Method for preparing cathode material of sodium-ion battery, namely sodium vanadium fluorophosphates
A technology of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate and sodium ion batteries, which is applied to battery electrodes, circuits, electrical components, etc., to achieve good electrochemical performance, low cost, and simple synthesis process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
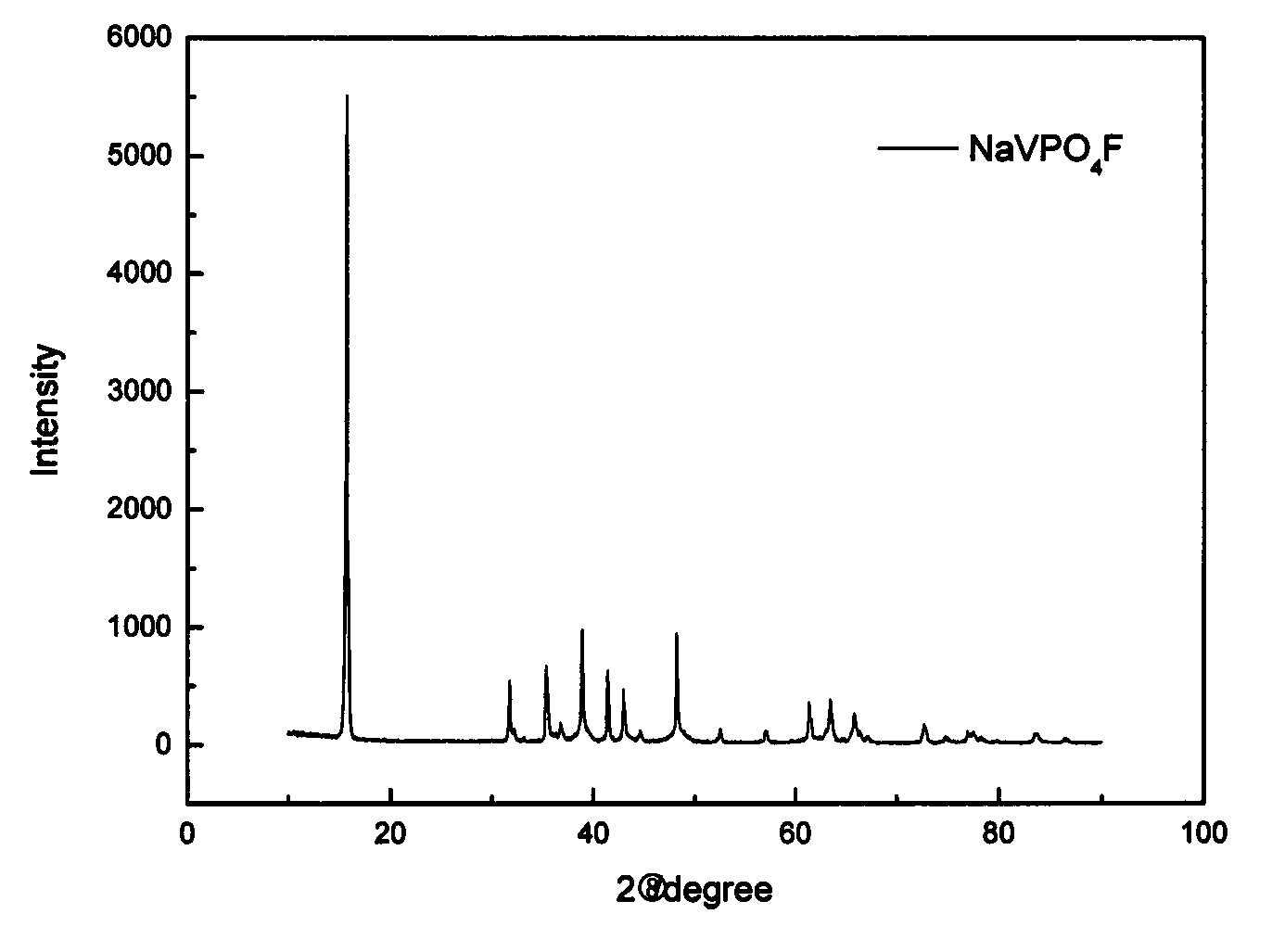
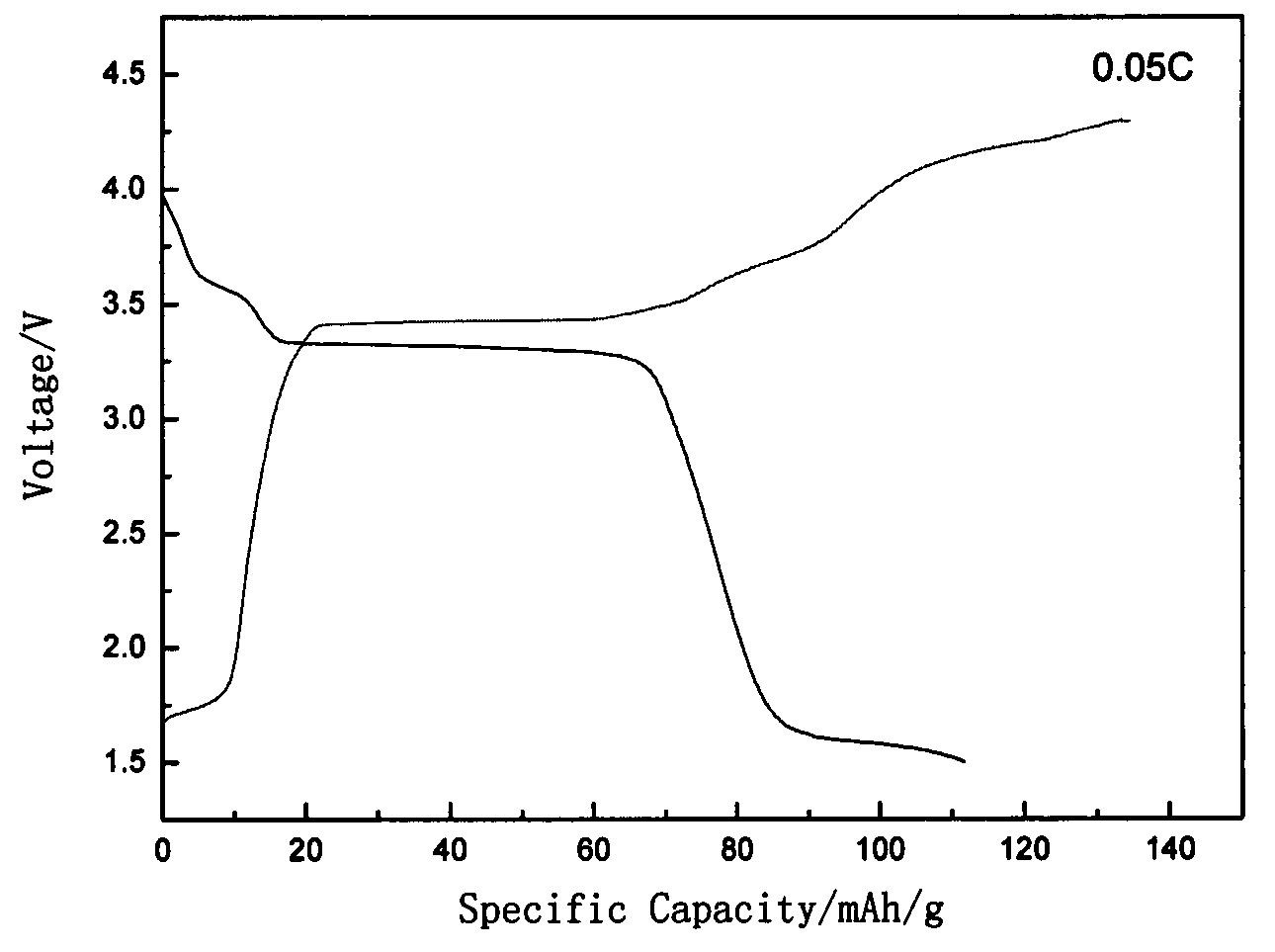
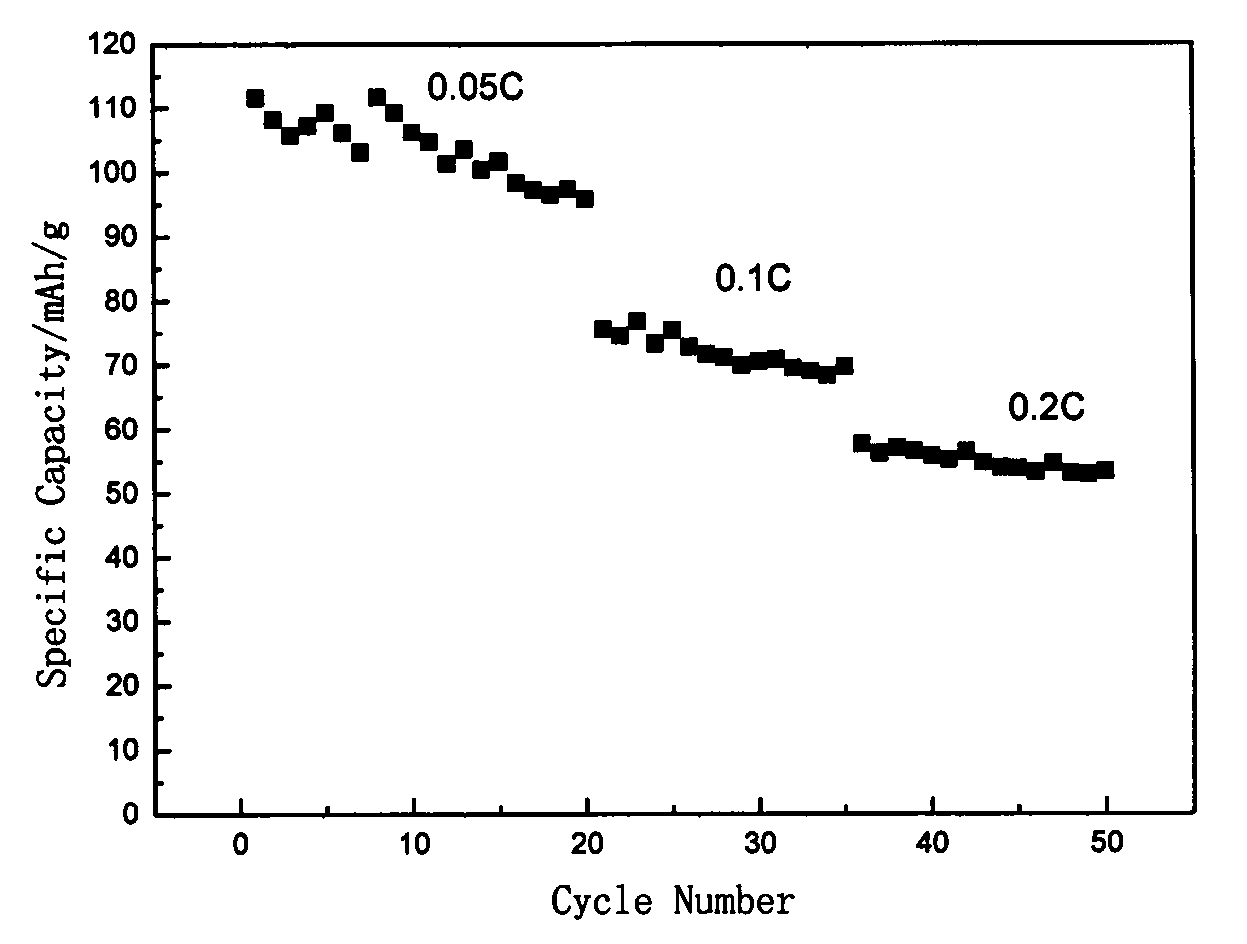
[0024] (1) Mixing materials: use pentavalent vanadium oxy compound, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, and carbon black as raw materials, dissolve in 80mL deionized water according to the molar ratio of vanadium: phosphorus: reducing agent carbon source element 1:1:1.2, and then Place in a water tank with a constant temperature of 80°C, stir for 6 hours until the solution evaporates to nearly dryness, and obtain a uniformly mixed light green slurry; (2) Pre-calcination: dry the slurry in a vacuum oven, and then transfer it to a tube In the furnace, pre-calcined at 750 ° C for 5 h in a nitrogen atmosphere at a temperature increase rate of 5 ° C per minute, and took it out after cooling to obtain VPO 4 / C precursor; (3) secondary calcination: VPO 4 / C and NaF are mixed according to the stoichiometric ratio, ball milled for 3 hours, sent into a tube furnace, and then roasted at 750°C for 1h in a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C per minute, and the temperature is lowered w...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Example 2: (1) Mixing: With trivalent vanadium oxy compound, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, and soluble starch as raw materials, dissolve in 80mL according to the molar ratio of vanadium: phosphorus: reducing agent carbon source element 1:1:1.2 Ionized water, then placed in a water tank with a constant temperature of 80°C, stirred for 6 hours until the solution evaporated to nearly dryness, and a uniformly mixed light green slurry was obtained; (2) pre-calcination: the slurry was dried in a vacuum oven, and then Transfer to a tube furnace, pre-calcined at 650°C for 5h in a nitrogen atmosphere at a rate of 5°C per minute, take it out after cooling, and obtain VPO 4 / C precursor; (3) secondary calcination: VPO 4 / C and NaF were mixed according to the stoichiometric ratio, ball milled for 3 hours, sent into a tube furnace, and then roasted at 650°C for 1h in a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C per minute, and the temperature was lowered with the furnace to obtai...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: (1) Mixing materials: use pentavalent vanadium oxy compound, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, and glucose as raw materials, and dissolve in 80mL deionized water, and then placed in a water tank with a constant temperature of 80°C, stirred for 6 hours until the solution evaporated to nearly dryness, and a uniformly mixed light green slurry was obtained; (2) Pre-calcination: dry the slurry in a vacuum oven, and then transfer In a tube furnace, pre-calcined at 850°C for 5 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere at a rate of 5°C per minute, and then taken out after cooling to obtain VPO 4 / C precursor; (3) secondary calcination: VPO 4 / C and NaF are mixed according to the stoichiometric ratio, ball milled for 3 hours, sent into a tube furnace, and then roasted at 850°C for 1h in a nitrogen atmosphere at a heating rate of 5°C per minute, and the temperature is lowered with the furnace to obtain the positive active material NaVPO 4 F / C. Other steps are with embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com