Melanoma therapeutic plasmid DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) vaccine pSVK-CAVA preparation method as well as dedicated engineering bacterium and fermentation culture medium thereof
A DNA vaccine and fermentation medium technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of difficult separation of plasmid DNA, poor therapeutic effect of open-loop and linearized plasmid DNA, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0041] 1) Preparation of seed liquid: Resuscitate one E.coli XL10-Gold / CAVA working seed from -70°C, inoculate it in 5 mL of LB liquid medium at a ratio of 1:100, and incubate at 37°C and 200 rpm for 12 hours. Transfer to 100mL LB liquid medium according to the ratio of 1:100, culture at 37°C and 200rpm for about 12 hours, and obtain seed liquid at this time;
[0042] 2) Fermentation culture: The seed liquid was planted in a 5L fermenter (pilot production) according to the ratio of 1:100 for fermentation culture. The amount of high-yield fermentation medium ITB contained in the fermenter was 3L, and the pH value was controlled at 7.0±0.1 (Automatically added H through the fermenter 2 SO 4 and NH 3 .H 2 0 to adjust the pH value of the medium), the culture temperature was 37°C, and the dissolved oxygen was controlled at about 30% (when the dissolved oxygen decreased to this value, it was adjusted by supplementing pure oxygen and increasing the stirring speed). After 6 hours ...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1. Screening and Stability Detection of High Stability Host Bacteria of Melanoma Therapeutic Plasmid DNA Vaccine pSVK-CAVA
[0052] The melanoma therapeutic plasmid DNA vaccine pSVK-CAVA plasmid DNA was transformed into different genotypes of Escherichia coli competent cells DH5α, DH10β, Top10 and XL10-Gold respectively, and the transformation method was Hananhan method (Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition) 87 -92 pages), Inoue method (Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition) pages 93-96), calcium chloride method (Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide (Third Edition) pages 96-99), electric shock transformation method (Molecular Cloning Experiment Guidelines (Third Edition) pp. 99-102).
[0053] Take the conversion of XL10-Gold by calcium chloride method as an example to illustrate:
[0054] The pSVK-CAVA plasmid DNA can be found in literature (Zhang Liang, Yan Jinqi, Wang Yue, et al. Construction and in vivo and in vitro expression of repli...
Embodiment 2
[0061]Example 2, identification of melanoma therapeutic plasmid DNA vaccine pSVK-CAVA engineering bacteria E.coliXL10-Gold / CAVA
[0062] 1. Detection of genetic stability and structural stability of the working seed bank
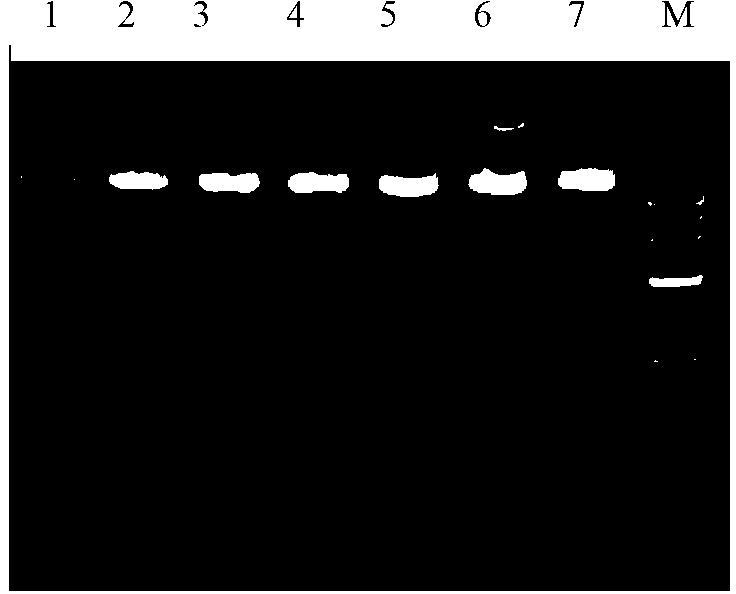
[0063] One working seed was revived by heating in a water bath at 37°C, inoculated into 5 mL of LB medium, cultured at 37°C and 200 rpm for 12 hours, and then subcultured at a ratio of 1:100. This method was continuously passed down for 30 generations. Plasmids were extracted from the strains of the 1st, 15th, 20th, 25th, and 30th generations, and the structural stability of the working seed bank was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and enzyme digestion.
[0064] Results The engineering bacteria E.coli XL10-Gold / CAVA was continuously subcultured for 30 generations, and the plasmid was extracted every 5 generations. The 1% agarose gel electrophoresis pattern of the plasmid (see figure 2 ) showed that the engineered bacteria exhibited good genetic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com