Compound biological flocculant and preparation method thereof
A microbial flocculant and composite technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problem of not jointly preparing microbial flocculants, etc., and achieve the effects of good application prospects, simple process and low cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0042] Implementation Case 1 Screening and identification of high-efficiency flocculation bacteria
[0043] Alternative microorganisms with flocculation can be selected from activated sludge (derived from the activated sludge of Chongqing Heishizi Food Waste Treatment Plant), landfill leachate (derived from the comprehensive wastewater of Chongqing Fuling Lameizi Mustard Plant)
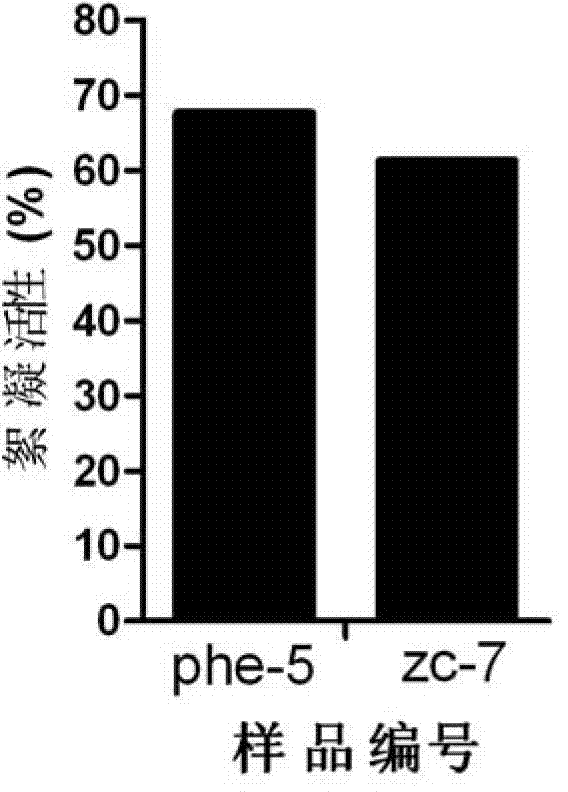
[0044] In the middle screening, the isolated strains were respectively inserted into 250ml wide-mouth Erlenmeyer flasks containing 50ml of fermentation medium, placed in a shaking table at 30°C and 200rpm for 24h, and the fermentation broth was taken for flocculation activity testing. figure 1 The flocculation activity test result of the bacterial strain obtained for screening, wherein Serratia marcescens (also known as phe-5) (biological deposit number is CTCC M 2013041) and Klebsiella (also known as ZC-7) (biological deposit number CCTCCM2013043) had the highest flocculation activity among the scree...
Embodiment example 3
[0050] Implementation Case 3 Preparation of Composite Microbial Flocculants
[0051] The flocculant-producing strains CTCC M2013041 and CCTCC M 2013043 with the best flocculation activity screened in Example 1 were respectively inserted into sterilized seed culture medium, and vibrated at 30°C and 220rpm for 24 hours to obtain Serratia marcescens respectively. Bacteria liquid and Klebsiella bacterium liquid, the raw material of described seed culture medium is made up of following ratio: glucose, 10.0g; K 2 HPO 4 , 5.0g; MgSO 4 .7H 2 O, 0.2g; KH 2 PO 4 , 2.0g; NaCl, 0.1g; urea, 0.5g; yeast powder, 0.5g, distilled water 1L.
[0052] Mix the Serratia marcescens bacterium liquid obtained in step A and or the Klebsiella bacterium liquid in a quantitative ratio of 1:1, inoculate it into the fermentation medium at an inoculum size of 1%, and culture it with shaking at 220 rpm for 24 hours at 30°C Finally, the thallus or bacterium liquid are microbial flocculants, and the raw m...
Embodiment 4
[0054] Example 4 Distribution of flocculation activity of composite microbial flocculants
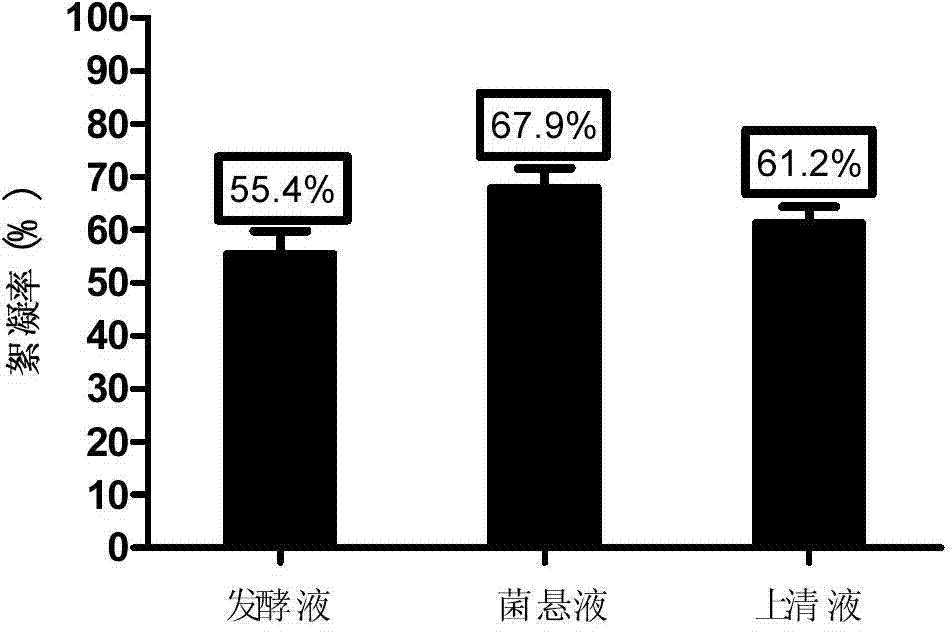
[0055] Collect the composite microbial flocculant similar or equivalent to that prepared in Example 3, centrifuge at 5000rpm for 10min, collect the fermentation broth and bacteria respectively, wash the bacteria cells twice with pure water, and then resuspend with pure water equal to the volume of the fermentation broth . According to Example 2, the flocculation activity of the fermentation broth, cell suspension and supernatant were measured respectively. The results show( figure 2 ), cell suspension (10 10 The flocculation activity of CFU / mL) is 67.9%, obviously higher than fermentation liquid (flocculation activity is 55.4%) and supernatant liquid (flocculation activity is 61.2%), shows that the composition of the flocculation activity that bacterial strain produces mainly exists in the bacterial cell sediment .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com