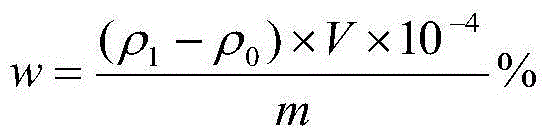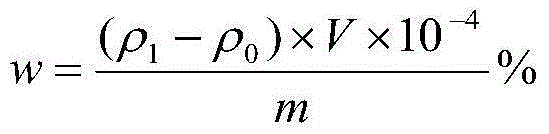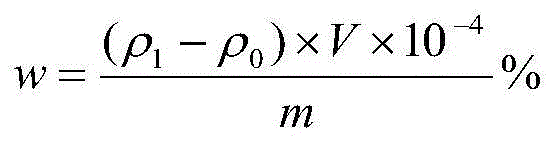Analysis method of trace impurity elements fe and cu in tin oxide electrode
A technology of trace impurity and analysis method, which is applied in the field of analysis of trace impurity elements in tin oxide electrodes, can solve the problems that tin oxide electrodes are not easy to dissolve, and achieve the effects of low loss, overcoming difficult dissolution, and accurate measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The analysis method of trace impurity elements Fe and Cu in the tin oxide electrode of the present invention comprises sample processing, experimental conditions, standard solution preparation, draws working curve, test, calculation, and the concrete steps of this method are:
[0033] 1. Sample treatment: Randomly take tin dioxide electrode samples, crush and grind them, pass the particle samples through a sieve to obtain particle samples no larger than 10 mesh, use an analytical balance to accurately weigh 0.3845g sample particles; weigh 1.2050gNaOH and 0.5032gKOH and mix; Put the ground tin oxide electrode powder in a platinum crucible and pre-fire it at 850°C for 30 minutes; take out the crucible, pour the mixture of NaOH and KOH into the crucible, put it in a muffle furnace at 900°C for 30 minutes; take it out and cool it to room temperature; Add warm water to the beaker for leaching, and take out the platinum crucible; add 15ml hydrochloric acid and 5ml nitric acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The standard solution preparation of the present embodiment, drawing working curve, test and calculation are the same as Example 1, and the sample processing and experimental conditions are different, as follows:
[0051] 1. Sample treatment: Randomly take tin dioxide electrode samples, crush and grind them, pass the particle samples through a sieve to obtain particle samples no larger than 10 meshes, use an analytical balance to accurately weigh 0.5238g sample particles; weigh 1.8640gNaOH and 0.6730gKOH and mix; Put the ground tin oxide electrode powder in a platinum crucible and pre-fire it at 950°C for 20 minutes; take out the crucible, pour the mixture of NaOH and KOH into the crucible, put it in a muffle furnace at 950°C for 45 minutes; take it out and cool it to room temperature; Add warm water to the beaker for leaching, and take out the platinum crucible; add 21ml of hydrochloric acid and 7ml of nitric acid into the beaker, heat to dissolve and clarify; cool to r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com