Influenza virus vaccine strain
A technology of influenza virus and avian influenza virus, applied in the direction of antiviral agents, viruses/bacteriophages, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of lack of virus replication ability, avoid vaccine production lag, increase combination mode, and selection range wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Example 1. Rescue and purification of recombinant virus using reverse genetic manipulation technology
[0051] 1. Extract the RNA of A / Chicken / Hebei / YT / 2010 and A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 34 viruses.
[0052] 2. Reverse transcription was carried out using the RNAs of the two viruses as templates respectively.
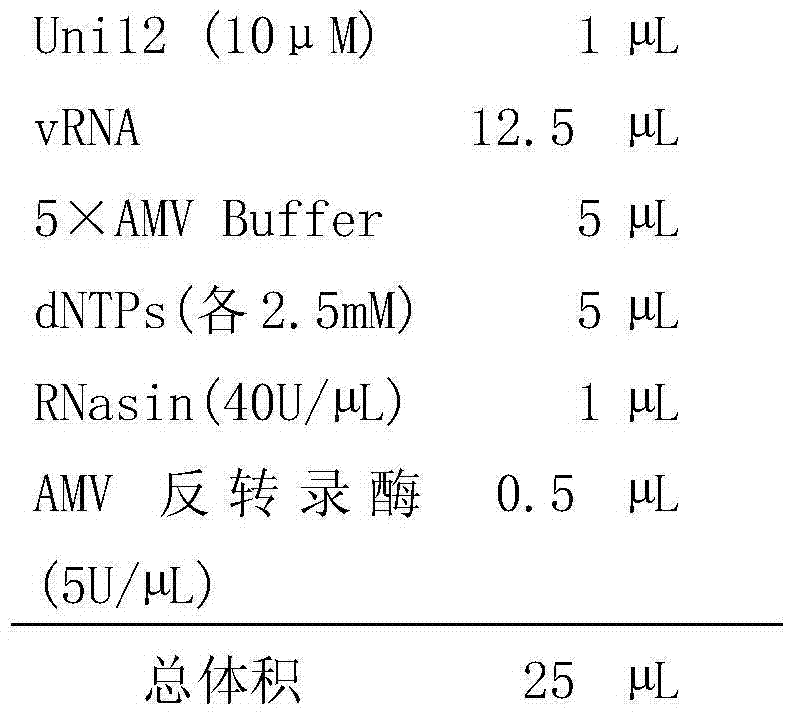
[0053] The reverse transcription system is as follows:
[0054]
[0055] Add the above-mentioned ingredients in turn to the reaction tube, mix well, and centrifuge briefly.
[0056] Wherein vRNA refers to the RNA of the virus obtained in step one.
[0057] Reverse transcription conditions: 42°C for 1h, 94°C for 5min.
[0058] The cDNA product after reverse transcription was used as a template for PCR reaction.
[0059] 3. PCR amplification
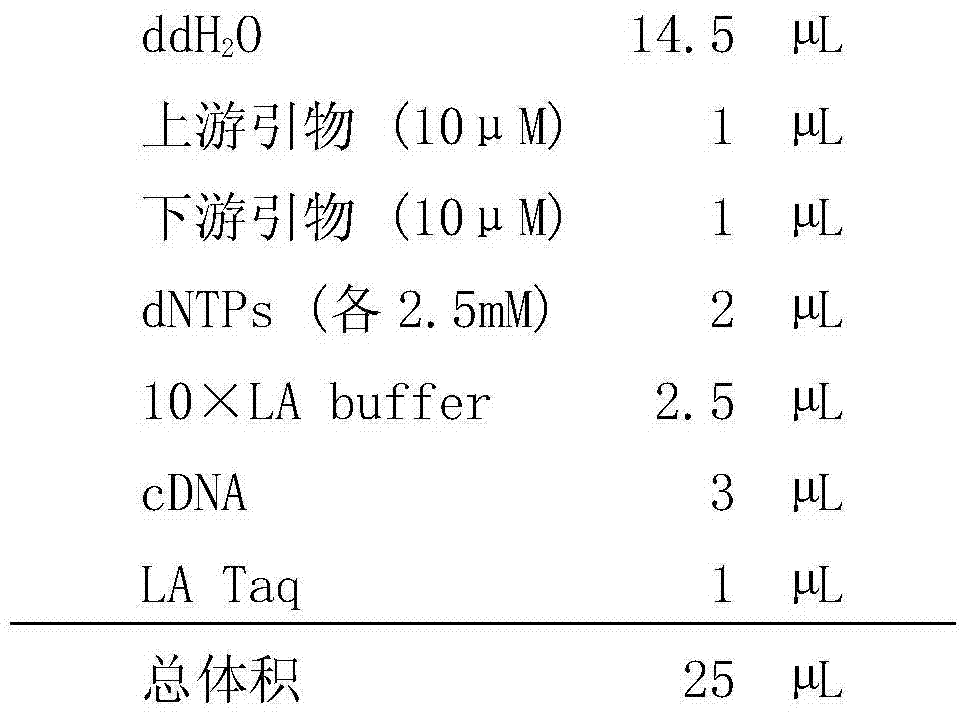
[0060] The PCR reaction system is as follows:
[0061]
[0062] Wherein the cDNA is the cDNA of the A / Chicken / Hebei / YT / 2010 or A / Puerto Rico / 8 / 34 virus obtained in step 2.
[0063] Add the above ingredients in sequence, cen...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Embodiment 2, passage, purification and identification of recombinant virus
[0175] One, the 18 strains of recombinant viruses that embodiment 1 obtains are carried out serial passage on MDCK cell, and specific method is as follows: the mixed solution that contains the cell of virus and supernatant is mixed with 10 respectively. -2 、10 -3 、10 -4 Infect MDCK cells at a dilution ratio (DMEM containing 1% double antibody), select the virus with the highest HA titer (that is, the highest dilution factor at which the virus can agglutinate red blood cells) at each dilution ratio, and then use the selected virus as Infect MDCK cells in the same way, and continuously select the virus with the highest HA titer (that is, the highest dilution factor at which the virus can agglutinate red blood cells) at each dilution. In this way, 18 strains of recombinant virus were continuously transmitted to the 10th generation.
[0176] 2. Plaque purification of passaged virus
[0177] (1...
Embodiment 3
[0191] Embodiment 3, passage poison TCID 50 / mL and determination of hemagglutination titer
[0192] 1. Preparation of MDCK monolayer cells
[0193] Transfer MDCK cells to a 96-well cell culture plate 24 hours before the experiment. When the cells grow to 70%-90%, remove the culture solution in the well with a 10mL pipette, wash the cells with PBS, discard the washing solution, and repeat the washing 3 times.
[0194] 2. Doubling dilution of virus solution
[0195] (1) Take out the purified virus solution of 18 strains obtained in Example 2 in a -80°C refrigerator 30 minutes before the experiment, put it in a 4°C refrigerator, and let it melt naturally.
[0196] (2) Each virus was sequentially diluted to 10 times with DMEM containing 1% double antibody. -8 , mark it.
[0197] (3) Store the doubly diluted virus solution on ice.
[0198] 3. Inoculate the virus
[0199] (1) Inoculate MDCK cells on a 96-well plate, inoculate 3 cell wells with each dilution of virus solution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com