, add 1uL of 25mM EDTA at 65°C for 10min to terminate the reaction.
[0077] Take 1 ug of total RNA as a template, add oligo(dT)18 as a reverse transcription primer, add DEPC-treated water to 12uL, mix slightly, incubate at 65°C for 5min, and briefly bathe in ice. Add the following components in sequence: 5×Reaction Buffer 4uL, Ribolock RNase Inhibitor (200u / uL) 1uL, 10mM dNTP Mix 2uL, RevertAid M-MuL V Reverse Transcriptase (200u / uL) 1uL. Mix lightl...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Example 3 Determining the fatty acid content of the recombinant strain when the three functional domains are co-expressed and then verifying the function of the gene
[0089] A large number of recombinant strains were induced to express, and the bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation, frozen at -80°C for 3 hours, and then vacuumized and freeze-dried. Using water bath method (Li et al., 2006) to extract bacterial fatty acids, the steps are as follows:
[0090] (1) Reagent preparation: 5% (volume percent) concentrated sulfuric acid / methanol solution; 0.2% (mass percent) BHT / methanol solution; 2.5mg / mL carbon seventeen fatty acid methyl ester / petroleum ether (90°C-120°C) solution ; 0.9% (mass percentage) NaCl / water solution;
[0091] (2) Grind the dried bacteria with a mortar, weigh 50 mg with an analytical balance and add it to a 20 mL crimp headspace bottle, add 2 mL of 5% concentrated sulfuric acid methanol solution (add in two times, 1 mL each time), and put...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com