Fiber enhanced silicon carbide porous ceramic and preparation method and application thereof
A porous ceramic and fiber-reinforced technology, applied in the direction of ceramic products, chemical instruments and methods, applications, etc., can solve the problems of low toughness and limited applications, achieve high flexural strength, expand the scope of practical applications, and improve the flexural strength Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
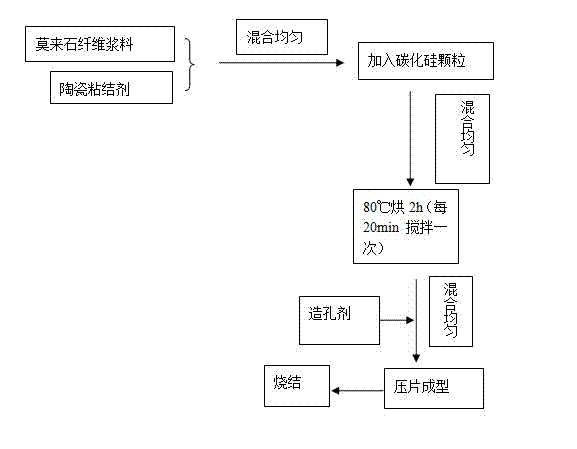
[0054] First prepare mullite fiber slurry, heat and stir 4g sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and sufficient deionized water to boil until the total weight of the solution is 200g to obtain a 2% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution, and then add 40g of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose The mullite fiber is added to the 2% CMC solution in a small amount and multiple times (5-8 times), initially dispersed, and then ball milled to obtain a uniform mullite fiber slurry.
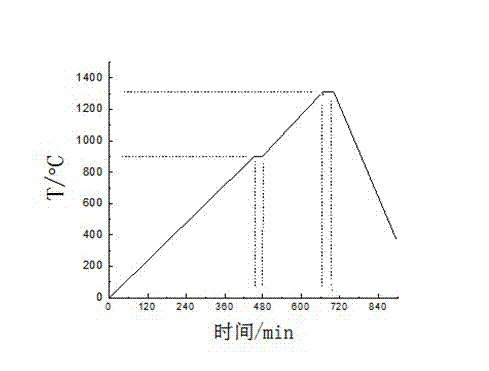
[0055] First mix the ceramic binder (mainly composed of 64.53% potassium feldspar, 12.20% kaolin and 23.27% quartz) and mullite fiber slurry at a mass ratio of 1:1, and then add Silicon carbide particles, stirred and mixed evenly, put them in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours to semi-dry, then added graphite and activated carbon as pore-forming agents, stirred and mixed evenly, and then pressed into tablets under a molding pressure of 3MPa. Sintered at a temperature of 1300°C.
[0056] The test results are: use 230μm...
Embodiment 2
[0058] First mix the ceramic binder (the main components are potassium feldspar 64.53%, kaolin 12.20% and quartz 23.27%) and the mullite fiber slurry prepared in Example 1 in a mass ratio of 1:2, and then add the average Silicon carbide particles with a particle size of about 230 μm, stirred and mixed evenly, then placed in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours to semi-dry, then added graphite and activated carbon as pore-forming agents, stirred and mixed evenly, and then molded under a molding pressure of 3MPa The lower tablet is formed and sintered at a temperature of 1300°C.
[0059] The test results are: use 230μm silicon carbide particles, add 10% ceramic binder and mullite fiber slurry with a mass fraction of 2 times the binder, and add a pore-forming agent with a mass fraction of 10% (5% graphite + 5% activated carbon), after forming at 3MPa and sintering at 1300℃, the porosity of the prepared support is 30%, and the bending strength is 34.91MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0061] First mix the ceramic binder (mainly composed of potassium feldspar 64.53%, kaolin 12.20% and quartz 23.27%) and the mullite fiber slurry prepared in Example 1 in a mass ratio of 1:3, and then add the average Silicon carbide particles with a particle size of about 230 μm, stirred and mixed evenly, then placed in an oven at 80°C for 2 hours to semi-dry, then added graphite and activated carbon as pore-forming agents, stirred and mixed evenly, and then molded under a molding pressure of 3MPa The lower tablet is formed and sintered at a temperature of 1300°C.
[0062] The test results are: use 230μm silicon carbide particles, add 10% ceramic binder and mullite fiber slurry with a mass fraction of 3 times the binder, and add a pore-forming agent with a mass fraction of 10% (5% graphite + 5% activated carbon), after forming at 3MPa and sintering at 1300℃, the porosity of the prepared support is 30.36%, and the bending strength is 35.66MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com