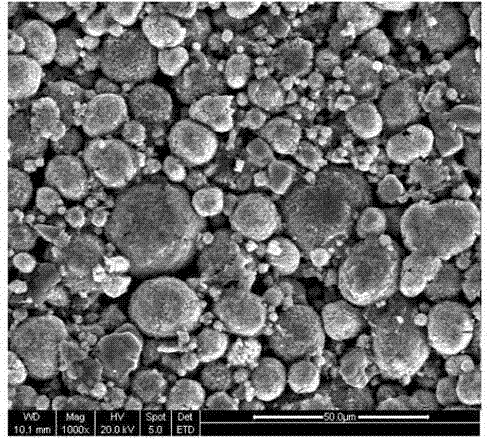
A kind of preparation method of lithium iron phosphate electrode
A technology for lithium iron phosphate and electrodes, which is applied in the field of preparation of lithium iron phosphate electrodes, can solve the problems of lower capacity density of lithium iron phosphate batteries, increase the amount of conductive agent, and reduce active materials, etc., so as to improve low-temperature discharge performance, increase capacity and Effects of Energy Density and Rate Performance Improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A preparation method for a lithium iron phosphate electrode, comprising the following steps:
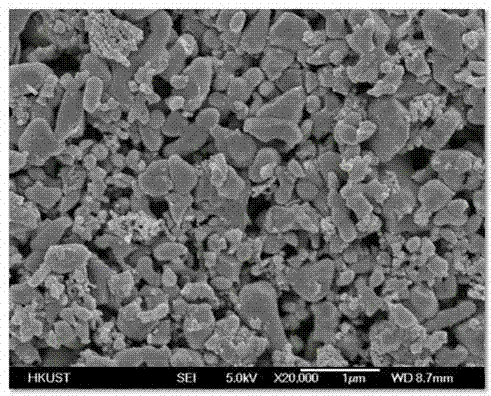
[0027] Step 1: Disperse the nano-scale lithium iron phosphate particles in acetone, and then spray-dry the nano-scale lithium iron phosphate particles for secondary granulation at 250°C. The spray-drying time is 2 hours to form a median particle Lithium iron phosphate secondary particles with a diameter of 4.5 μm; the equipment used for spray drying is a spray dryer.
[0028] Step 2, stirring polytetrafluoroethylene and lithium iron phosphate secondary particles obtained in step 1 in a dry mixing device for 1 hour to obtain a mixture of lithium iron phosphate and polytetrafluoroethylene; the dry mixing device can use a planetary mixer;
[0029] Step 3, uniformly disperse polyvinylpyrrolidone, spherical conductive carbon black and chain-like carbon nanotubes in N-methylpyrrolidone to form a dispersion, wherein the mass of spherical conductive carbon black and chain-like carbon ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] A preparation method for a lithium iron phosphate electrode, comprising the following steps:
[0034] Step 1: Disperse the nanoscale lithium iron phosphate particles in N-methylpyrrolidone, and then perform secondary granulation on the nanoscale lithium iron phosphate particles by spray drying at 300°C. The duration of spray drying is 4h. Lithium iron phosphate secondary particles with a median diameter of 5 μm were formed.
[0035] Step 2: Stir the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose and lithium iron phosphate secondary particles obtained in step 1 in a dry mixing device for 1 hour to obtain a mixture of lithium iron phosphate and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
[0036] Step 3, uniformly dispersing polyvinylpyrrolidone, spherical graphene and chain-like carbon nanofibers in water to form a dispersion, wherein the mass ratio of spherical graphene to chain-like carbon nanofibers is 4:6.
[0037] Step 4, adding the mixture of lithium iron phosphate and sodium carboxymethyl c...
Embodiment 3
[0040] A preparation method for a lithium iron phosphate electrode, comprising the following steps:
[0041] Step 1: Disperse the nano-scale lithium iron phosphate particles in methanol, and then carry out secondary granulation on the nano-scale lithium iron phosphate particles by spray drying at 180°C. The duration of spray drying is 1h to form median particles Lithium iron phosphate secondary particles with a diameter of 4 μm.
[0042] In step 2, the styrene-butadiene rubber and the lithium iron phosphate secondary particles obtained in step 1 were stirred for 0.5 hours in a dry mixing device to obtain a mixture of lithium iron phosphate and styrene-butadiene rubber.
[0043] Step 3: uniformly disperse polyvinylpyrrolidone, chain-like Ketjen black and spherical conductive graphite in water to form a dispersion, wherein the mass ratio of chain-like Ketjen black to spherical conductive graphite is 1:1.
[0044] Step 4, add the mixture of lithium iron phosphate and styrene-butad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com