Method for production of citric acid through fermentation of wheat B-starch
A technology of B starch and citric acid, which is applied in the field of fermentation to produce citric acid, can solve the problems of high cost and low output, and achieve the effects of reducing grain consumption, reducing viscosity, and improving fermentation conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
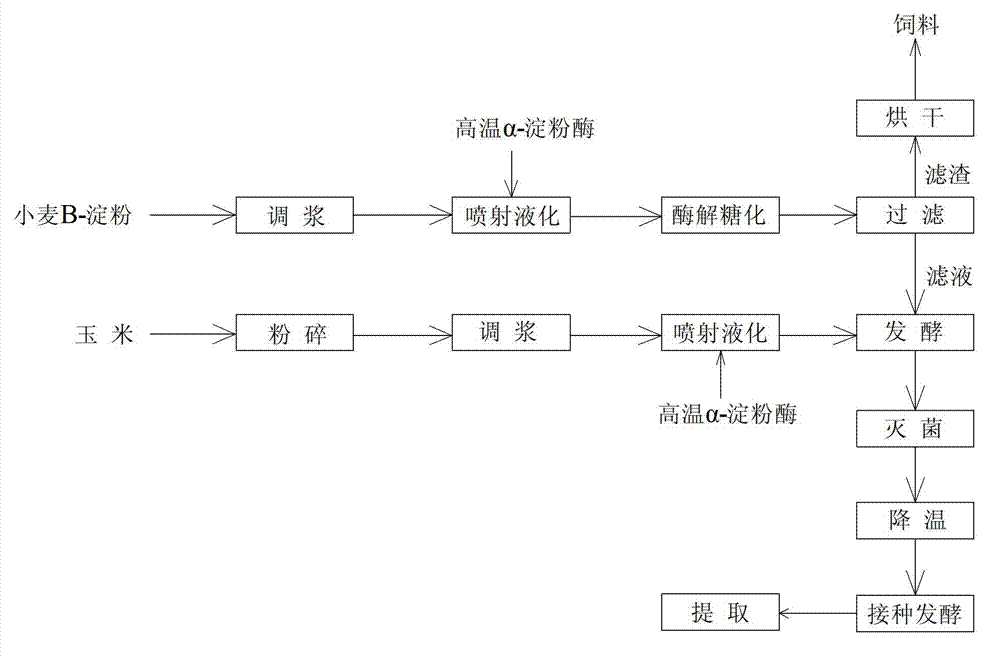
[0031] A method for fermenting wheat B starch to produce citric acid, comprising pulping, liquefaction, saccharification, and fermentation, characterized in that: its specific steps are:
[0032] (1) Measure 70 tons of wheat B starch on a dry basis, add water to prepare a B starch slurry with a mass fraction of 25%;
[0033] (2) Add 35kg of high-temperature α-amylase to the B starch slurry, and input it into the high-temperature jet liquefaction system for liquefaction to obtain the B starch slurry liquefaction solution; the liquefaction temperature is 110°C, and the time is 0.5h;
[0034] (3) Cool down the B starch slurry liquefaction solution to 67°C, adjust the pH to 4.0, add 15kg cellulase, 20kg xylanase, 5kg lysophospholipase, and enzymatically hydrolyze for 5 hours to obtain an enzymolyzed solution;
[0035] (4) Add 50kg of acidic compound glucoamylase to the enzymolysis solution, and saccharify for 16 hours to obtain a saccharification solution;
[0036] (5) Filtration...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for fermenting wheat B starch to produce citric acid, comprising pulping, liquefaction, saccharification, and fermentation, characterized in that: its specific steps are:
[0042] (1) Measure 70 tons of wheat B starch slurry on a dry basis, add water to prepare the B starch slurry with a mass fraction of 27%;
[0043] (2) Add 42kg of high-temperature α-amylase to the B starch slurry, and input it into the high-temperature jet liquefaction system for liquefaction to obtain the B starch slurry liquefaction solution; the liquefaction temperature is 100°C, and the time is 1h;
[0044](3) Cool down the B starch slurry liquefaction solution to 70°C, adjust the pH to 4.2, add 7 kg of cellulase, 30 kg of xylanase, and 7 kg of lysophospholipase, and perform enzymatic hydrolysis for 10 hours to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis solution;
[0045] (4) Add 70 kg of acidic compound glucoamylase to the enzymatic hydrolysis solution, and saccharify for 10 hours to obtain a sacch...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for fermenting wheat B starch to produce citric acid, comprising pulping, liquefaction, saccharification, and fermentation, characterized in that: its specific steps are:
[0052] (1) Measure 70 tons of wheat B starch slurry on a dry basis, add water to prepare the B starch slurry with a mass fraction of 30%;
[0053] (2) Add 25kg of high-temperature α-amylase to the B starch slurry, and input it into the high-temperature jet liquefaction system for liquefaction to obtain the liquefaction solution of B starch slurry; the liquefaction temperature is 95°C and the time is 2 hours;
[0054] (3) Cool down the B starch slurry liquefaction solution to 65°C, adjust the pH to 4.5, add 20kg of cellulase, 14kg of xylanase, and 3.5kg of lysophospholipase, and perform enzymatic hydrolysis for 7 hours to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis solution;
[0055] (4) Add 60 kg of acidic compound glucoamylase to the enzymolysis solution, and saccharify for 12 hours to obtain a sacchari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com