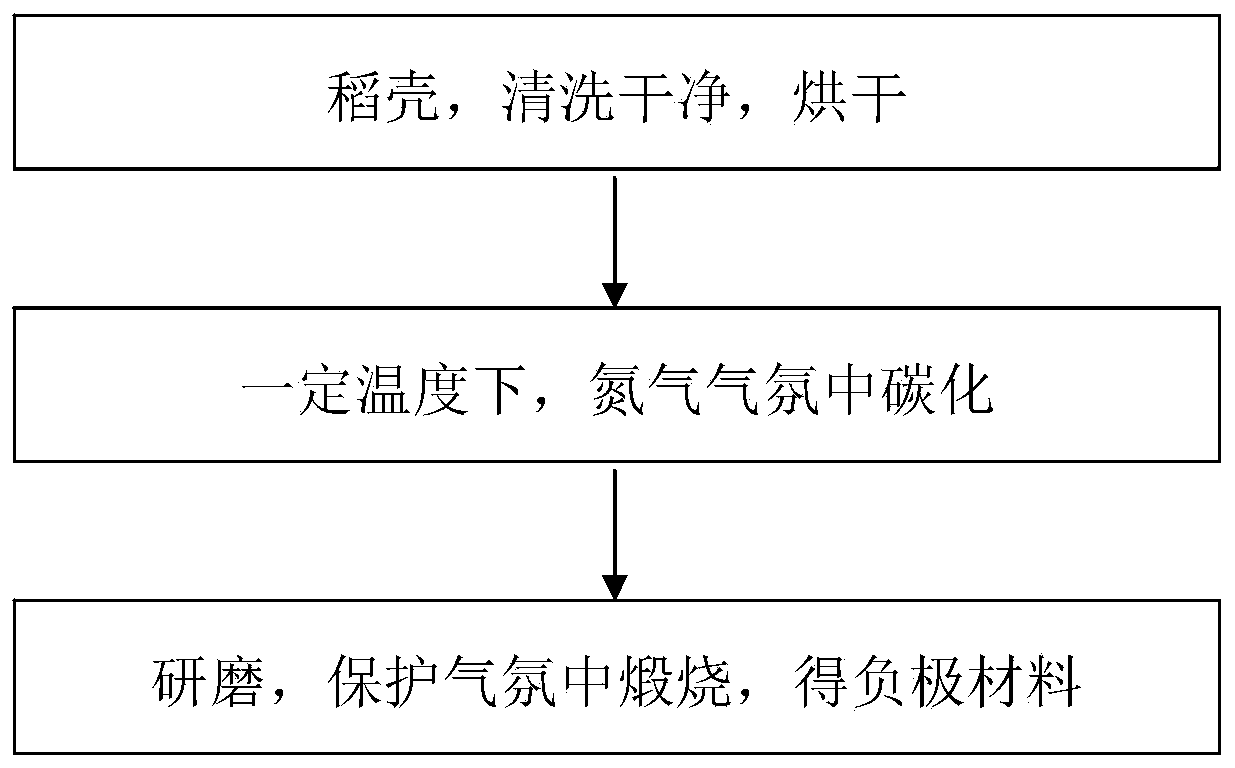
Method for preparing negative electrode material of lithium ion secondary battery
A technology for secondary batteries and negative electrode materials, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of many controlled parameters, difficult cost control, complicated preparation process, etc., and achieve stable storage, low cost, and abundant sources. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The cleaned rice husks were carbonized at 450°C for 1 hour under nitrogen atmosphere, and the temperature was naturally lowered to obtain carbonized rice husks. 2 The mixed atmosphere was kept at 900°C for 5 hours, and the temperature was naturally lowered to obtain the electrode material.
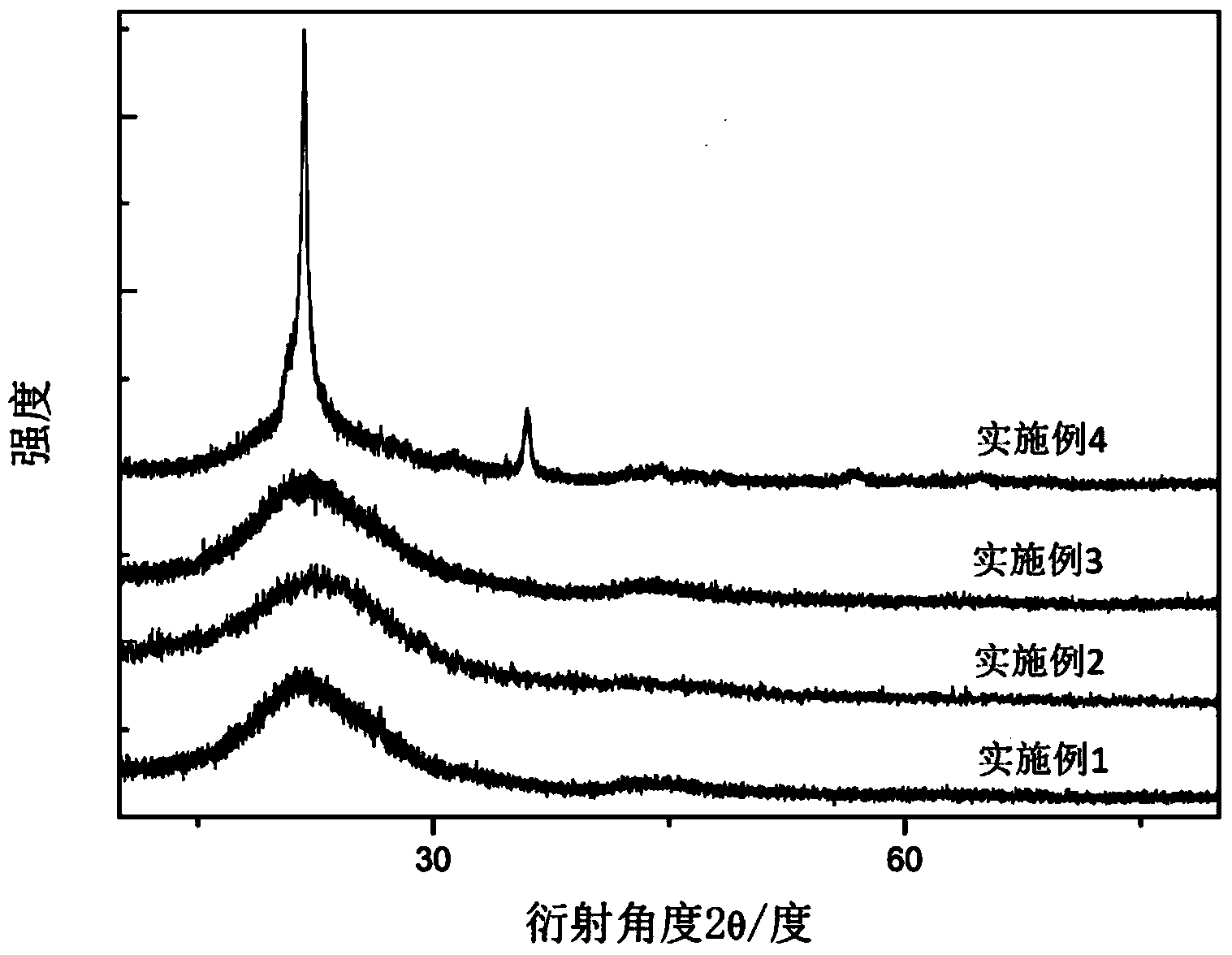
[0025] Synthetic SiO 2 The XRD pattern of / C negative electrode material, such as figure 2 shown.
[0026] The active material (prepared electrode material), conductive agent (super P), and binder (PVDF) are mixed according to the mass ratio of 6:3:1, coated on the copper foil, and lithium is used as the counter electrode to make a battery, and the electrolyte Selected as commonly used lithium-ion battery electrolyte: lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF 6 ) / ethylene carbonate (EC): dimethyl carbonate (DMC): methyl carbonate (EMC) mixture = 1:1:8.
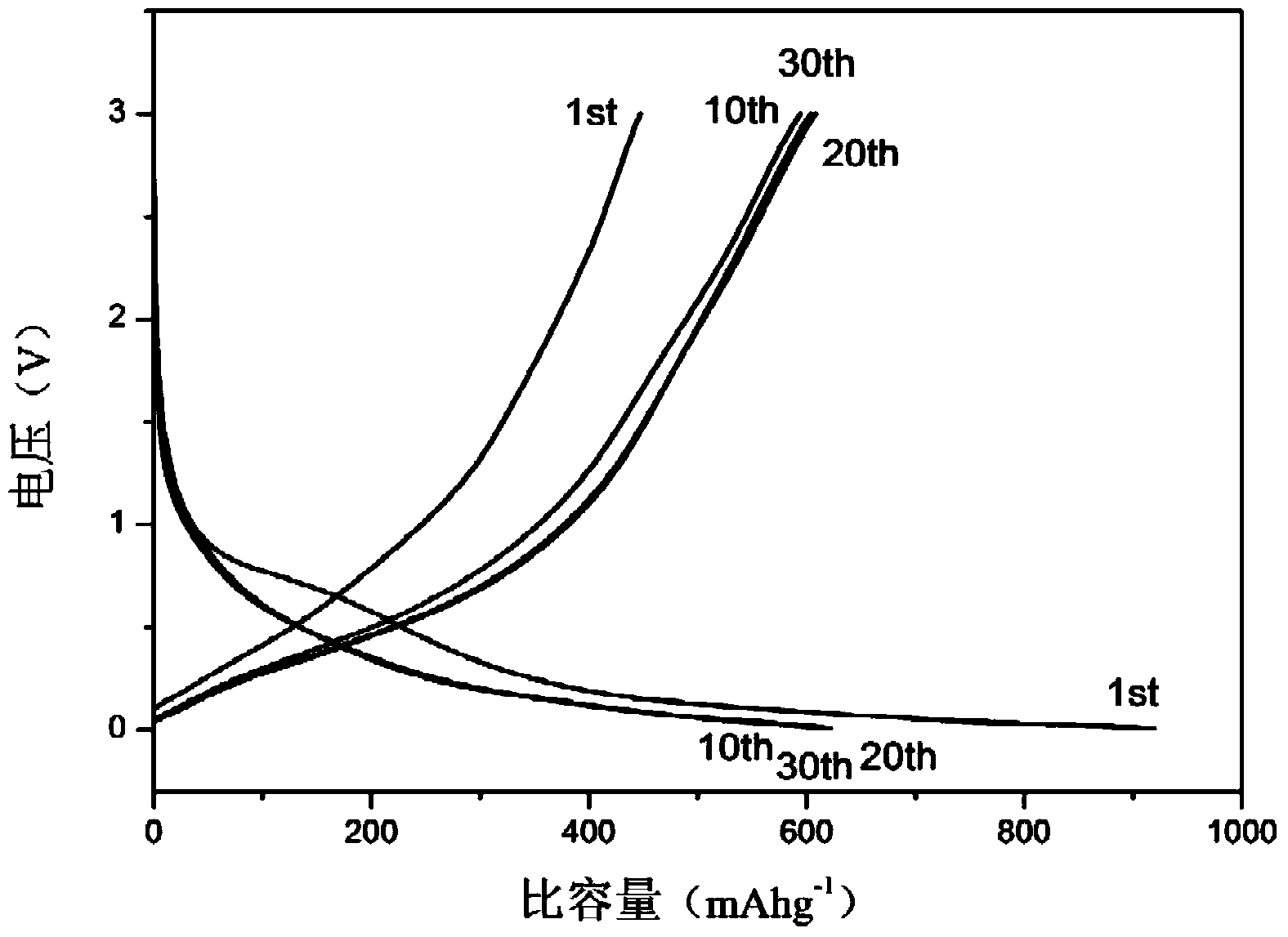
[0027] The prepared battery charge-discharge curve and cycle performance curve are as follows: image 3 and 4 As shown, the charge ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The difference between Example 2 and Example 1 is that it is only carbonized at 450° C. for 1 hour without subsequent high-temperature treatment. The battery material obtained is made battery according to the method of embodiment 1, and cycle performance curve is as follows Figure 5 As shown, the charge and discharge capacity after 30 cycles is 409.9mAhg -1 / 401.1mAhg -1 .
[0030] Synthetic SiO 2 The XRD pattern of / C negative electrode material, such as figure 2 shown.
[0031] If the carbonization temperature is higher than 450°C and the carbonization time is longer than 1h, electrode materials can also be obtained. The cycle performance of the fabricated battery is basically the same as that of the electrode material obtained by carbonizing at 450°C for 1 hour.
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference between Example 3 and Example 1 is that the high temperature treatment temperature is different, and the carbonized rice husk is kept at 800° C. for 5 hours, and the rest are the same. The battery material that makes is made battery by the method of embodiment 1, and battery cycle performance curve is as follows Figure 6 As shown, the charge and discharge capacity after 30 cycles is 443.3mAhg -1 / 451.9mAhg -1 .
[0034] Synthetic SiO 2 The XRD pattern of / C negative electrode material, such as figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com