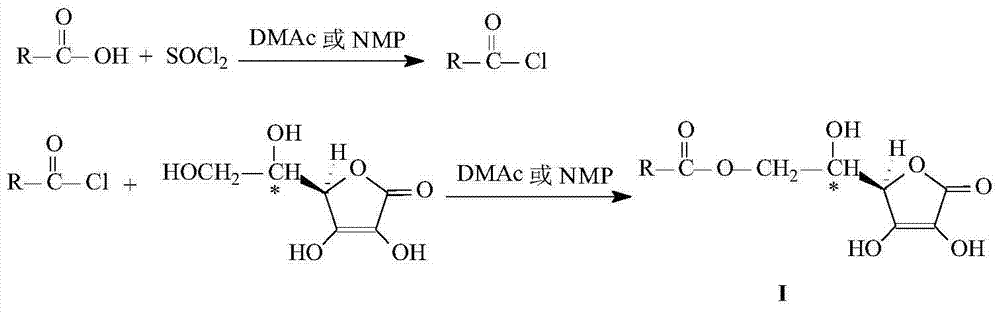
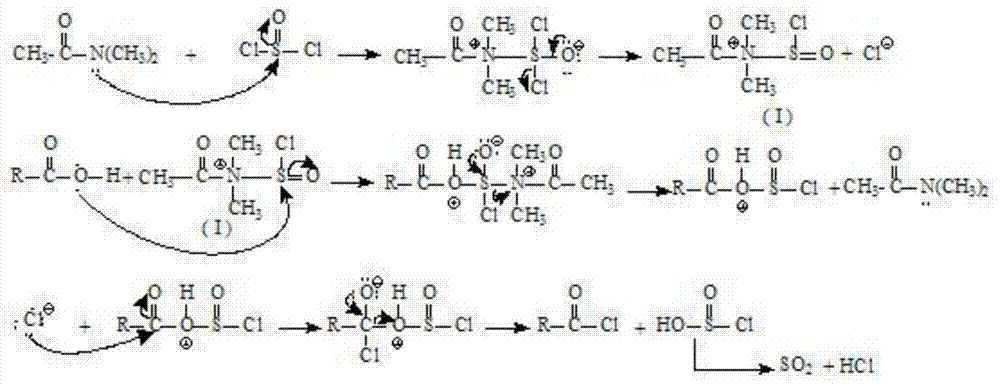
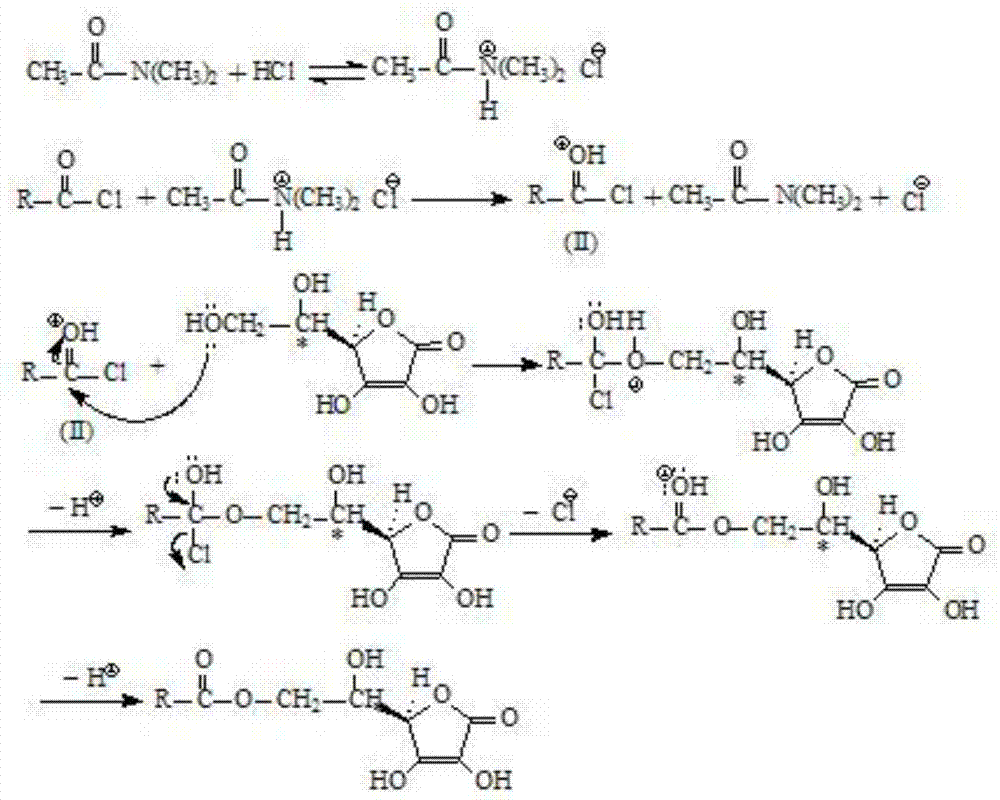
Method for preparing L-ascorbic acid or D-erythorbic acid carboxylate by using acyl chloride
A technology of ascorbic acid carboxylate and erythorbic acid, which is applied in the field of preparing L-ascorbic acid carboxylate or D-erythorbic acid carboxylate, can solve the problems of many by-products, long cycle, and influence on reaction yield, and achieve The effect of mild reaction conditions, short reaction cycle and high reaction yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] L-Ascorbyl Palmitate preparation.
[0018] Add 2.564g (10mmol) palmitic acid and 15mL DMAc and 5mL CH to the reaction flask 2 Cl 2 , stirred and dissolved at room temperature, cooled to 0°C and added dropwise 1.368g (11mmol) SOCl 2 , 0°C, reacted for 2h under stirring, then added 2.818g (16mmol) L-ascorbic acid, raised the temperature and maintained at 25°C for 8h. After the reaction was completed, 50 mL of ethyl acetate and 100 mL of distilled water were added to the reaction mixture, and stirred at room temperature for 1 h. Transfer to a separatory funnel, extract the separated aqueous layer twice with 80 mL ethyl acetate, and combine the organic layers. The organic layer was washed with saturated NaCl aqueous solution, anhydrous NaCl 2 SO 4 After drying, filtering, rotary evaporation of ethyl acetate, and oil pump vacuum drying for 1 h, the crude product was obtained. The crude product was recrystallized from a mixed solvent of ethyl acetate-petroleum ether t...
Embodiment 2
[0021] L-Ascorbyl Benzoate preparation.
[0022] Add 1.221g (10mmol) benzoic acid and 10mL DMAc to the reaction flask, stir and dissolve at room temperature, and add 1.368g (11mmol) SOCl dropwise after cooling to 0°C 2 After reacting for 2 hours at 0°C under magnetic stirring, 2.818g (16mmol) of L-ascorbic acid was added, and the temperature was raised and maintained at 25°C for 10h. The separation and purification method of the product was the same as in Example 1, and 1.761 g of white powder was obtained, with a content of 98.9%, a melting point of 180.5-183.3° C., and a reaction yield based on benzoic acid of 62.8%.
[0023] NMP was used to replace the above DMAc, and other reaction conditions were the same as the separation and purification conditions, and the reaction yield based on benzoic acid was 63.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0025] D-Erythorbyl Cinnamate preparation.
[0026] Add 1.482g (10mmol) cinnamic acid and 20mL DMAc to the reaction flask, stir and dissolve at room temperature, and add 1.368g (11mmol) SOCl dropwise after cooling to 0°C 2 , 0°C, reacted for 2h under stirring, then added 5.284 (30mmol) L-ascorbic acid, raised the temperature and maintained at 25°C for 12h. The separation and purification method of the product was the same as in Example 1 to obtain 2.254 g of a pale yellow waxy solid with a melting point of 57.5-61.2° C. and a reaction yield based on cinnamic acid of 73.6%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com