Method and device for processing oxidized tail gas of anthraquinone process-based hydrogen peroxide production
A technology for oxidizing tail gas and hydrogen peroxide, applied in the direction of peroxide/peroxy hydrate/peroxyacid/superoxide/ozonide, chemical instruments and methods, combined devices, etc., can solve the problem of decreased adsorption capacity of activated carbon fibers , the circulating water volume and temperature are not easy to control, and the recovery function decays quickly, etc., to achieve the effect of being conducive to comprehensive utilization, not easy to freeze, and meeting environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
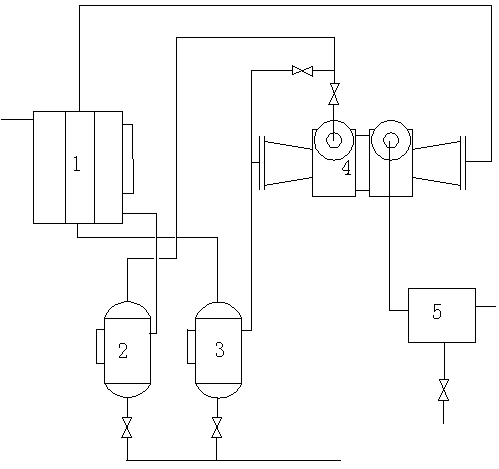
[0021] Example 1: The oxidation tail gas at 20°C first passes through the heat exchanger 1 for heat exchange; after the oxidation tail gas is cooled to 5°C, it enters the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 for gas-liquid separation; from the top of the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 The discharged uncondensed gas then enters the expansion chamber of the turbo expander 4, and is cooled by the turbo expander 4 for capacity expansion and cooling. After cooling down to 0°C, it enters the second gas-liquid separation tank 3 for gas-liquid separation; from the second gas-liquid separation The uncondensed gas discharged from the top of the tank 3 is heat-exchanged through the heat exchanger 1; after being heated to 6°C, it enters the turbo expander 4 for compression and boosting; the pressure is raised to 0.05MPa, the temperature is 15°C, and then enters the activated carbon adsorption device 5.
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: The oxidation tail gas at 40°C first passes through the heat exchanger 1 for heat exchange; after the oxidation tail gas is cooled to 15°C, it enters the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 for gas-liquid separation; from the top of the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 The discharged uncondensed gas then enters the expansion chamber of the turbo expander 4, and is cooled by the turbo expander 4 to perform work and cooling. After cooling down to 5°C, it enters the second gas-liquid separation tank 3 for gas-liquid separation; from the second gas-liquid separation The uncondensed gas discharged from the top of the tank 3 is heat-exchanged through the heat exchanger 1; after being heated to 20°C, it enters the turbo expander 4 for compression and boosting; the pressure is raised to 0.1MPa, the temperature is 40°C, and then enters the activated carbon adsorption device 5.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3: The oxidation tail gas at 30°C first passes through the heat exchanger 1 for heat exchange; after the oxidation tail gas is cooled to 10°C, it enters the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 for gas-liquid separation; from the top of the first gas-liquid separation tank 2 The discharged uncondensed gas then enters the expansion chamber of the turbo expander 4, and is cooled by the turbo expander 4 to expand the capacity and cool down. After cooling down to 2.5°C, it enters the second gas-liquid separation tank 3 for gas-liquid separation; from the second gas-liquid separation The uncondensed gas discharged from the top of the tank 3 is heat-exchanged through the heat exchanger 1; after being heated up to 8°C, it enters the turbo expander 4 for compression and boosting; the pressure is raised to 0.08MPa, the temperature is 28°C, and then enters the activated carbon adsorption device 5.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com