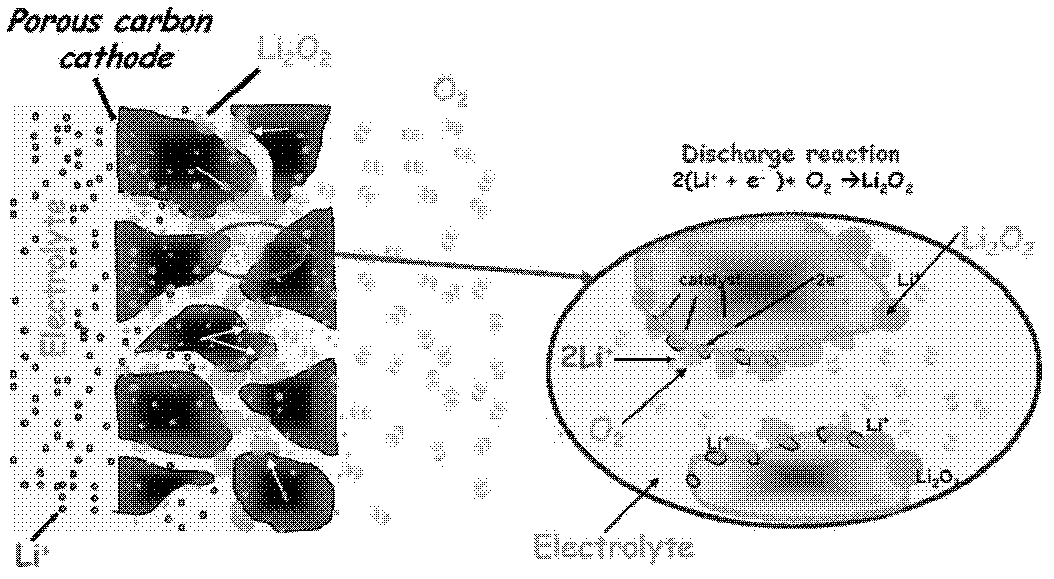
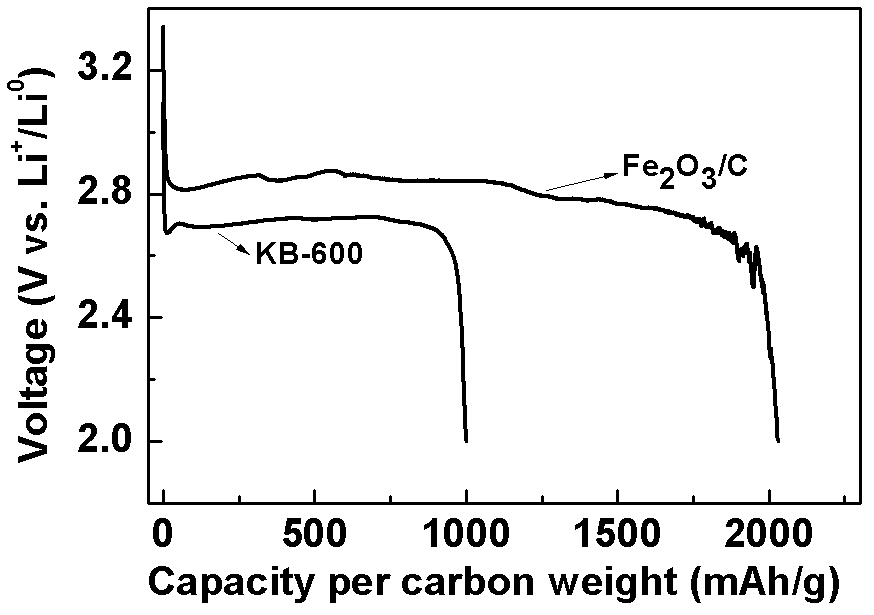
Application of carbon material containing in-situ doped component with catalytic activity to lithium-air battery
A catalytic activity, in-situ doping technology, applied in battery electrodes, physical/chemical process catalysts, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of limited uniformity between catalysts and carbon materials, limited catalyst Problems such as particle size and low catalyst utilization rate can be solved to improve dispersion and coverage, reduce charge and discharge polarization potential, and improve energy efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0031] SBA-15 ordered mesoporous SiO 2 The preparation of, as reference Zhao, D., Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50to 300Angstrom Pores.Science 1998, 279 (5350), 548-552.
[0032] Specifically, it can be prepared according to the following steps: dissolve the surfactant in a solvent to obtain a solution A with a concentration of 1-10wt%; After heating for 12-48h, filtering, washing, and drying, burn off the surfactant at 300-550°C to obtain SBA-15 ordered mesoporous SiO 2 .
[0033] The surfactant is one or more than two of F127, F108 or P123; the solvent is one or more of water, ethanol, isopropanol, methanol; the acid solution is dilute hydrochloric acid, Sulfuric acid or nitric acid; the silicon source is ethyl orthosilicate.
Embodiment 1
[0035]Porous carbon materials were prepared using nano-magnesium carbonate powder as a template. Accurately weigh 5g of sucrose and 0.29g of nickel nitrate hexahydrate, add 15ml of deionized water and stir until completely dissolved, then add 5g of magnesium carbonate, heat in a water bath at 80°C and stir mechanically to make them completely soluble, the power range of mechanical stirring It is 200w, and the stirring speed is 300rpm. After the water evaporated completely, put it into 80℃ for vacuum drying for 24h. Then put the dried product into a high-temperature tube furnace for carbonization, the atmosphere is nitrogen, and the gas flow is controlled at 30ml / min. Take out the nanoparticle / carbon composite by carbonization at 800°C for 2 hours, add an appropriate amount of 2M dilute hydrochloric acid to remove nano-magnesium carbonate, and vacuum dry at 80°C for 24 hours after filtration to obtain a porous carbon material doped with NiO nanoparticles in situ.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Porous carbon materials were prepared using nano-magnesia powder as a template. Accurately weigh 5g of sucrose and 0.267g of zirconium oxynitrate dihydrate, add 8ml of deionized water and stir until completely dissolved, then add 8g of magnesium oxide, heat and stir mechanically in a water bath at 80°C to make them completely soluble, the power of mechanical stirring The range is 200w and the stirring speed is 300rpm. After the water evaporated completely, put it into 80℃ for vacuum drying for 24h. Then put the dried product into a high-temperature tube furnace for carbonization, the atmosphere is nitrogen, and the gas flow is controlled at 30ml / min. Carbonate at 900°C for 2 hours to obtain nanoparticle / carbon composites, then use appropriate amount of 2M dilute hydrochloric acid to remove nano-magnesium oxide, filter and dry in vacuum at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain in-situ doped ZrO 2 Nanoparticle porous carbon materials.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com