Method for producing caffeic acid by using blue algae
A technology of caffeic acid and cyanobacteria, applied in the field of genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
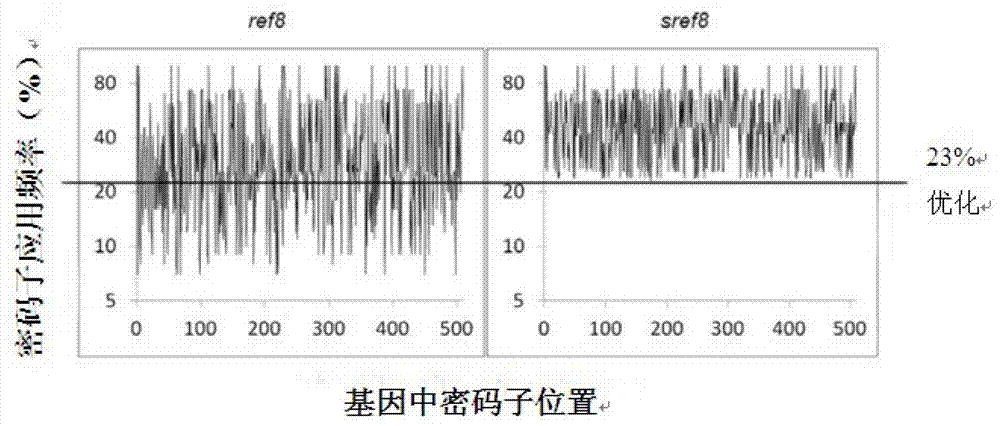
[0051] The sref8 gene synthesis of embodiment 1 codon optimization
[0052] According to the codon preference of Synechocystis sp., codon optimization was performed on the ref8 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana, and the sref8 gene was synthesized. The nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The amino acid sequence of the C3H protein expressed by the sref8 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. For codon optimization, see figure 1 , 23% of the coding sequence in the ref8 gene was optimized. During the optimized synthesis, an EcoRI restriction site was added to the 5' end of the sref8 gene, and a PstI restriction site was added to the 3' end.
Embodiment 2
[0054] Isolate and clone Synechocystis double homologous recombination upstream and downstream arm gene fragments, psbA2 promoter and Escherichia coli terminator T1T2 cDNA fragments used to construct the expression vector of transgenic Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. The DNA polymerase used in the PCR amplification fragment in this experiment was Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (purchased from NEB Company).
[0055] Cloning of upstream and downstream arm gene fragments of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 homologous recombination:
[0056] The homologous recombination arms are the upstream and downstream sequences near slr1285 of the Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 genome, and the amplified fragment sizes are 594bp and 606bp respectively (sequences such as SEQ ID NO: 13, and SEQ ID NO: 14, Synchocystis sp.PCC6803) amplification primers are designed as follows:
[0057] Upper arm forward primer: 5'-ATCggtaccGGCAATGCAATTAATTAAAAATGGC-3' (contains KpnI restriction site), (SEQ ID NO.3)
[0...
Embodiment 3
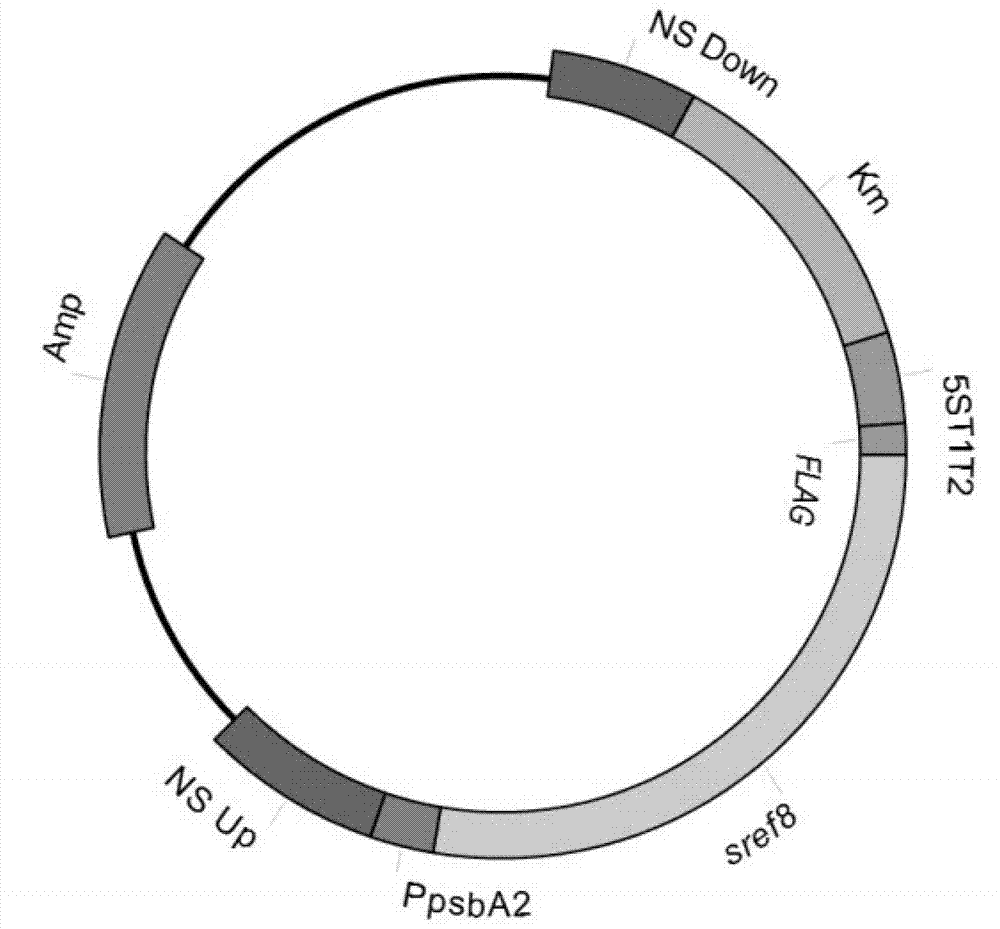
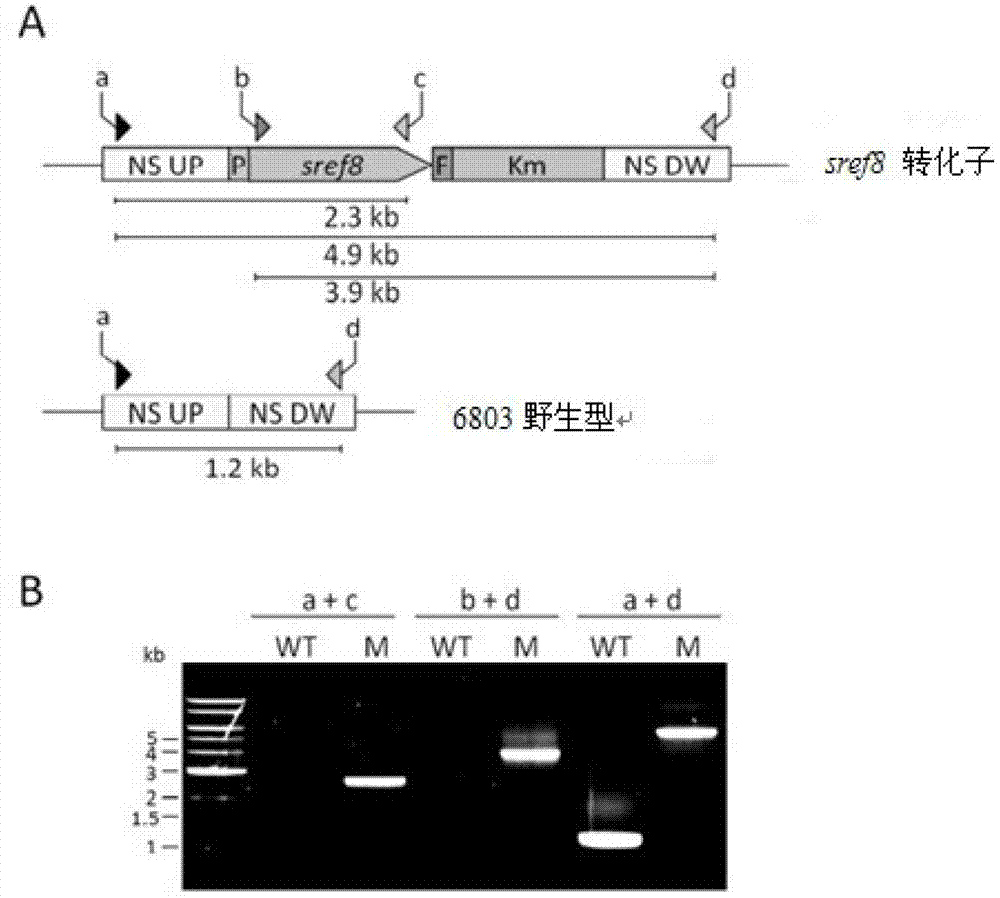
[0075] Example 3 Homologous Recombination Vector Construction
[0076] The 5ST1T2 positive clone (containing the T1T2 fragment) obtained in Example 2 was double-digested with pstI and BamHI to recover the T1T2 fragment; the pBluescript II SK (+) plasmid was also treated with pstI and BamHI restriction endonucleases to recover the vector fragment 1. The recovered T1T2 fragment was ligated with vector fragment 1 to obtain pBluescript SK T1T2 plasmid.
[0077] The homologous recombination upstream arm-positive clone obtained in Implementation 2 was double digested with KpnI and XhoI, and the upstream arm fragment was recovered. The pBluescript SK T1T2 plasmid was also double digested with KpnI and XhoI, and the vector fragment 2 was recovered. The recovered upstream arm fragment was ligated with vector fragment 2 to obtain pBluescript SK T1T2-ups plasmid.
[0078] The homologous recombination downstream arm-positive clone obtained in Implementation 2 was double digested with S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com