Preparation method of super-hydrophobic active carbon modified material
A modified material and activated carbon technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, can solve problems such as loss of low surface energy substances, plugging pores on the surface of activated carbon, and affecting hydrophobic performance. It achieves small consumables, easy recycling, and The effect of large pore volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0034] The concrete realization steps of this preparation method are:
[0035] Step S11, pretreating coal-based columnar and coconut shell granular activated carbon
[0036] Step S111, the specific surface area is 600-1500m 2 / g of coconut shell granular activated carbon and coal-based columnar activated carbon as raw materials, first use a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 1-4mol / L to immerse and shake for 10-24 hours, and filter to obtain the filtrate;
[0037] Step S112, washing with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral, then soaking and shaking with 3.83-18.09 wt% hydrochloric acid solution for 10-24 hours, filtering, and washing with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral;
[0038] Step S113, put the sample into a beaker and add an appropriate amount of deionized water, then put it into an ultrasonic instrument with a power of 500-1000W, wash it for 30-90min, filter it and place it in a drying oven at 80-130°C for 14-20 hours;
[0039] St...
Embodiment 1
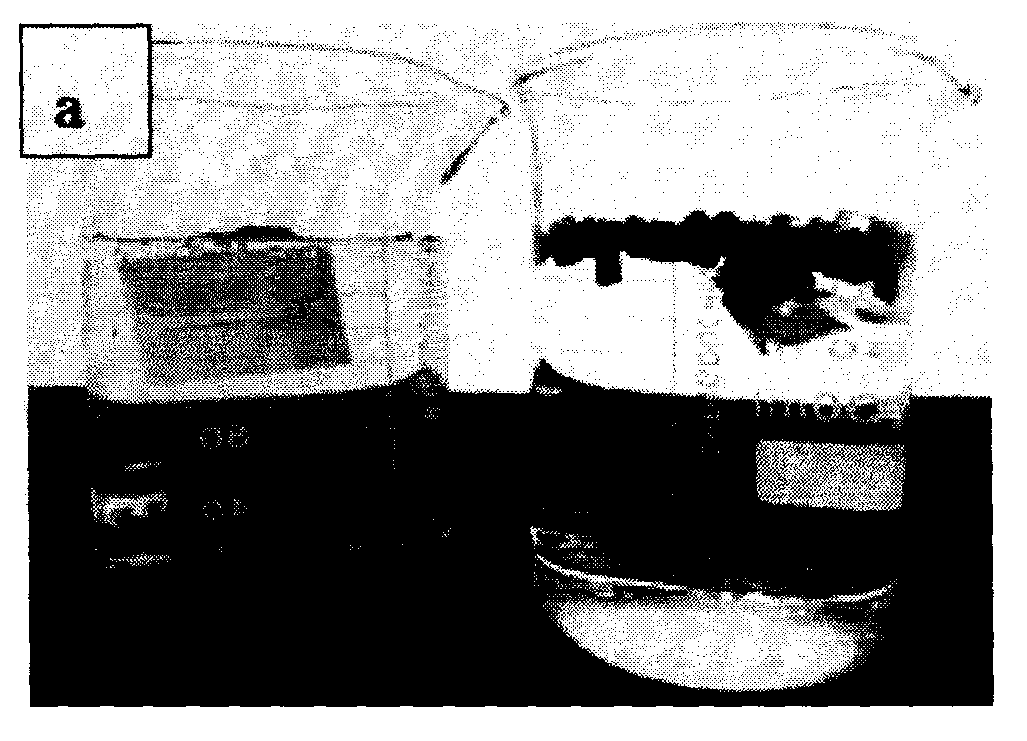
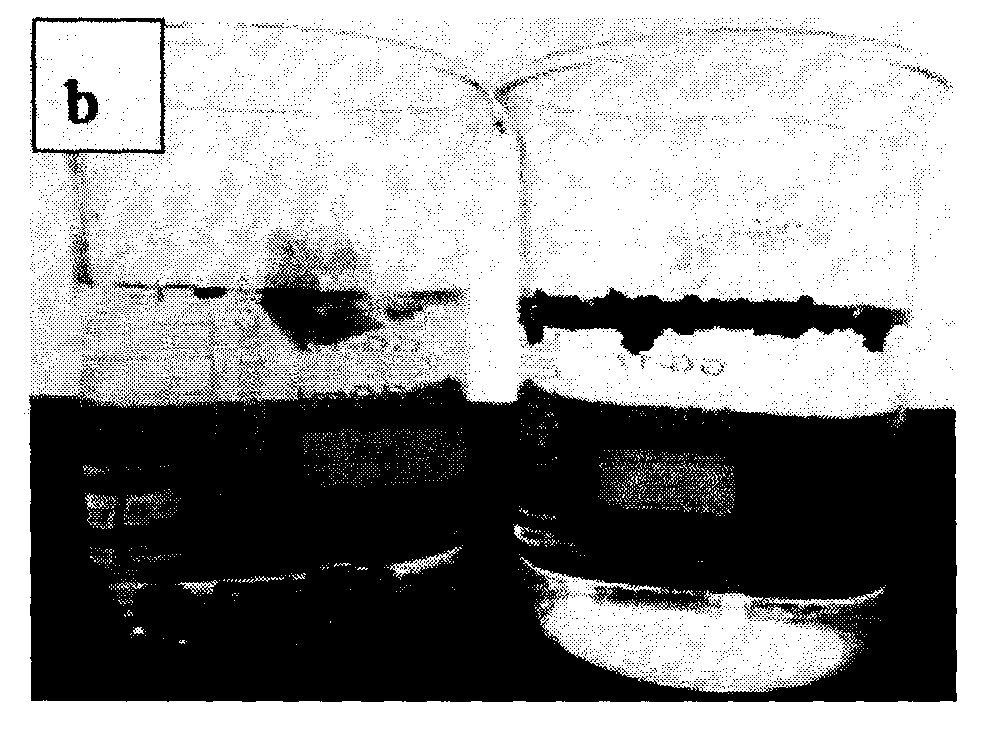
[0053] Example 1: The modified coconut shell activated carbon and coal-based activated carbon were tested for contact angle respectively. First, the activated carbon raw material and the modified preparation material were ground into powder, and then the powdered activated carbon was evenly spread on different glass surfaces. On the chip, the contact angle with water is obtained by adding water droplets, photographing, and measuring. The contact angles of coconut shell carbon materials with water before and after modification are 29.1° and 159.8°, respectively, and the contact angles of coal-based carbon materials with water before and after modification are 28.1° and 157.8°, respectively. This shows that the activated carbon modified material prepared by the present invention has superhydrophobic properties.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: The coconut shell activated carbon and coal-based activated carbon prepared by modification were tested for water absorption respectively. The conditions were to place carbon materials of equal mass before and after modification in water at 25°C at room temperature, and use the difference method to determine the water absorption. The adsorption capacity of activated carbon for water in different time periods. The experimental results show that after standing in water at 25°C for 8 hours, the relative water absorption rates of coconut shell carbon materials before and after modification are 33.08% and 92.61%, respectively, and the relative water absorption rates of coal-based carbon materials before and after modification are 31.71% and 97.35%, respectively. . The experimental results show again that the activated carbon modified material prepared by the present invention has super-hydrophobic properties.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com