Method for replenishing nitrogen source culture fungus in batch to produce cellulase
A cellulase and production method technology, applied in the field of enzymatic fermentation, can solve the problems of high mass transfer, increased osmotic pressure, unfavorable bacterial growth in the lag phase, etc., and achieves the effects of reducing production cost, facilitating mycelial absorption, and promoting mass synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: take Trichoderma reesei Rutc-30 as fermentation strain
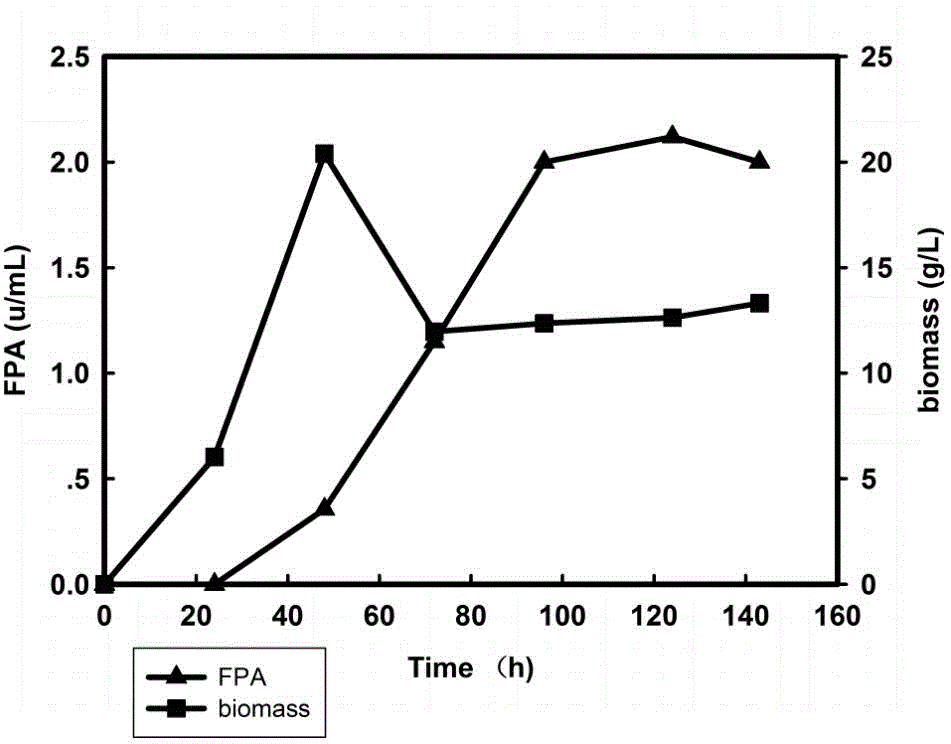
[0027] In a 50L fermenter, pretreated rice straw was used as the only carbon source for enzyme production and a medium was prepared with an enzyme inducer. The medium components were: pretreated straw 30g / L, corn steep liquor (CSL) 3g / L , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.4 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 2 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 5mg / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.4mg / L, MnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.6mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 2mg / L, CaCl 2 0.01g / L; Sterilize at 121°C for 20 minutes, cool down to 30°C, inoculate 2L of cultured Rutc-30 seeds with 5% inoculum in the sterilized fermenter, and ferment at 30°C for 7 days to produce enzymes. Fermentation ends , the highest measured enzyme activity is 2.12u / ml, the growth and enzyme production curve is as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: Taking Trichoderma reesei Rutc-30 as fermentation strain
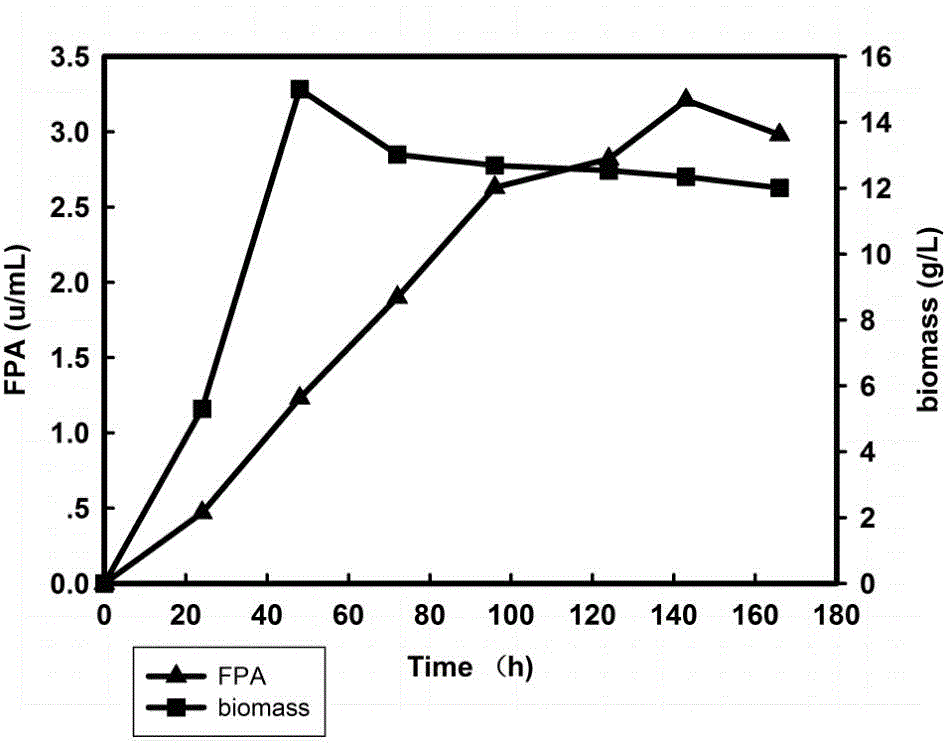
[0029] In a 50L fermenter, pretreated rice straw was used as the only carbon source for enzyme production and a medium was prepared with an enzyme inducer. The medium components were: pretreated straw 30g / L, corn steep liquor (CSL) 1g / L , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 1.4 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 2 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 5mg / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.4mg / L, MnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.6mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 2mg / L, CaCl 2 0.01g / L; sterilize at 121°C for 20min, cool down to 30°C, inoculate 1L of the cultivated Rutc-30 seeds with 2.5% inoculum in the sterilized fermenter, and ferment on the 3rd and 5th day respectively Add 100ml of 100g / L corn steep liquor solution, and ferment at 30°C for 7 days to produce enzyme; the highest enzyme activity is 3.21u / ml, and the growth and enzyme production curve is as follows: figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: take Trichoderma reesei Rutc-30 as fermentation strain
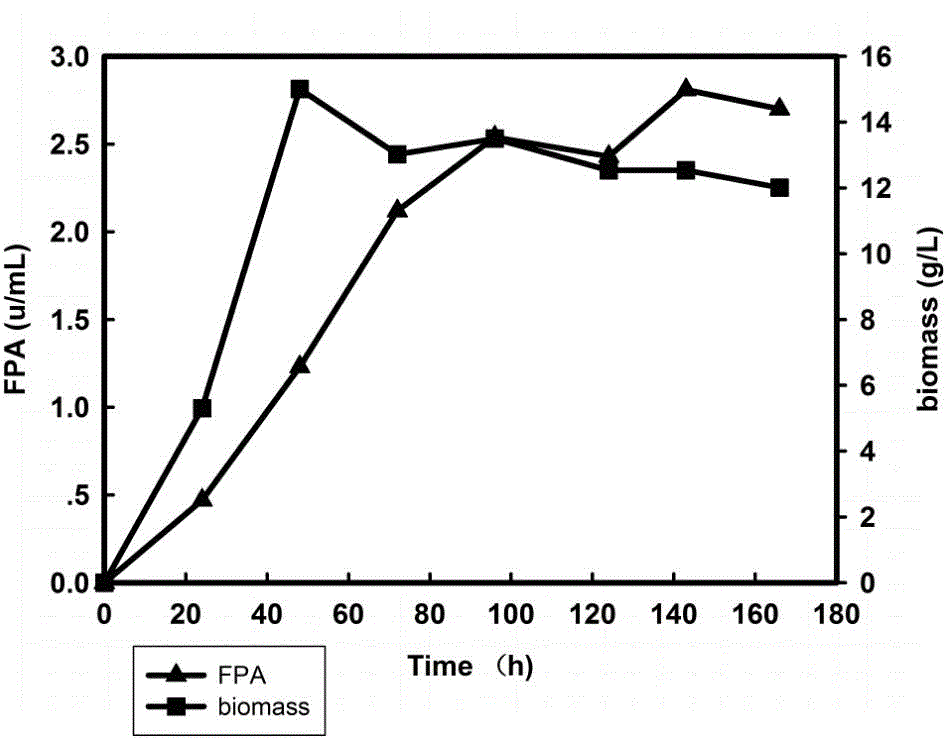
[0031] In a 50L fermenter, pretreated rice straw was used as the only carbon source for enzyme production and a medium was prepared with an enzyme inducer. The medium components were: pretreated straw 30g / L, corn steep liquor (CSL) 3g / L , (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.5 g / L, KH 2 PO 4 2 g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 5mg / L, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.4mg / L, MnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 1.6mg / L, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 2mg / L, CaCl 20.01g / L; sterilize at 121°C for 20min, cool down to 28°C, inoculate 400ml of cultured Rutc-30 seeds with 1% inoculum in the sterilized fermenter; Add 100g / L (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 100ml, fermented at 28°C for 7 days to produce enzymes; the enzyme activity was measured up to 2.85u / ml, and the growth and enzyme production curves were as follows: image 3 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com