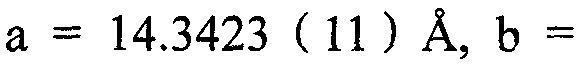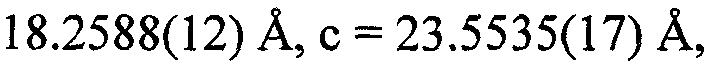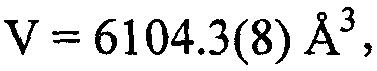Binuclear cuprous complex luminescent material and preparation method thereof
A technology of luminescent materials and complexes, applied in luminescent materials, copper organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient luminous efficiency and thermal stability of luminescent materials, scarcity of RGB three-color materials, etc., and achieve energy transfer Efficiency improvement, low production cost, and the effect of suppressing non-radiative attenuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Binuclear Cu(I) Complex [Cu(POP)Br] 2 Preparation of:
[0028] 1) Weigh 0.3mmol of POP each, pour it into a Shenlek bottle, add 30ml of dichloromethane, fill with nitrogen, and stir thoroughly to obtain a clear solution A;
[0029] 2) Weigh 0.3 mmol of CuBr with a stoichiometric ratio of 1:1, pour it into solution 1, continue to react under nitrogen atmosphere, and stir for 6 hours in the dark to obtain a colorless slightly turbid solution B;
[0030] 3) Filter solution B, take its filtrate, and remove the solvent by rotary evaporation of the filtrate under reduced pressure to obtain a white microcrystalline powder product, which is dried to obtain Cu(I) complex luminescent material [Cu(POP)Br] 2 .
Embodiment 2
[0032] Binuclear Cu(I) Complex [Cu(POP)Br] 2 Single crystal acquisition and characterization:
[0033] The single crystal was obtained by solvent diffusion method, and 0.1 mmol of [Cu(POP)Br] was weighed2 Powder, dissolved in 1ml of dichloromethane, placed in a small test tube, slowly added isopropanol (the volume ratio of isopropanol to dichloromethane solution is 1.5:1), and stood for several days to obtain a colorless transparent block shape crystal, select a single crystal with a size of 0.38×0.32×0.26mm for X-ray single crystal diffraction, and analyze [Cu(POP)Br] 2 molecular structure. The molecular structure of the compound is shown in the attached figure 1 , the unit cell packing structure diagram is shown in the appendix figure 2 .
[0034] For dinuclear complexes [Cu(POP)Br] 2 A series of performance tests were carried out on pure phase crystal samples. TG test shows that the material has good thermal stability, and its initial decomposition temperature reache...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com