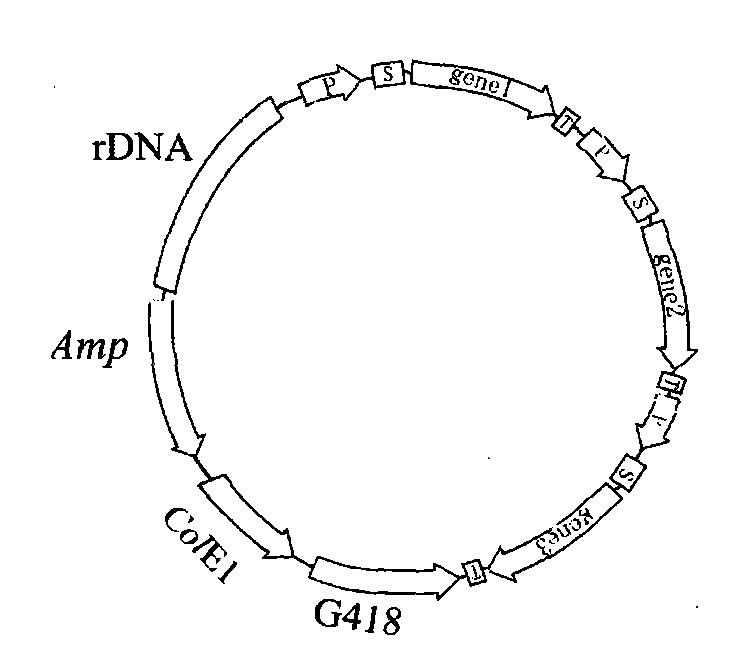
Method for degrading plant lignin by using Bacillus subtilis engineering bacterial
A technology for degrading Bacillus subtilis and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the field of constructing and applying microbial engineering bacteria, can solve the problems of low enzyme yield, long period of degrading lignin, slow growth of white rot fungi, etc., and achieves rapid growth and reproduction and low nutritional requirements. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1.1 Obtain the relevant originals required for the enzyme gene and the construction of the expression vector
[0024] (1) PCR amplification of the glyceraldehyde triphosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence of Bacillus megaterium.
[0025] Extract the genomic DNA of Bacillus megaterium, use the genomic DNA as a template, and apply primer 5'TT TACGTA GATCCATTATCGGTGAACCA 3' and 5'GG GCATGC GGGAATACATTACGGCCGAT3 ') carries out PCR amplification, and PCR product is through the sequence determination and the BLAST software analysis that NCBI provides proves to be the promoter sequence of its glyceraldehyde triphosphate dehydrogenase gene.
[0026] (2) PCR amplification of the laccase gene of Bacillus subtilis
[0027] The cell wall of Bacillus subtilis was cleaved with helicase, the genomic DNA of Bacillus subtilis was extracted, and the upstream primer (5'AA CCTAGG ATGACACTTGAAAAATTTGTGGATGC3') and downstream primer (5'AA GCGGCCGC CTATTTATGGGGATCAGTTATA3') PCR ampl...
Embodiment 2
[0060] 2.1 Obtain the relevant originals required for the enzyme gene and the construction of the expression vector
[0061] (1) PCR amplification of the glyceraldehyde triphosphate dehydrogenase promoter sequence of Bacillus megaterium.
[0062] Extract the genomic DNA of Bacillus megaterium, use the genomic DNA as a template, and apply primer 5'TT TACGTA GATCCATTATCGGTGAACCA 3' and 5'GG GCATGC GGGAATACATTACGGCCGAT3 ') carries out PCR amplification, and PCR product is through the sequence determination and the BLAST software analysis that NCBI provides proves to be the promoter sequence of its glyceraldehyde triphosphate dehydrogenase gene.
[0063] (2) PCR amplification of the laccase gene of Bacillus subtilis
[0064] The cell wall of Bacillus subtilis was cleaved with helicase, the genomic DNA of Bacillus subtilis was extracted, and the upstream primer (5'AA CCTAGG ATGACACTTGAAAAATTTGTGGATGC3') and downstream primer (5'AA GCGGCCGC CTATTTATGGGGATCAGTTATA3') PCR ampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com