Process method for processing solid waste of steelworks by utilizing smelting furnace
A technology of solid waste and process method, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of difficult treatment of slag steel solid waste, large investment cost, large floor area, etc., and achieve significant economic and environmental benefits, and the scope of treatment wide and high production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
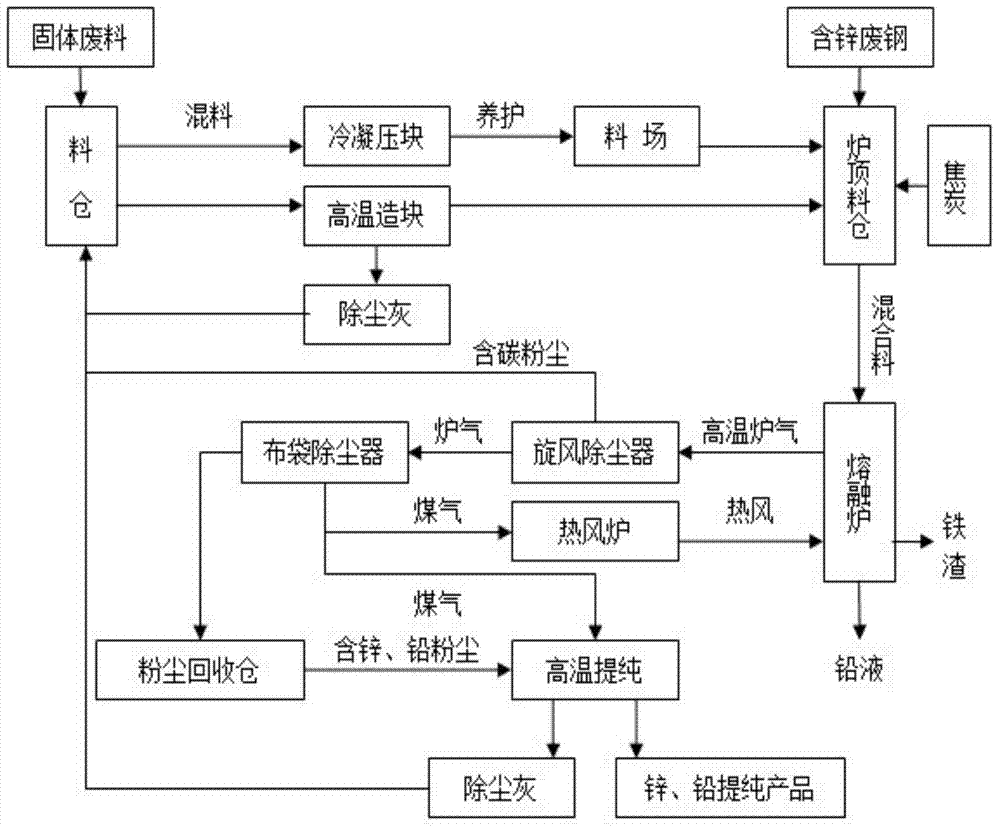
[0017] A blast furnace dust and converter sludge are selected as raw materials. The composition of blast furnace dust is Fe: 35%, Zn: 10%, Pb: 3%, C: 20%, and the composition of converter sludge is: Fe: 55% , Zn: 1%, H 2 O: 30%. Lime is used as flux. According to the ratio of blast furnace dust: converter sludge: quicklime: cement: water is about 60:25:2:5:8, mix well and press into blocks under a pressure of not less than 20MPa, at a temperature of 20 ~ 30 ℃, humidity ≥ 95% environment for 72 hours, after the curing is completed, it will be sent to the stockyard for stacking. This method can make full use of the carbon in the dust removal dust of the blast furnace, does not need to add additional reducing agent, and can reduce the amount of flux added; at the same time, the water in the converter sludge can be used to reduce the amount of water added.
[0018] The cured briquettes and coke are sent to the top silo of the melting furnace, fed into the melting furnace throug...
Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Choose a kind of electric furnace dust as raw material, its composition is Fe: 35%, Zn: 15%, Pb: 3%; choose coke powder as reducing agent, its fixed carbon content is about 85.5%, ash content is about 12.5%, volatile The content is about 2%; silica powder is used as the flux, and its SiO 2 The content is about 98%; cement is used as the binder. Add coke powder, silica powder, cement and water according to the ratio of electric furnace dust: coke powder: silica powder: cement: water is about 65:10:5:5:15, mix well and under the pressure of not less than 20MPa Pressed into blocks, cured for 72 hours in an environment with a temperature of 20-30°C and a humidity of ≥95%, and then sent to the stockyard for storage after curing.
[0021] The dust agglomerates and coke from the electric furnace are sent to the furnace top silo, and then fed into the melting furnace through the material bell for smelting. The subsequent smelting process is the same as the first embodiment. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com