Lithium ferric phosphate battery adopting compound conductive agent and manufacturing method thereof
A lithium iron phosphate battery and composite conductive agent technology, which is applied in the manufacture of electrolyte batteries, non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, battery electrodes, etc., can solve the problems of conductive polymer volume shrinkage, reduced conductivity efficiency, and high production costs, and achieve improved conductivity stability Performance, capacity and ratio increase, and the effect of reducing harsh requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
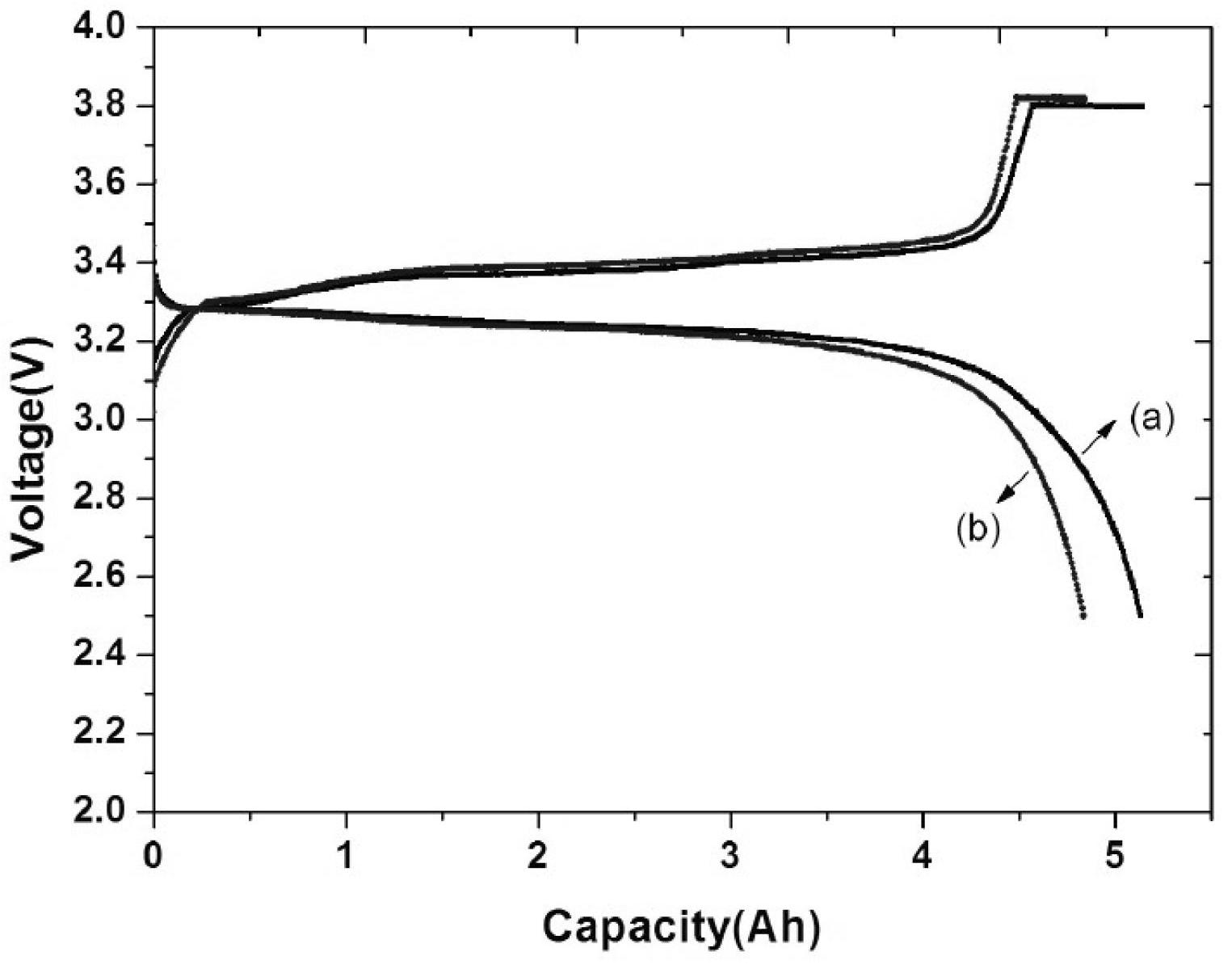
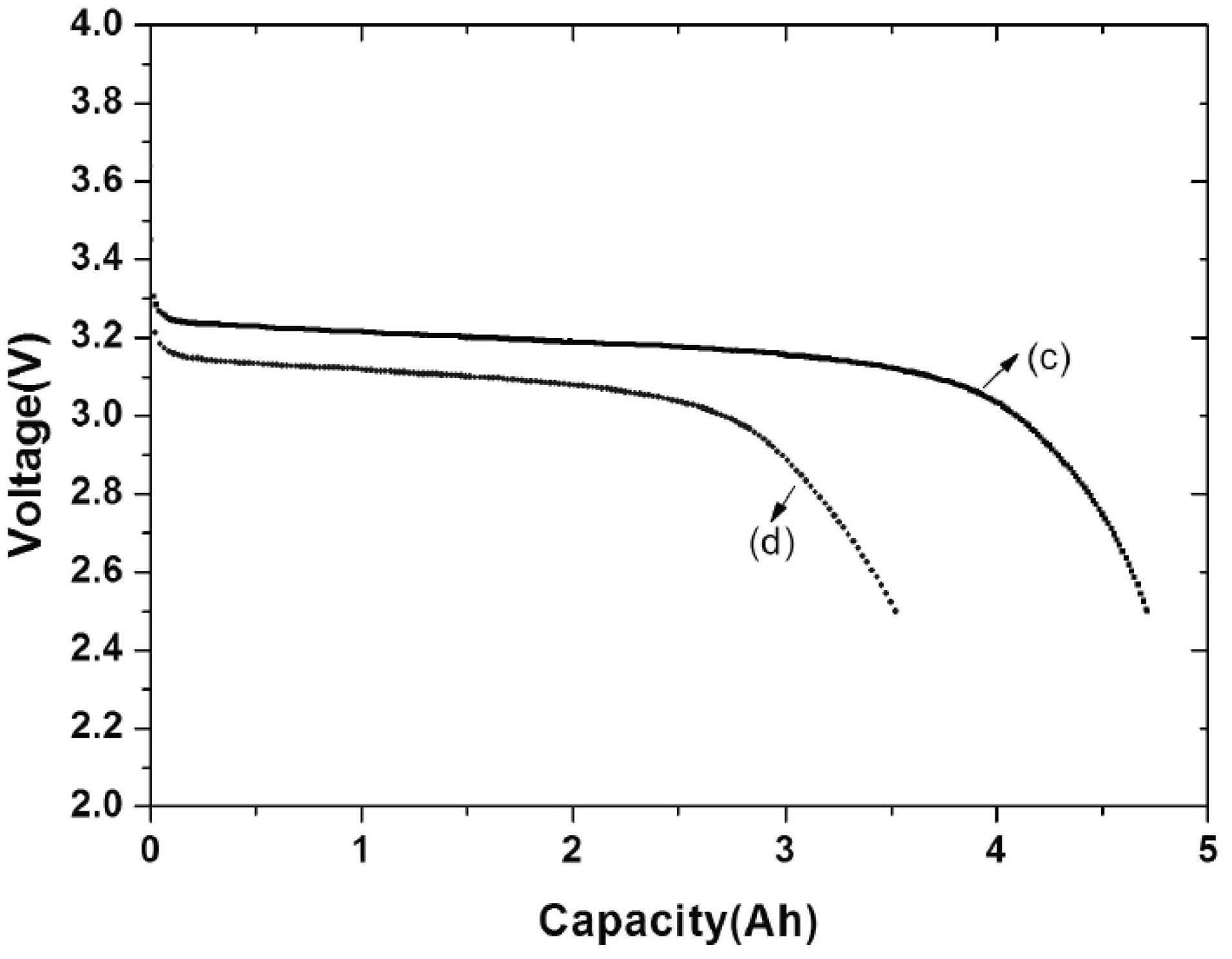
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
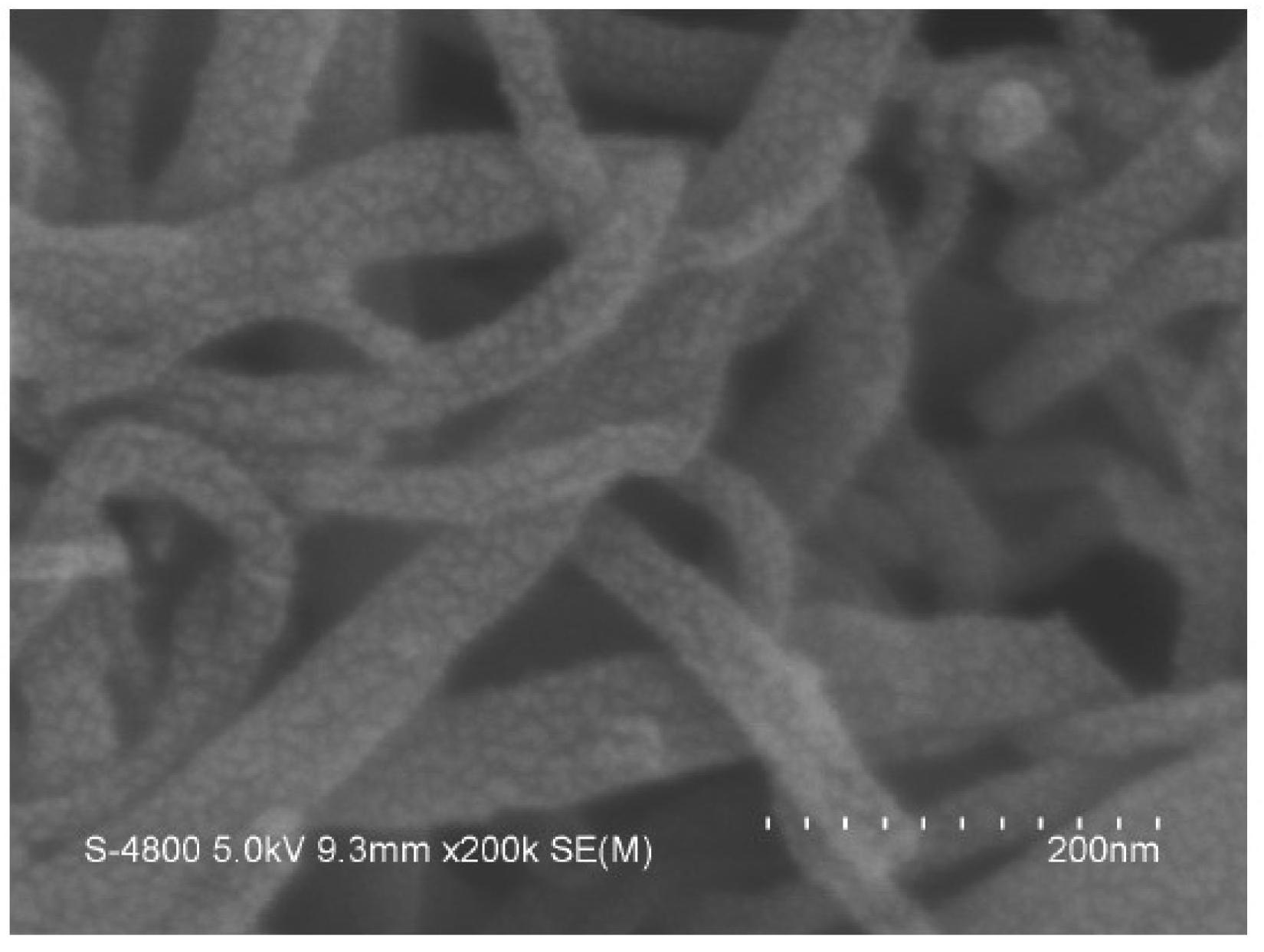
[0020] Dissolve 3 parts of the positive electrode binder polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF into 30 parts of 100% N-methylpyrrolidone and stir to prepare the positive electrode gel. Add 1 part of carbon nanotubes / polypyrrole to the positive electrode gel for dispersion, and finally add 96 parts The positive electrode active material LiFePO 4 Stirring is carried out to prepare positive electrode slurry. The positive electrode slurry is uniformly coated on both sides of the aluminum foil, and after drying, the positive electrode sheet is obtained by rolling and cutting. Mix 97 parts of graphite, 0.5 parts of carbon nanotubes / polypyrrole, 16.7 parts of water-based binder LA132 (the water-based binder LA132 is a solution, and the solute content is 15%), and 145.5 parts of deionized water are evenly mixed to make negative electrode slurry , evenly coated on both sides of the copper foil, after drying, rolling and slitting to obtain the negative electrode sheet. Using the winding method...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Dissolve 2.3 parts of the positive electrode binder polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF into 23 parts of 100% N-methylpyrrolidone and stir to prepare the positive electrode gel. Add 0.7 parts of carbon nanotubes / polypyrrole to the positive electrode gel for dispersion, and finally add 97 parts of positive active material LiFePO 4 Stirring is carried out to prepare positive electrode slurry. The slurry is evenly coated on both sides of the aluminum foil, and after drying, the positive electrode sheet is obtained by rolling and cutting. Mix 97 parts of graphite, 0.5 parts of carbon nanotubes / polypyrrole, 16.7 parts of water-based binder LA132 (the water-based binder LA132 is a solution with a solute content of 15%), and 145.5 parts of deionized water to make a negative electrode The slurry is evenly coated on both sides of the copper foil, and after drying, the negative electrode sheet is obtained by rolling and cutting. Using the winding method, place the negative electrode s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com