Preparation and/or formulation of proteins cross-linked with polysaccharides
A protein and protein matrix technology, applied in skin care preparations, animal/human proteins, albumin peptides, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the natural structure of molecules, toxicity, carcinogenicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
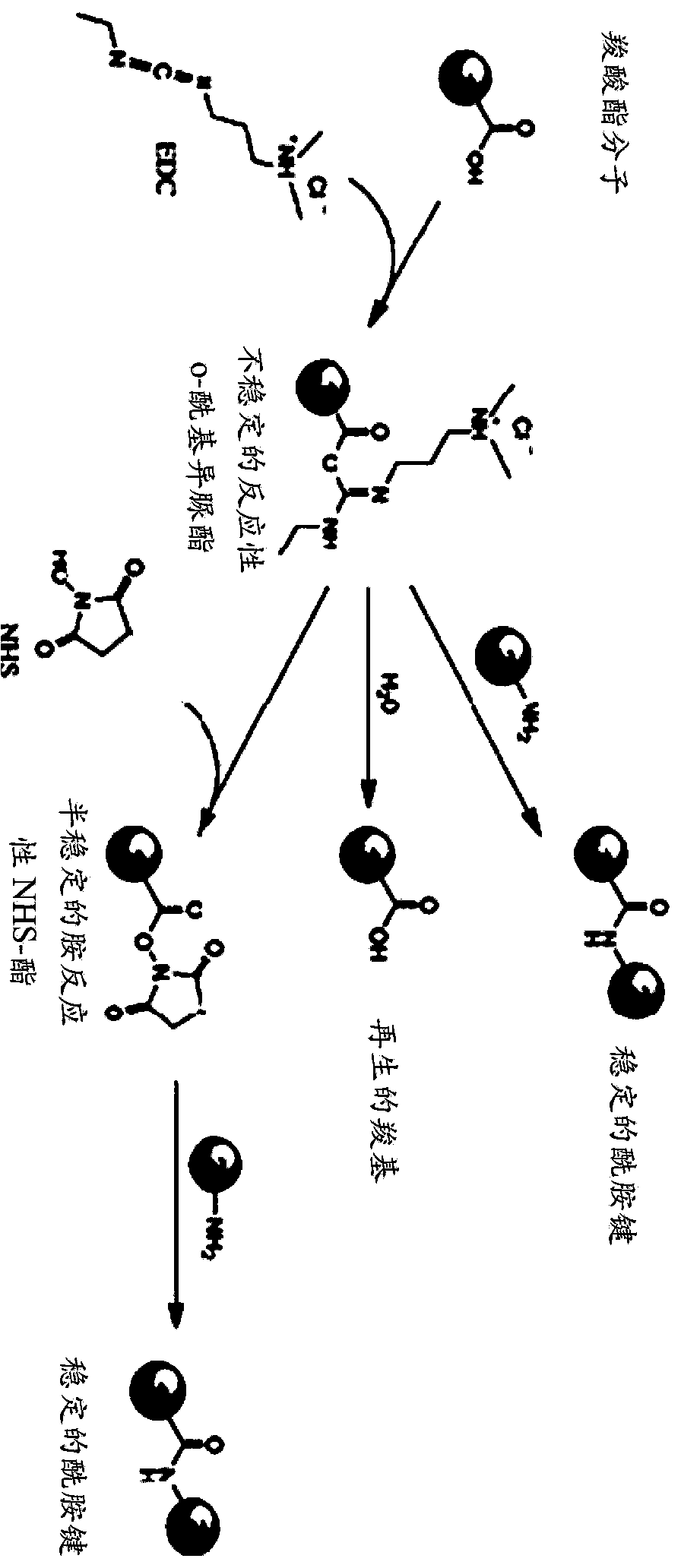
[0198] Schematic representation of the preparation of soluble hyaluronic acid crosslinkers using carbodiimide and N-succinimide (NHS):
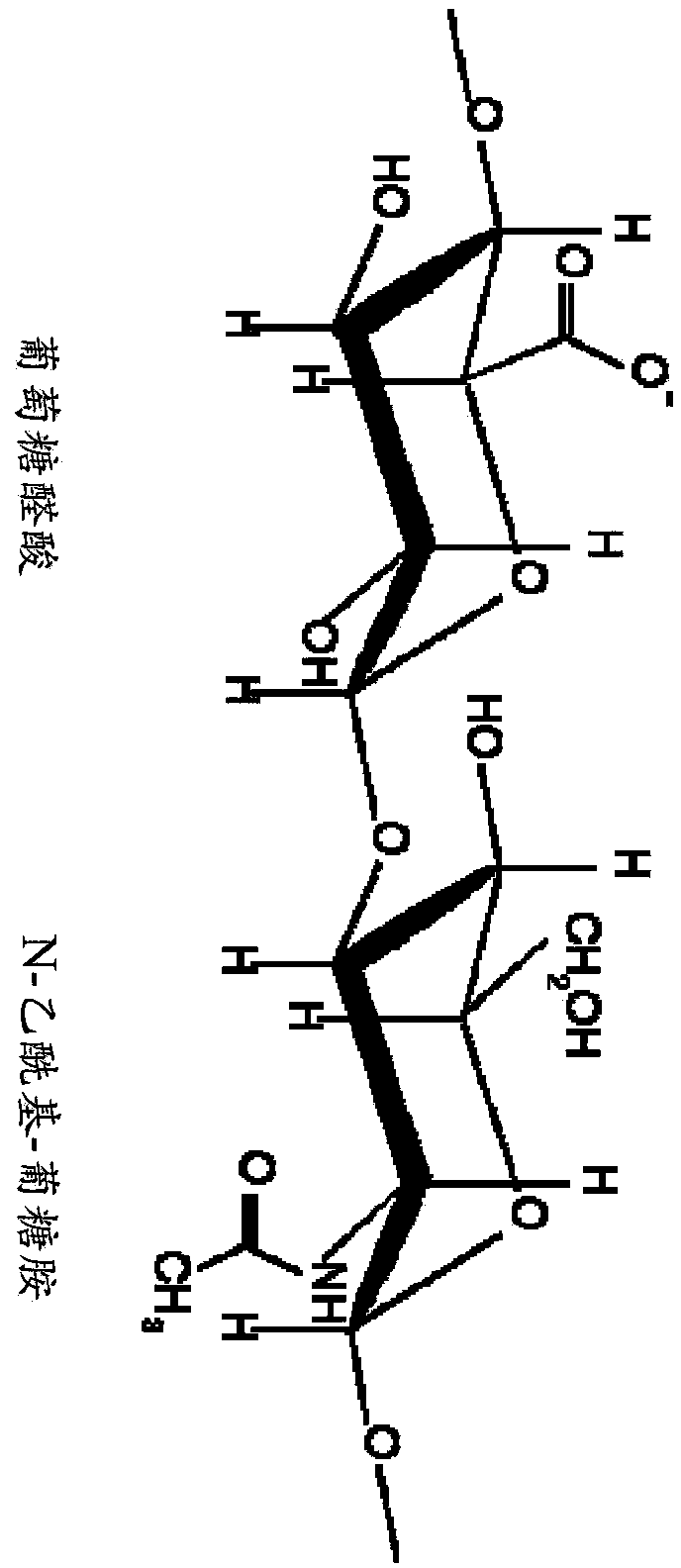
[0199] Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a polysaccharide containing β-D-glucuronic acid-[1-3]-β-D-N-acetylglucosamine disaccharide units. The ideal structure of HA is shown in figure 1 middle.
[0200] As can be seen, HA contains one carboxyl / disaccharide unit, which is a functional group that can be used in at least one of the crosslinking methods disclosed herein. In this method, a covalent chemical bond is formed between the carboxyl groups of HA and the free amino groups of the protein. This can be done by reacting HA with a carbodiimide such as 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDC) to form a reactive o-acylisourea ester. When this compound is reacted with a nucleophile such as a primary amino group, it is also unstable and hydrolyzes rapidly in water without any suitable reactive group. Therefore, the formation of more stable i...
Embodiment 2
[0203] Schematic representation of the preparation of soluble hyaluronic acid crosslinkers using the heterobifunctional reagent allyl glycidyl ether (AGE)
[0204] The method is based on derivatizing hyaluronic acid (HA) with heterobifunctional reagents, which is a two-step method of cross-linking proteins with HA. The method chosen in this example uses allyl glycidyl ether (AGE), where the initial incorporation of AGE occurs when the oxirane group reacts with the hydroxyl group of HA under strongly basic conditions to form a stable ether linkage . The allyl group thus incorporated can then be converted to a halohydrin by reaction with a halide such as bromine. These halohydrins can then react with proteins to form stable secondary amine linkages through primary amino groups. The reaction between halohydrins and primary amino groups occurs more efficiently at high pH, but some reactions begin to occur above pH 8.5-9.
[0205]
[0206] 2.HA-R-CH=CH 2 +Br 2 +H 2 O→HA-...
Embodiment 3
[0210] Preparation of polysaccharide cross-linking agent A:
[0211] In this example, 5ml of 1% low molecular weight hyaluronic acid solution, 1ml of H 2O. 100 mg of NHS (Sigma) and 100 mg of EDC (Sigma) were mixed together and reacted at room temperature for 1 hour. Derivatized hyaluronic acid was then precipitated with two volumes of IPA, briefly pressed to reduce the water and solvent content of the precipitate, rinsed with 66% ethanol, and then redissolved in 4 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (Sigma) at room temperature. The derivatized HA dissolved completely within 1 hour. The concentration of derivatized HA was measured using a temperature analyzer and then diluted to a 2% solution prior to protein crosslinking. All preparations were sterile and experiments were performed in a laminar flow hood when possible.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com