Preparation method for resistive random access memory
A resistive memory, plasma technology, applied in electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of large erasing voltage, large resistance change range in high resistance state, and poor resistance stability, so as to reduce the erasing voltage and improve stability. , the effect of high reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
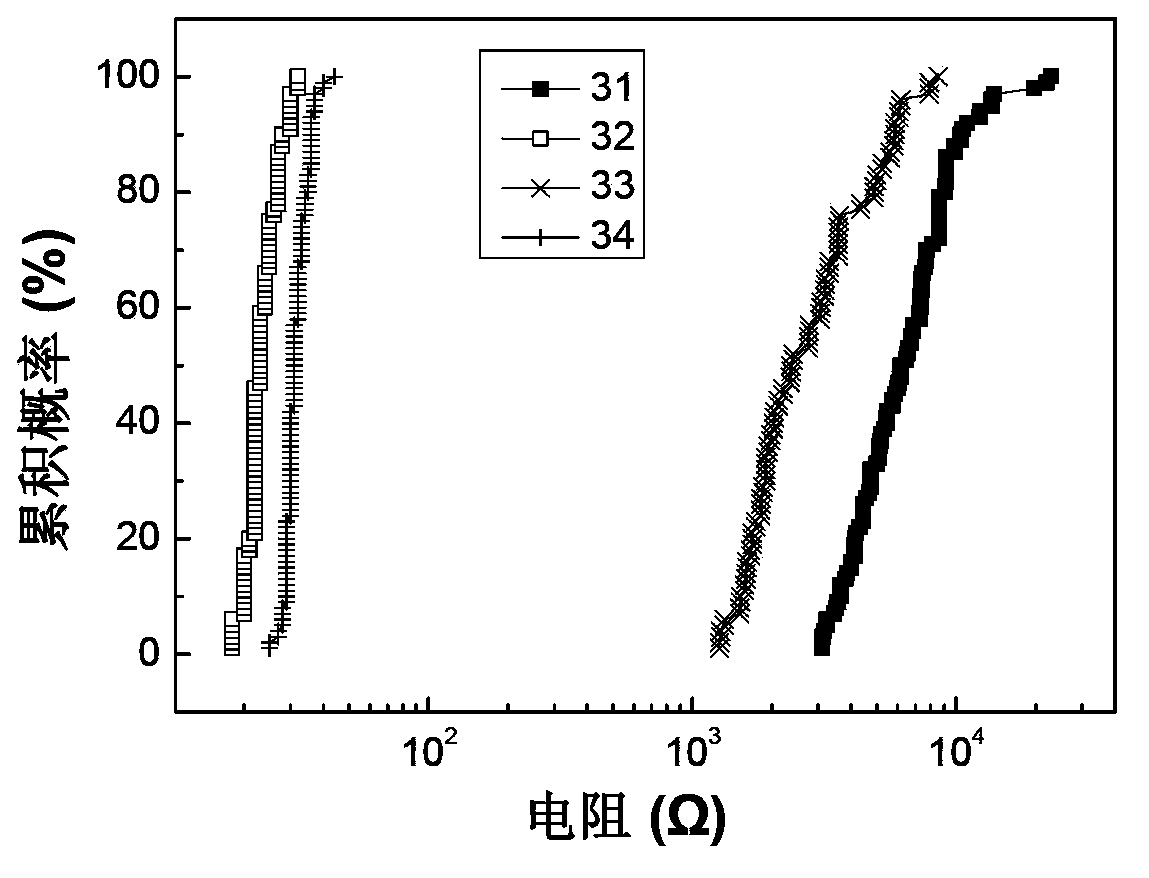
Embodiment 1
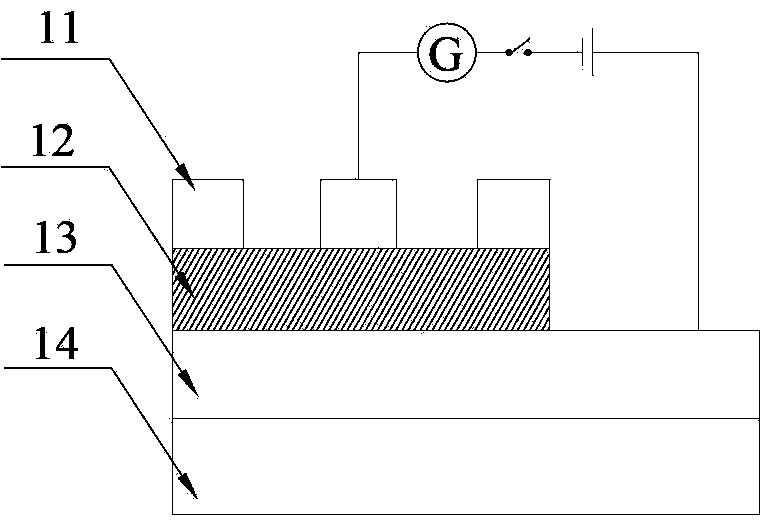
[0064] 1) Using magnetron sputtering method on SiO 2 (300nm) / Si(100) substrate surface prepared inert metal Pt bottom electrode, the thickness of the obtained bottom electrode was 150nm, the preparation temperature was 150°C, the main deposition gas was argon, the pressure was 0.5Pa, and the sputtering power was 300W.
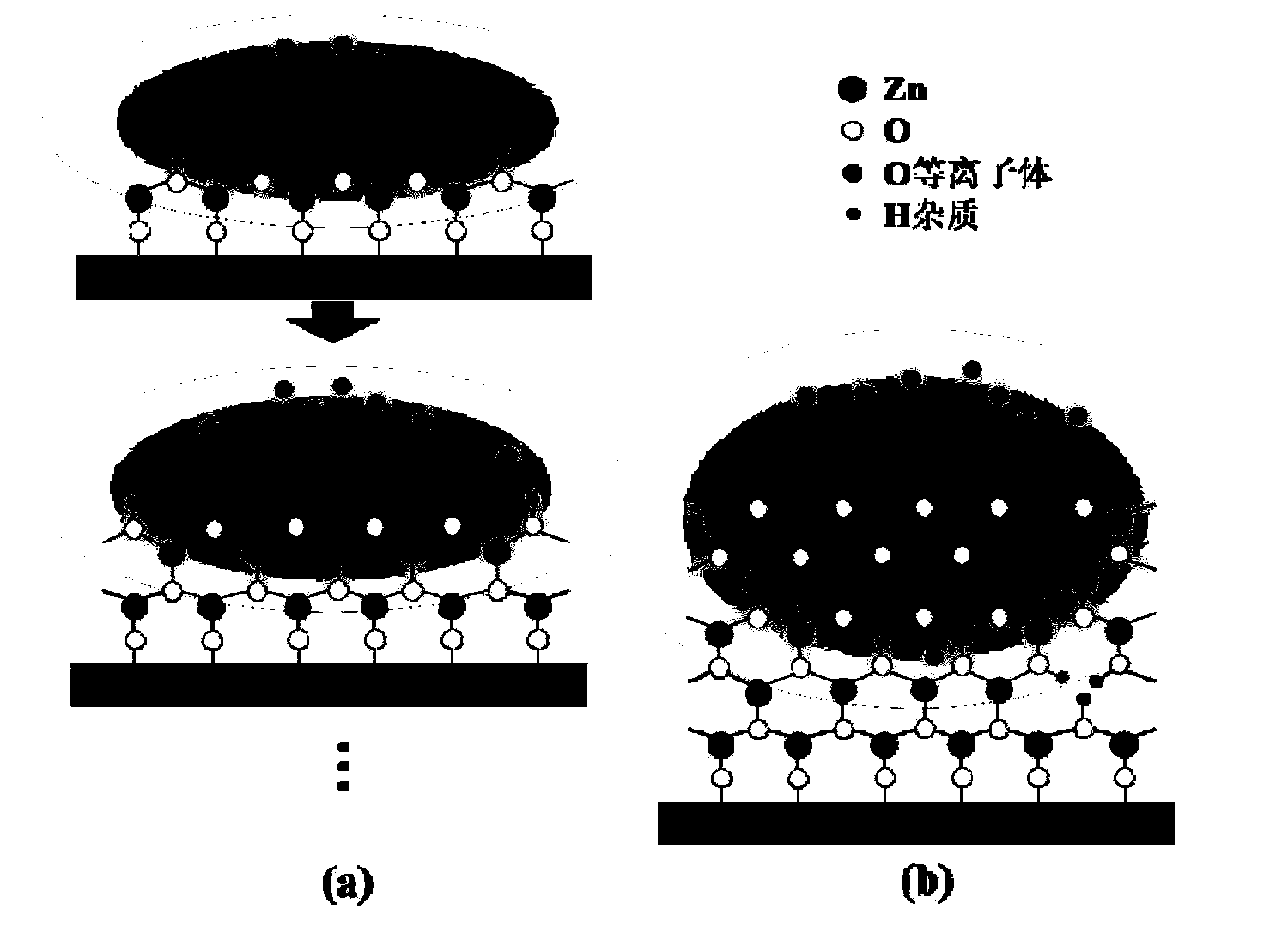
[0065] 2) Using the in-situ plasma enhanced thermal atomic layer deposition method, diethyl zinc was used as the first precursor, water vapor was used as the second precursor, and argon was used as the cleaning gas. After thermal atomic layer deposition, the Pt bottom electrode was first A single-layer zinc oxide film was formed on the film, and then the film was subjected to in-situ plasma treatment with oxygen plasma, and repeated 250 cycles to finally obtain a zinc oxide film with a thickness of about 42nm. The temperature of the Pt bottom electrode was 150°C; the flow rate of argon carrier gas was 20 sccm; the deposition and processing pressure was 1 Torr; ...
Embodiment 2
[0074] 1) Using magnetron sputtering method on SiO 2 (300nm) / Si(100) substrate surface prepared inert metal Pt bottom electrode, the thickness of the obtained bottom electrode was 150nm, the preparation temperature was 150°C, the main deposition gas was argon, the pressure was 0.5Pa, and the sputtering power was 300W.
[0075] 2) Using the in-situ plasma enhanced thermal atomic layer deposition method, diethyl zinc was used as the first precursor, water vapor was used as the second precursor, and argon was used as the cleaning gas. After thermal atomic layer deposition, the Pt bottom electrode was first A single-layer zinc oxide film was formed on the film, and then the film was subjected to in-situ plasma treatment with oxygen plasma, and repeated 250 cycles to finally obtain a zinc oxide film with a thickness of about 42nm. The temperature of the Pt bottom electrode is 150° C.; the flow rate of argon carrier gas is 20 sccm, the deposition and processing pressure of the react...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The aluminum oxide thin film resistive memory is prepared by thermal atomic layer deposition technology, and hydrogen plasma is used for in-situ treatment, including the following steps:
[0082] 1) Using magnetron sputtering method on SiO 2 (300nm) / Si(100) substrate surface prepared inert metal bottom electrode Pt, the thickness of the obtained bottom electrode was 150nm, the preparation temperature was 150°C, the main deposition gas was argon, the pressure was 0.5Pa, and the sputtering power was 300W.
[0083] 2) Using atomic layer deposition technology, using trimethylaluminum as the first precursor, water vapor as the second precursor, and argon as the cleaning gas, a single layer is first formed on the Pt bottom electrode after thermal atomic layer deposition Aluminum oxide thin film, and then use hydrogen plasma to process in-situ plasma on the thin film, repeat 200 cycles, finally obtain aluminum oxide thin film, the thickness of the thin film is about 20nm. The...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com