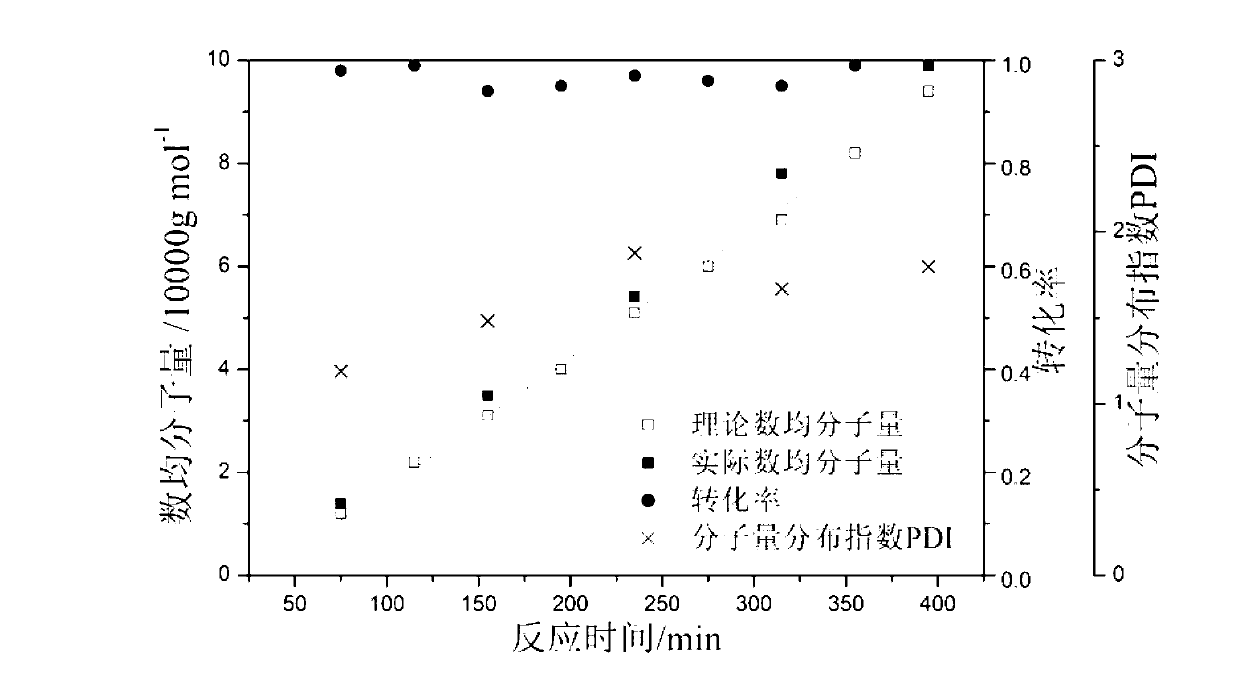
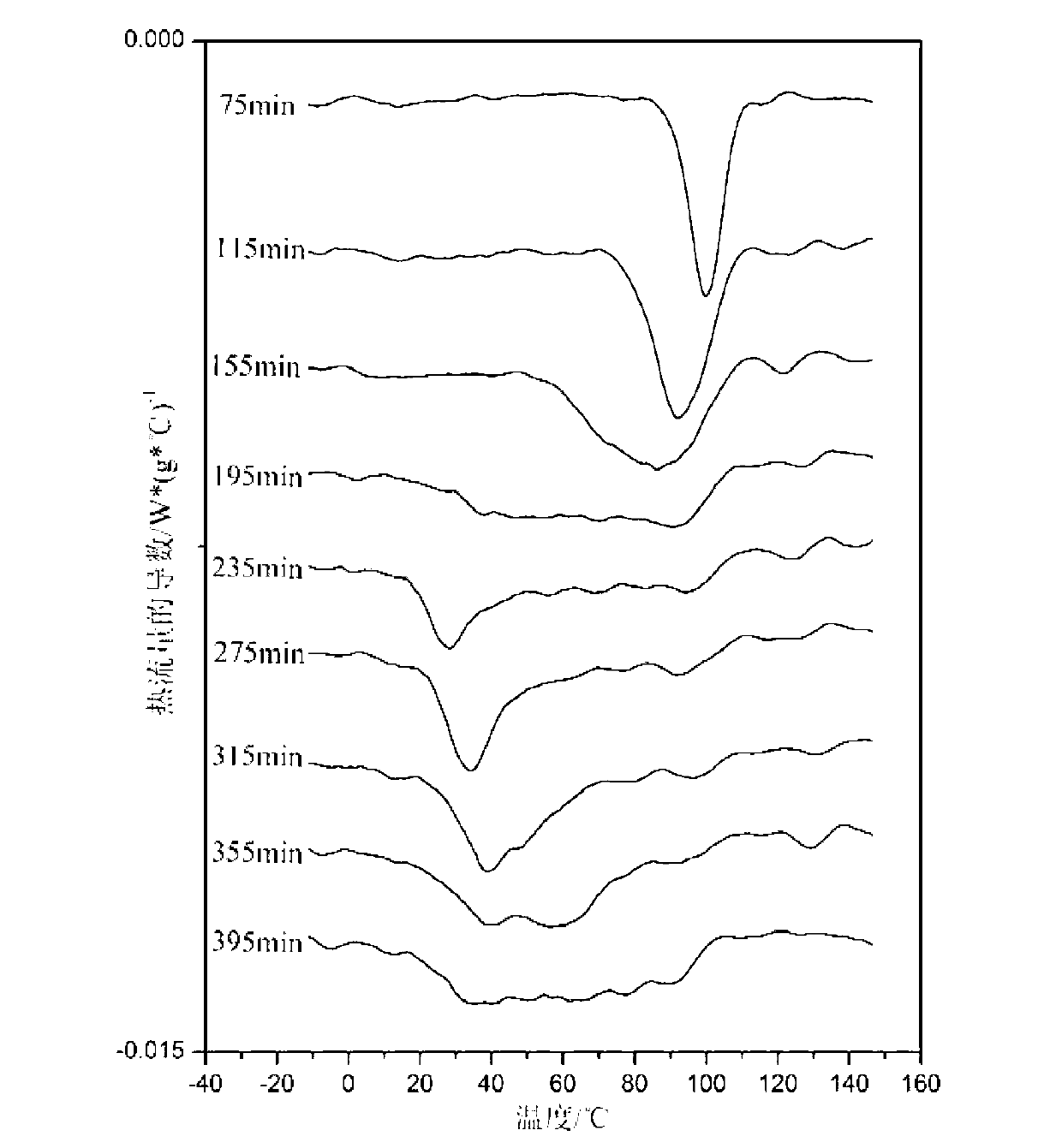
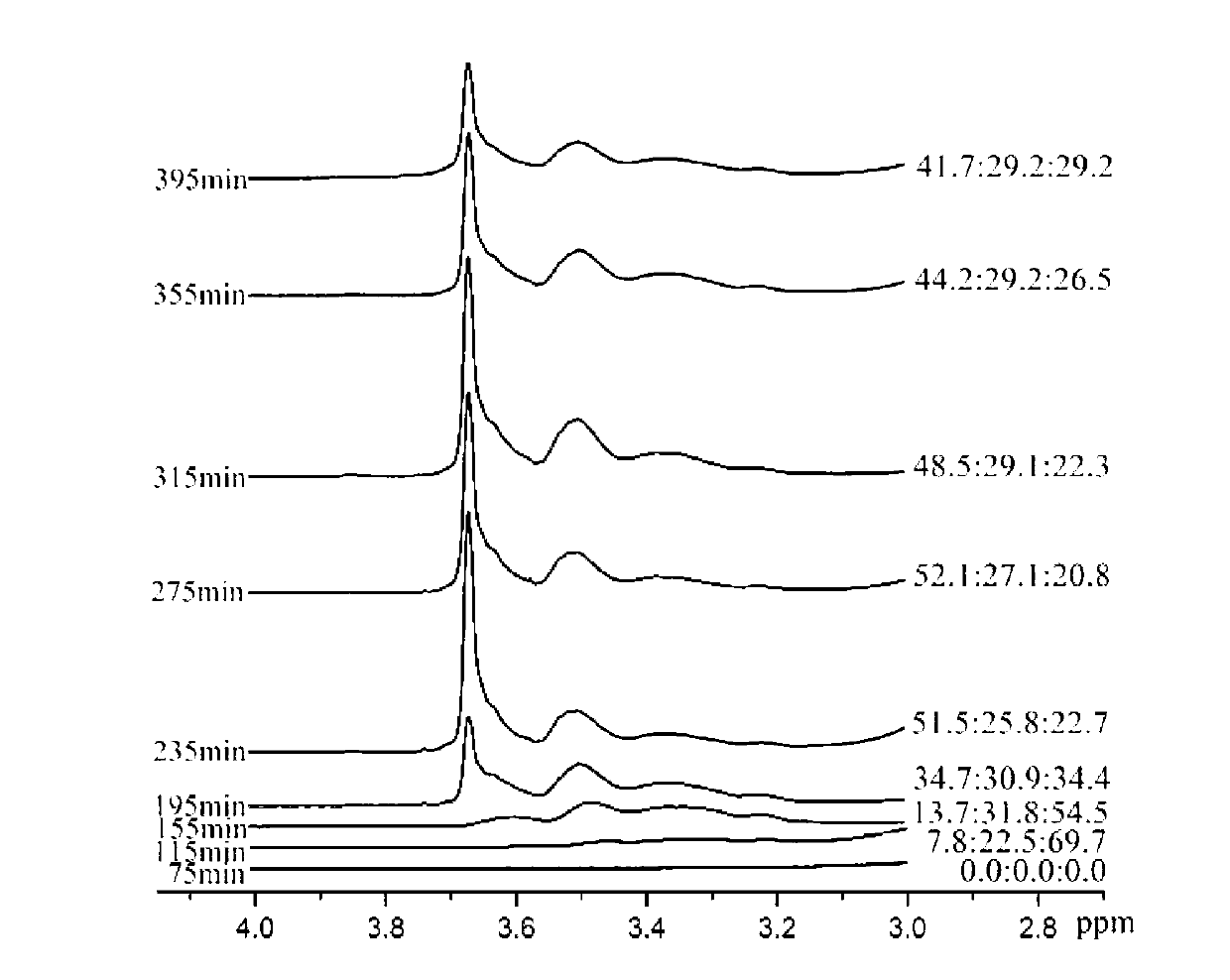
V-shaped gradient copolymer and preparation process thereof
A technology of gradient copolymers and copolymers, applied in the field of copolymers, achieves the effects of wide glass transition temperature, flexible synthesis methods, and excellent shape memory function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] The preparation method of V-type gradient copolymer of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0030] The first step: stirring and dissolving 0.69-3.45 parts by weight of the amphiphilic macromolecular reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer reagent in 150 parts by weight of water to form a uniform water phase, and then adding 5-15 parts by weight of oil phase monomer A, After stirring into an emulsion, they are poured into the reactor together to keep stirring to keep uniform. The reactor was heated to 50-80° C., kept stirring, and nitrogen was passed through the reactor for deoxygenation for 30-60 minutes at the same time. Then add 0.0171~0.0855 parts by weight of water-soluble initiator, and after initiating polymerization for 30~35 minutes, gradually add 50 parts by weight of an aqueous solution containing 0.3~1.0 parts by weight of sodium hydroxide (in advance nitrogen bubbling and deoxygenation for 30~60 minutes). Continue the reaction for...
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1 : Copolymerization of styrene (St) and methyl acrylate (MA), molecular weight 9w.
[0051] The first step: 2.3 parts by weight of amphiphilic macromolecular RAFT was stirred and dissolved in 150 parts by weight of water to form a uniform water phase, and then 10 parts by weight of St was added, stirred into an emulsion, and then poured into the reactor to continue stirring to maintain evenly. The reactor was heated to 70°C and kept stirring while nitrogen was passed through the reactor to deoxygenate for 30 minutes. Then, 0.0285 parts by weight of potassium persulfate was added to the system, and 50 parts by weight of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide containing 0.6 parts by weight was gradually added after 35 minutes of polymerization (purging with nitrogen to deoxygenate for 30 minutes in advance). The reaction was continued for 40 minutes to complete the polymerization process of the first step.
[0052] Step 2: Add 10 weights each time according ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 : Copolymerization of styrene (St) and methyl acrylate (MA), molecular weight 9w.
[0056] The first step: 2.3 parts by weight of amphiphilic macromolecular RAFT was stirred and dissolved in 150 parts by weight of water to form a uniform water phase, and then 10 parts by weight of St was added, stirred into an emulsion, and then poured into the reactor to continue stirring to maintain evenly. The reactor was heated to 70°C and kept stirring while nitrogen was passed through the reactor to deoxygenate for 30 minutes. Then, 0.0285 parts by weight of potassium persulfate was added to the system, and 50 parts by weight of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide containing 0.6 parts by weight was gradually added after 35 minutes of polymerization (purging with nitrogen to deoxygenate for 30 minutes in advance). The reaction was continued for 40 minutes to complete the polymerization process of the first step.
[0057] Step 2: Add 10 weights each time according ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com