Write-in circuits and read-out circuits of arbitrary-K-value DRAM and eight-value DRAM
A technology for writing circuits and reading circuits, which is applied in information storage, static memory, digital memory information, etc., and can solve problems such as complex structure, inability to control the threshold value by the user later, and different opening properties of the threshold voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: Description of the circuit information function of the storage unit.
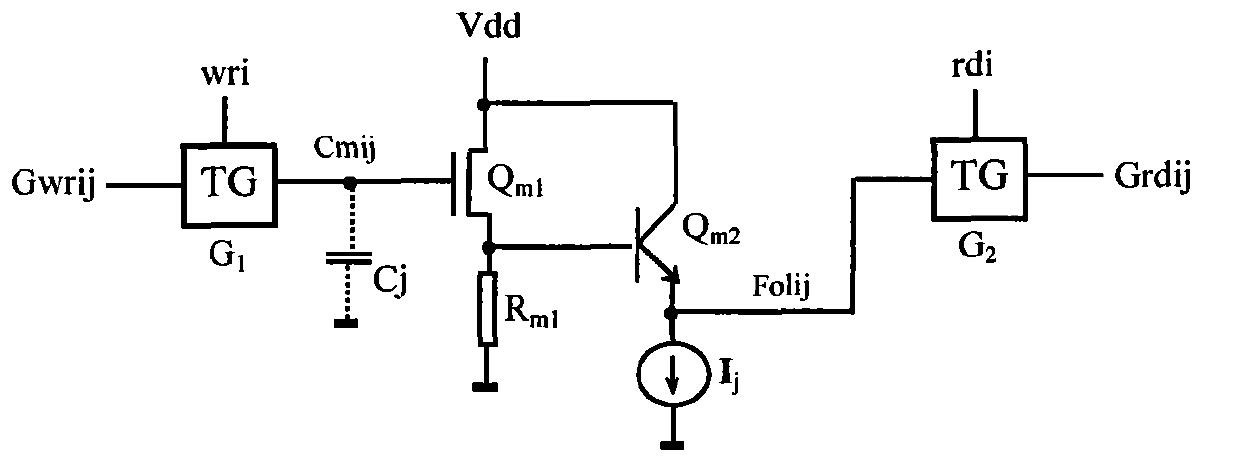
[0045] The storage unit circuit has three information functions of multi-value information storage, multi-value information reception and multi-value information sending: ①Information reception: by figure 1 It can be seen that the write pulse w ri When coming, the transfer gate G 1 conduction, will write the bit line G wrij The multi-valued information is transferred to the storage capacitor C j , so that the capacitor C j Receive multi-valued information C mij ; Capacitance C j Reception is a charging and discharging process, whether charging or discharging depends on the capacitance C j The original stored information and the current received information, the charging and discharging time constant is C j Capacitance related, C j Usually only a few picofarads, no larger; ②Information storage: write pulse w ri When the future arrives, the transmission gate G 1 due by figure...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: Proof that the writing circuit of arbitrary K value and 8-value DRAM satisfies design requirements.
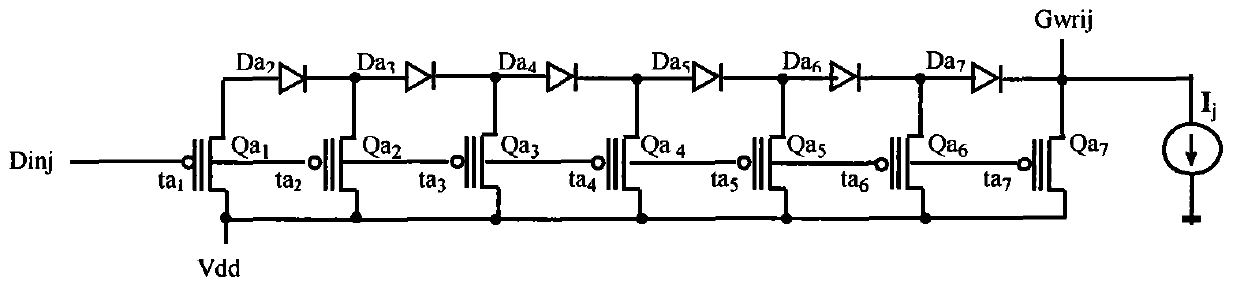
[0050] The writing circuit of any K value DRAM is shown as Figure 4 , it is necessary to prove that the design requirements are met: when writing into the circuit input D inj When the logic value is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ..., L-2, L-1, L, write circuit output G wrij Logical values are still sequentially 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ..., L-2, L-1, L; but G wrij Logical value corresponds to logic level V Gwrij (n) than D except 0 level inj Logical value corresponds to logic level V Dinj (n) High Δ (n=1~L), the 0 level is still 0, that is, V Gwrij (0)=V Dinj (0) = 0V, V Gwrij (1) = V Dinj (1)+Δ, V Gwrij (2) = V Dinj (2)+Δ,...,V Gwrij (L-1)=V Dinj (L-1)+Δ, V Gwrij (L)=V Dinj (L)+Δ, V Dinj (k)>V Dinj (k-1); ta k Adjacent logic level V for the write circuit input Dinj (k) and V Dinj The middle value of (k-1), satisfying V Dinj (k-1)k Dinj (k), k=1, 2, 3, 4, ......
Embodiment 3
[0053] Embodiment 3: Proof that the readout circuit of any K value and 8-value DRAM satisfies the design requirements.
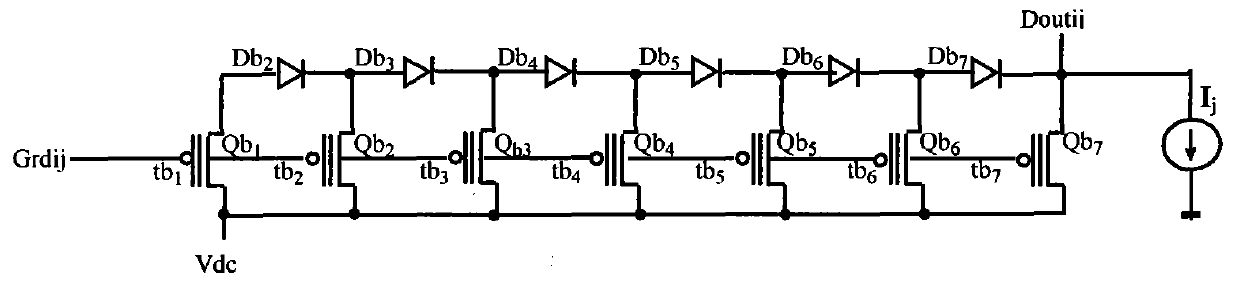
[0054] The readout circuit of any K value DRAM is shown as Figure 5 , it is necessary to prove that the design requirements are satisfied: when the input G of the readout circuit rdij When the logic value is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ..., L-2, L-1, L, the input D of the readout circuit outj Logical values are still sequentially 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ..., L-2, L-1, L; G rdij ,D inj and D outj The logic value corresponds to the logic level in order of V Grdij (n), V Dinj (n) and V Doutj (n)(n=0~L), where input G rdij It is a non-standard K value signal, and it is required to output D outj is the standard equal-step K value signal, that is, V Doutj (0)=V Dinj (0) = 0V, V Doutj (1) = V Dinj (1) = V Don , V Doutj (2) = V Dinj (2) = 2V Don , V Doutj (3) = V Dinj (3) = 3V Don ,...V Doutj (L-2)=V Dinj (L-2)=(L-2)V Don , V Doutj (L-1)=V Dinj (L-1)=(L-1)V Do...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com