Method for using levulinic acid to prepare gamma-valerolactone by hydrogenation
A technology of levulinic acid and levulinic acid solution, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in adapting to large-scale industrial production and product GVL yield Low cost and high cost of chemical reduction method, to achieve excellent hydrogenation activity and product selectivity, high product yield and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
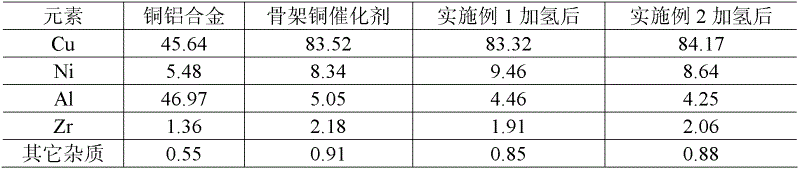
[0014] Example 1: 10 grams of copper-aluminum alloy powder containing 5.48% nickel, slowly add 65 milliliters of inorganic alkali solution containing 15 grams of NaOH at room temperature, heat up to 70°C for activation for 1 hour under stirring, and use 500 milliliters of 60°C deionized Wash with water until the pH is 8, and then replace the deionized water with absolute ethanol. Levulinic acid was slightly heated to be liquid, and 50 milliliters and 200 milliliters of methanol and the skeleton copper catalyst prepared above were added to the autoclave at the same time, and 0.6 grams of NaOH was added. The hydrogenation reaction temperature was controlled at 130-140° C., the hydrogen pressure was 3.0 MPa, and the reaction was continued for 2 hours. It was measured that the conversion rate of levulinic acid was 99.8%, and the selectivity of γ-valerolactone was 97.2%.
Embodiment 2
[0015] Example 2: 12 grams of copper-aluminum alloy powder containing 5.48% nickel, slowly add 70 milliliters of inorganic alkali solution containing 16 grams of NaOH at room temperature, heat up to 60 ° C for 1.5 hours under stirring, and use 500 milliliters, 50 ° C deionized Wash with water until the pH is 8, and then replace the deionized water with absolute ethanol. The levulinic acid was slightly heated to be in a liquid state, and 60 ml and 190 ml of dioxane and the skeleton copper catalyst prepared above were added to the autoclave at the same time, and 0.4 g of KOH was added. The hydrogenation reaction temperature is controlled at 130-140° C., the hydrogen pressure is 4.0 MPa, and the reaction is continued for 2.5 hours. The conversion rate of levulinic acid is 99.7%, and the selectivity of γ-valerolactone is 95.6%.
Embodiment 3
[0016] Embodiment 3: Change the copper-aluminum alloy powder activation condition in embodiment 1 into 70 ℃ of activation 1.5 hours, the levulinic acid hydrogenation reaction solvent is dehydrated alcohol, other catalyst activation methods and hydrogenation reaction conditions are the same as embodiment 1 The hydrogenation conversion rate of levulinic acid was 99.5%, and the selectivity of γ-valerolactone was 96.8%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com