Method for preparing nanocrystalline soft magnetic material employing microwave sintering
A nanocrystalline soft magnetic and microwave sintering technology, applied in the field of magnetic materials, can solve the problems of high cost and high energy consumption, and achieve the effects of simple operation, uniform powder particle size and energy saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0024] Preparation of manganese-zinc ferrite powder or nickel-zinc ferrite powder: add 0.25mol / L manganese nitrate or nickel nitrate, 1mol / L ferric nitrate, 0.25mol / L zinc nitrate solution into a beaker and mix evenly, and mix well in a magnetic stirrer After heating to 40°C, slowly add 1.5mol / L citric acid solution, then adjust the pH value to 5 with ammonia water, continue stirring for 30 minutes, and then heat and stir at 80°C for 6 hours to obtain a viscous colloid;
[0025] After the viscous colloid obtained above was left to stand for 24 hours, the clear liquid above the viscous colloid was filtered off, and the remaining viscous colloid was dried in a blast drying oven at 120°C for 1 hour, and then magnetic stirring was continued until the magnetic stirrer could no longer continue. Stir until it is stirred, then place it in a blast drying oven at 120°C and heat it for 6 hours, dry the moisture and complex compounds, and heat it at 220°C for 2 hours to decompose citric ac...
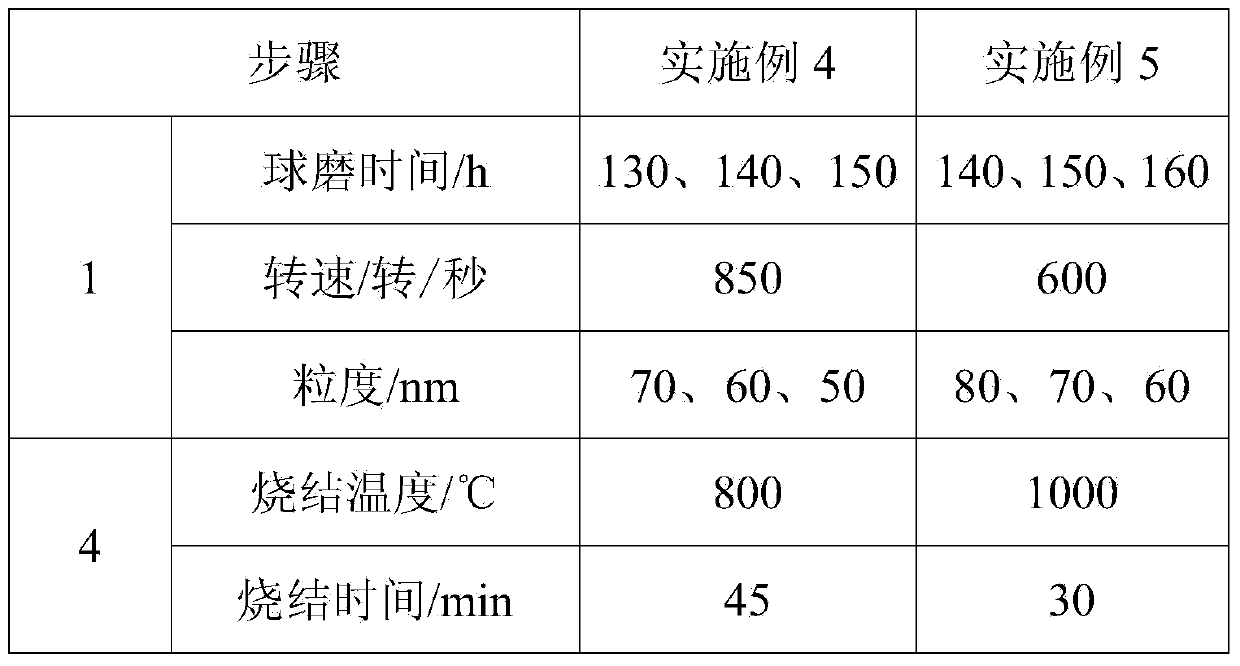
Embodiment 1
[0037] Microwave sintering of soft magnetic Mn-Zn ferrite with a mass of 100g "H type" (outer diameter 20mm, inner diameter 15mm, height 10mm), Fe in Mn-Zn ferrite 2 o 3 : MnO: ZnO = 53.5: 36.5: 10 (numbers represent mole percentages).
[0038] Step 1, according to Fe in Mn-Zn ferrite 2 o 3 : MnO: ZnO=53.5:36.5:10, calculated Fe 2 o 3 , MnO, ZnO mass ratio is: 71.5: 21.6: 6.9, and the element mass ratio of Fe, Mn, Zn is further obtained: 50.05: 16.63: 5.52, the mass of Mn-Zn ferrite is 100g, then calculate the Quality, i.e. iron nitrate (Fe(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O), manganese nitrate (Mn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O), zinc nitrate (Zn(NO 3 ) 2 ·6H 2 O) The masses are respectively: 361.1g, 54.1g, 25.2g, and then respectively configured into 1mol / L ferric nitrate solution, 0.25mol / L manganese nitrate solution and 0.25mol / L zinc nitrate solution;
[0039] Add 0.25mol / L manganese nitrate, 1mol / L ferric nitrate, 0.25mol / L zinc nitrate solution into the beaker and mix evenly. After heatin...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Cylindrical (dimensions ) Microwave sintering of pure metallic ferromagnetic materials.
[0047] Step 1. Mechanically grind the raw material pure iron powder, and grind according to different times. The specific requirements for ball milling are: the speed of rotation is 750 rpm, and the time of ball milling is: 120h, 140h, and 160h. Finally, iron powders with different particle sizes are obtained. Respectively: 80nm, 70nm, 60nm;
[0048] Step 2, place the iron powder ground in step 1 in a vacuum environment at 150°C (vacuum degree not greater than 10 -2 Pa) Annealing for 3 hours to eliminate work hardening and prepare for subsequent molding;
[0049] In step 3, iron powders of different particle sizes are pressed according to the requirements of the sample, and the specifications of the abrasive tools are: , the pressing pressure is 500MPa, the pressing time is 6min, and the holding time is 8min;
[0050] Step 4, put the pressed compact obtained in step 3 into a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com