Method of obtaining and separating rosmarinic acid, apigenin and luteolin from elsholtzia haichowensis
A technology of rosmarinic acid and luteolin, applied in the field of biological resource utilization of natural products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
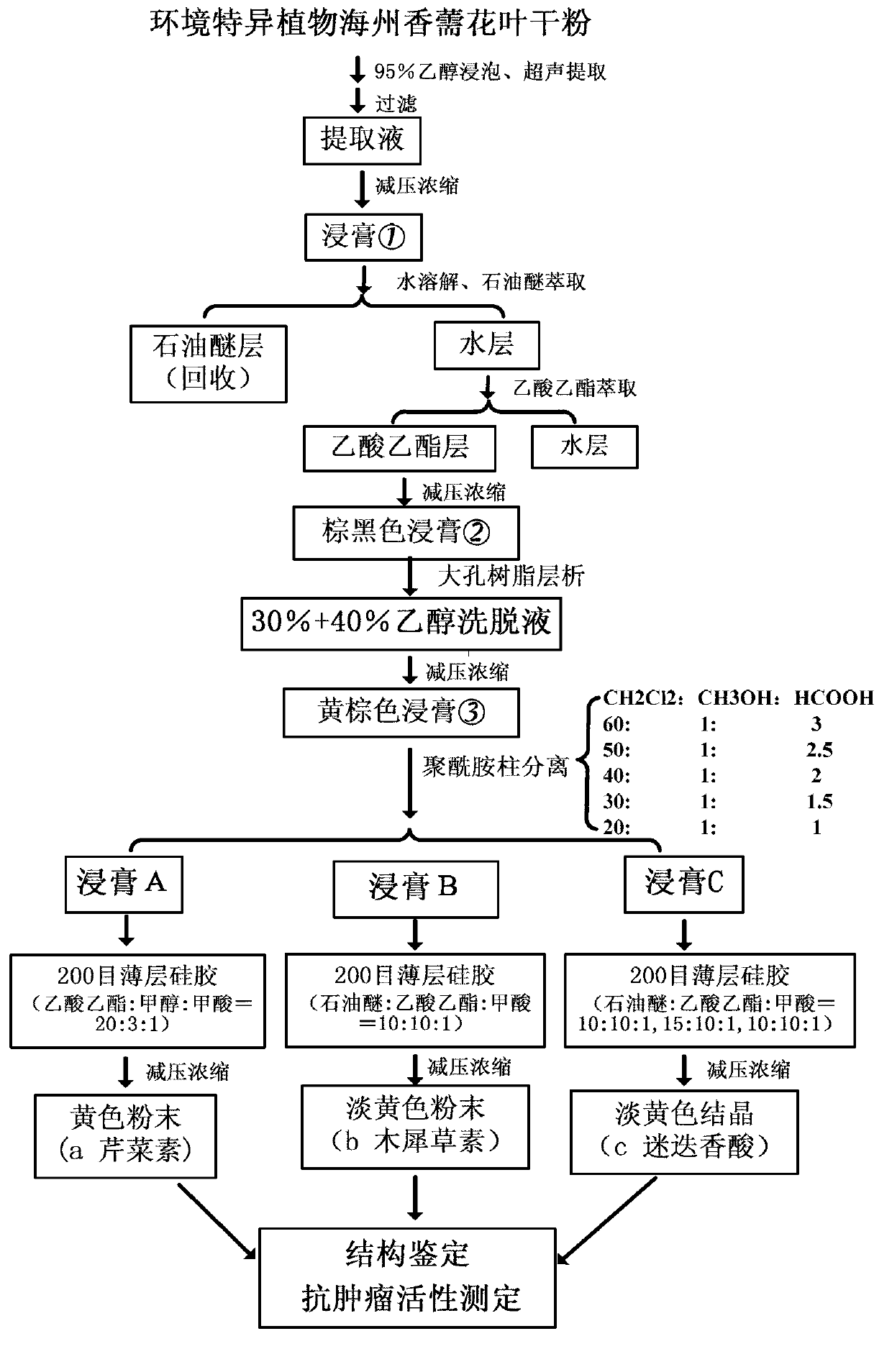
[0040] Embodiment 1, the solvent extraction and the separation of the dry powder of mosaic and leaf in the Rhizoma haizhou of the present invention
[0041] (1) Alcohol extraction
[0042] Air-dry the flowering branches and leaves of Rhizoma haizhou harvested at the full bloom stage and grind them into dry powder (moisture content is less than 0.5%, weight ratio), and pass through a 100-mesh sieve. Take the above 500g dry powder, put it into a 10L plastic bucket, add 5L of 95% (V / V) ethanol, stir evenly and soak for 3 days until the material is completely absorbed, treat with 40KHz ultrasonic frequency for 1 hour, and filter with suction to obtain the filtrate. Repeat the above-mentioned process twice for the residue obtained by suction filtration (that is, replace the dry powder with the residue, and repeat the above-mentioned leaching). The filtrates obtained from the three extractions were combined; then concentrated in vacuo at 45°C to obtain 126.1 g of extract ① (ie, cru...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2, thin-layer silica gel purification and refining of apigenin, luteolin and rosmarinic acid in Herba pilosula of the present invention
[0057] (1) Thin-layer silica gel purification and refining of apigenin
[0058] Dissolve 50 g of 200-mesh silica gel in 250 ml of ethyl acetate, stir to remove air bubbles, and pack the column under pressure.
[0059] 0.782g of extract A obtained in Example 1 was dissolved with 4ml of methanol, and 2g of silica gel was added to mix the sample, spin-dried and then mounted on the top of the column. Use the volume ratio of ethyl acetate:methanol:formic acid=20:3:1 as the development system to carry out pressurized column elution, a total of 400ml eluent is required, collect the effluent from each tube (collect 1 tube per 10ml), and keep Carry out TLC spot plate tracking, blue fluorescence under ultraviolet light, 1%AlCl 3 The solution is bright yellow and the iodine-fumed silica gel plate has no impurities, and the three indica...
Embodiment 3
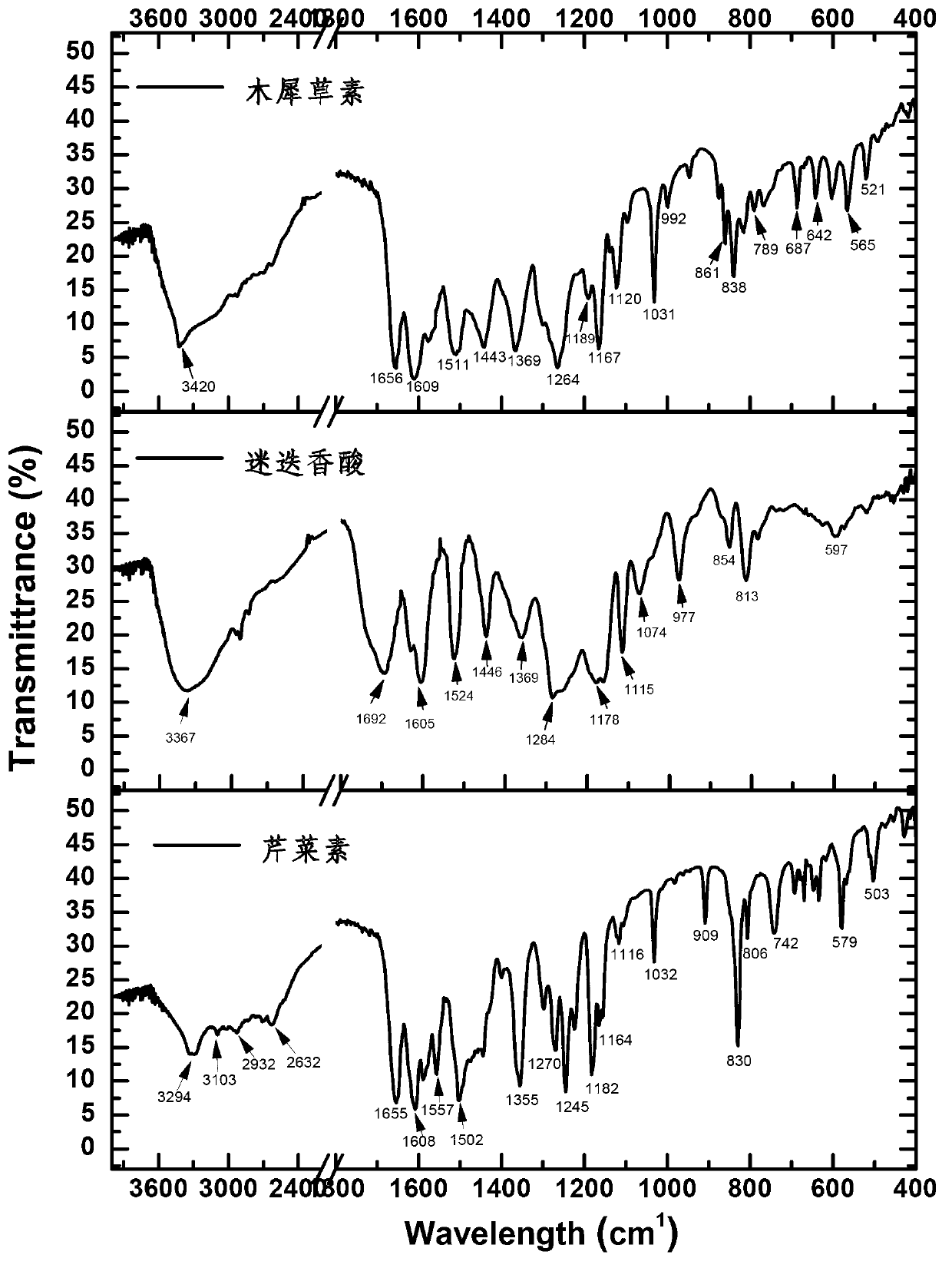
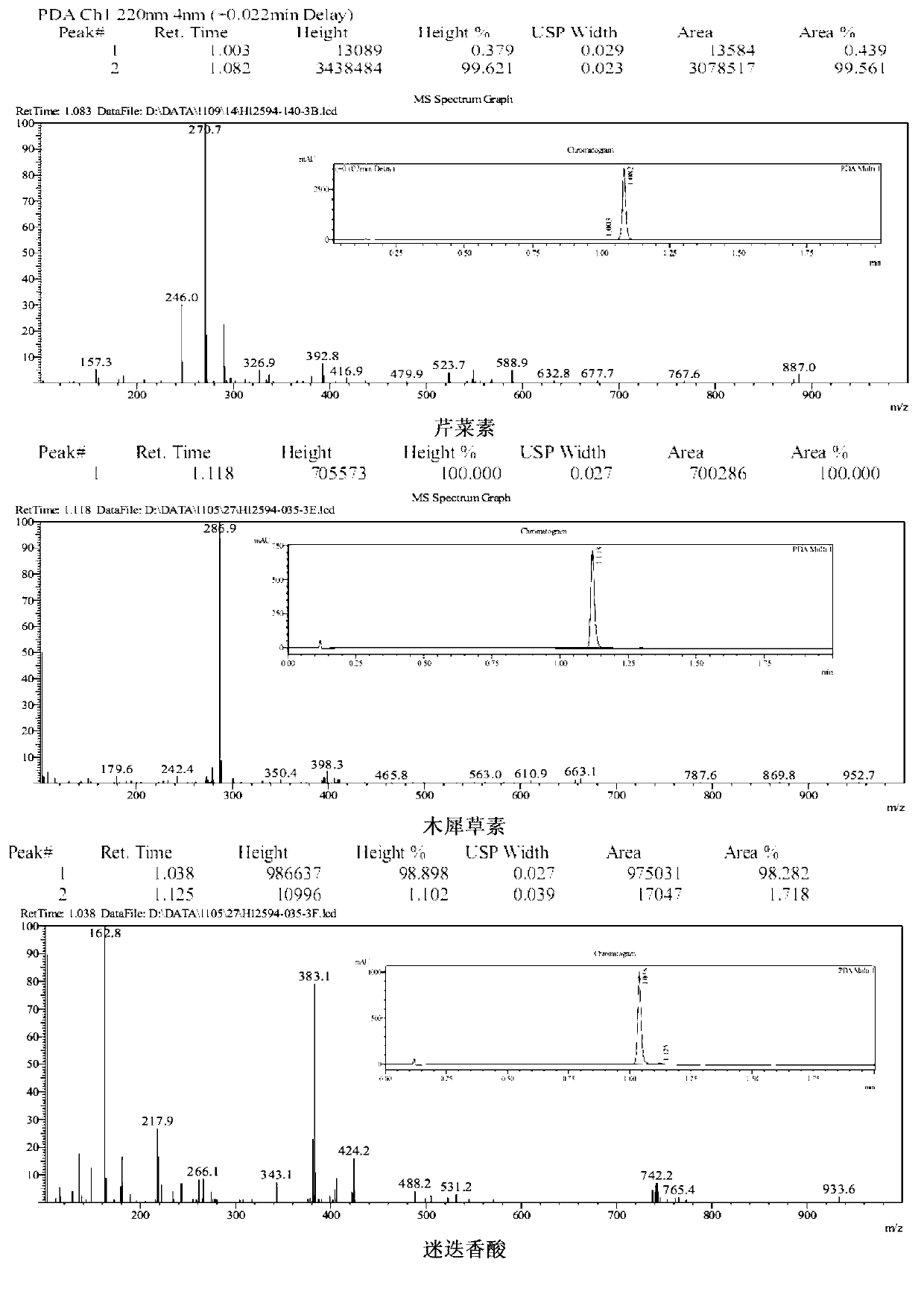
[0064] Embodiment 3, identification of the chemical structure of apigenin, luteolin, and rosmarinic acid in A. haizhouensis of the present invention
[0065] The light yellow compounds (compounds a, b, c) obtained in Example 2 were dissolved in 20ml of ultrapure water, frozen at -40°C for 2 hours, and dried in vacuum freezer (-80°C) to obtain the product. They were dissolved in deuterated DMSO, and the H-NMR and C-NMR spectra were measured, and the infrared spectrum was measured by the tablet method, which were used to identify the structure. Data are as follows:
[0066] The characteristic peaks of apigenin (purity 100%) are as follows: 1 H-NMR (500MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) δ (ppm) : 12.975(s,1H), 10.605 (s, 1H), 7.936(d,J=8.0Hz,2H), 6.938(d,J=8.3Hz,2H), 6.785(s,1H) , 6.487(s, 1H), 6.199(s, 1H). 13 C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d 6 ) δ(ppm): 182.208, 164.562, 164.179, 161.914, 161.547, 157.773, 128.927, 121.653, 116.369, 116.369, 104.126, 103.37, 99.26, 194.434 The main characteristic pea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com