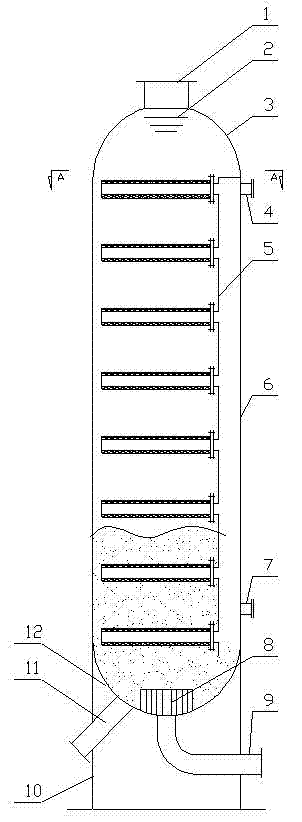
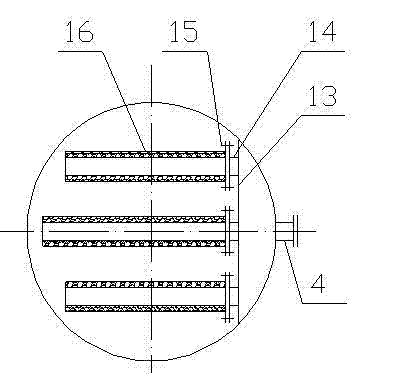
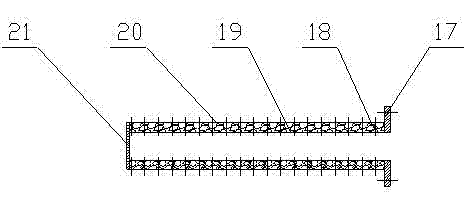
Naphtha hydrogenation method and decoking tank
A process method and naphtha technology, applied in the fields of hydrotreating process, petroleum industry, separation method, etc., can solve the problems of complex process, coking can not play an effective role, etc., and achieve large deposition amount, simple structure, and not easy to clog Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 and comparative example 1
[0034] Coking naphtha hydrorefining process. Coked naphtha is mixed with hydrogen and heated to 230°C in a heating furnace, and then enters the decoking tank and then enters the hydrogenation reactor. The hydrogenation catalyst FH-40A is a commercial hydrogenation refining catalyst developed and produced by Sinopec Fushun Petrochemical Research Institute. The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 1, and the operating conditions and results are shown in Table 2. The difference of the comparative example is that no decoking tank is provided.
[0035] Table 1 Raw oil properties.
[0036] raw material coker naphtha Distillation range, ℃ 36~192 Sulfur, μg / g 4960 Nitrogen, μg / g 126 Bromine value, gBr / (100mL) 48
[0037] Table 2 Operating conditions and product properties.
[0038] Example 1 Comparative example 1 Reaction hydrogen pressure, MPa 4.0 4.0 Hydrogen oil volume ratio 800:1 800:1 volumet...
Embodiment 2 and comparative example 2
[0041] Catalytic cracking heavy naphtha selective hydrodesulfurization process. Catalytic cracking naphtha adopts commercial AFS-12 catalyst (produced by Petroleum University), at a pressure of 0.5MPa, a temperature of 35℃~45℃, and a volume space velocity of 2.0h -1 , Deodorization is carried out under the condition of gas-oil volume ratio (air / gasoline) 4:1. The deodorized product is subjected to fractionation, and the fractionation point is 70°C to obtain catalytically cracked heavy naphtha. The catalytically cracked heavy naphtha is mixed with hydrogen and heated to 250°C in a heating furnace, and then enters the decoking tank for decoking and then enters the hydrogenation reactor. Hydrogenation catalyst FGH-11 is a commercial selective hydrodesulfurization catalyst developed and produced by Sinopec Fushun Petrochemical Research Institute. The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 3, and the operating conditions and results are shown in Table 4. The difference of...
Embodiment 3 and comparative example 3
[0047] Pre-hydrogenation of straight-run naphtha provides feedstock for catalytic reforming. Straight-run naphtha is mixed with hydrogen and heated to 300°C in a heating furnace, and then enters the decoking tank for decoking and then enters the hydrogenation reactor. Hydrogenation catalyst FH-40C is a commercial hydrogenation refining catalyst developed and produced by Sinopec Fushun Petrochemical Research Institute. The properties of raw materials are shown in Table 5, and the operating conditions and results are shown in Table 6. The difference of the comparative example is that no decoking tank is provided.
[0048] Table 5 Main properties of straight-run naphtha.
[0049] raw material straight run naphtha source Blended Straight Run Naphtha Density (20℃), g / cm 3 0.7348 Sulfur content, μg / g 800 Nitrogen content, μg / g 2.8
[0050] Table 6 Operating conditions and results.
[0051] Process conditions Example 3 Com...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com