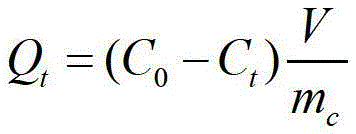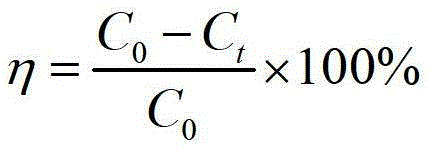Method for preparing amphoteric cellulose by using Canadian goldenrod
A technology of amphoteric cellulose and cellulose, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, adsorption water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of high cost of high-pressure steam flasher and low degree of carboxymethyl substitution Stability and other issues, to achieve the effect of strong treatment and adsorption capacity, production cost protection, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
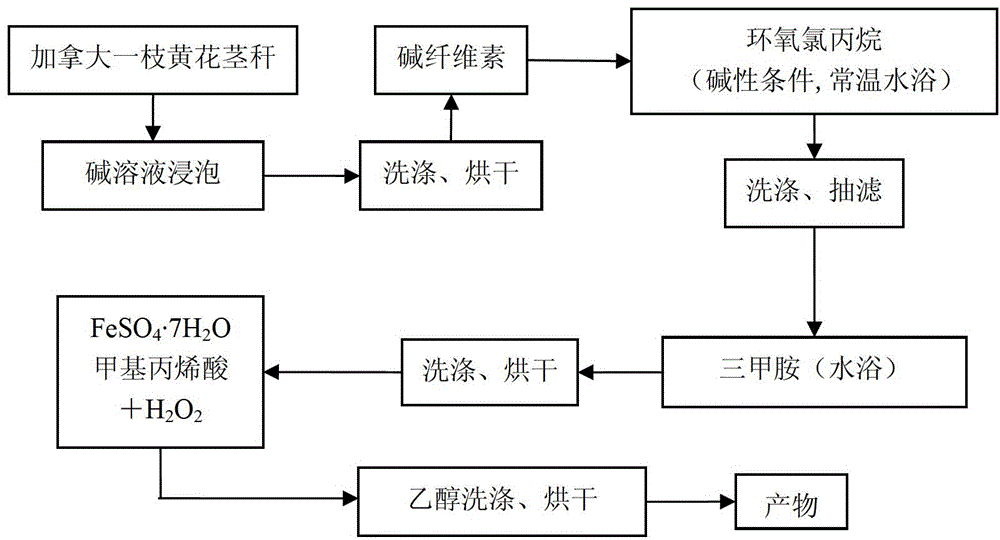
[0027] Crush the stalks of Solidago canadensis to 80 mesh, immerse in 17.5% sodium hydroxide solution, stir for 1 hour, soak for 24 hours, drain with vacuum filter, and then wash with distilled water until the pH is 6-8. Dry in a vacuum oven at 60°C to obtain alkali cellulose.
[0028] Put the alkali cellulose into a round bottom flask, then add 70mL of isopropanol, put it into a magnetic stirrer and stir for 20 minutes to dissolve the alkali cellulose. Add 2 drops of 40% concentrated sodium hydroxide solution dropwise to it, then add 20mL epichlorohydrin, stir and react at room temperature for 24 hours, stop the reaction, and wash the filtered cellulose with acetone, water, and acetone in sequence until pH It is 6-8.
[0029] Transfer the filtered cellulose into another round-bottomed flask, add 20mL trimethylamine aqueous solution to it, heat it in a water bath for 6 hours, stop the reaction, wash the cellulose with distilled water until the pH is 6-8, filter it with suctio...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Adsorption of hexavalent chromium on amphoteric cellulose.
[0033] Required drugs: (a) Potassium dichromate (AR), Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.
[0034] (b) Diphenylcarbazide (AR), Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.
[0035] Add 0.5 g of Solidago canadensis amphoteric cellulose to 250 mL of potassium dichromate solution with an initial mass concentration of 20 mg / L. After sealing with a parafilm, carry out vibration adsorption at 30°C with a shaker speed of 150r / min. After 240 minutes of adsorption, pipette 20.00ml of the solution into a small beaker, filter through a 0.45μm microporous membrane, and let stand.
[0036] Measure the remaining concentration C with a UV-visible spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 540nm t . Calculate the adsorption amount Q of Solidago canadensis amphoteric cellulose to each component at time t t and removal rate η:
[0037] Q t = ( C ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Add 0.5 g of Solidago canadensis amphoteric cellulose to 250 mL of crystal violet and methylene blue solutions with an initial mass concentration of 500 μmol / L, respectively. After sealing with a parafilm, carry out vibration adsorption at 30°C with a shaker speed of 150r / min. After 240 minutes of adsorption, pipette 20.00ml of the solution into a small beaker, filter through a 0.45μm microporous membrane, and let stand. Use a UV-visible spectrophotometer to measure the residual concentration C at wavelengths of 590nm and 662nm respectively t .
[0042] In Example 3, amphoteric cellulose was used to treat the crystal violet solution, and the adsorption equilibrium was reached within 35-37 minutes. At this time, the concentration of crystal violet was 1.085 μmol / L, and the removal rate reached 99.7%. The methylene blue solution was treated with amphoteric cellulose, and the adsorption equilibrium was reached within 10 minutes, and the removal rate was 99%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com