An oblique wide-field optical section scanning imaging microscope system and its imaging method
A scanning imaging and microscopic system technology, applied in the field of optical microscopy, can solve the problems of slow scanning speed and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
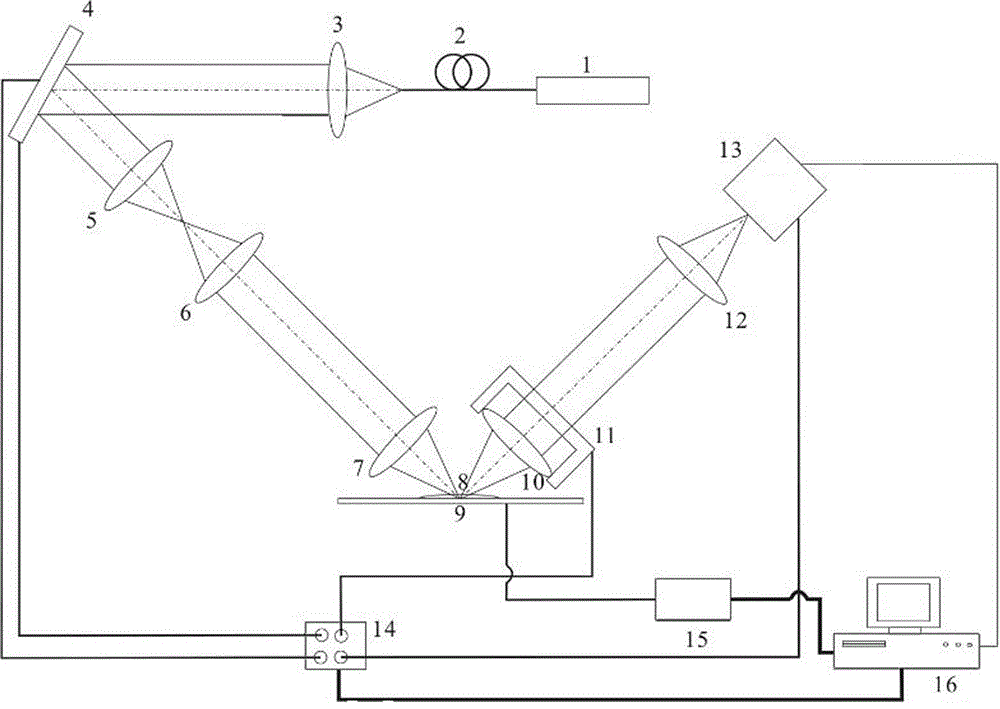
[0050] For an example of imaging a non-fluorescent sample, see figure 1 .
[0051] The imaging display control device is a main control computer 16, a control and imaging display program is installed in the main control computer, through the main control computer 16, a control signal instruction is sent to the data acquisition card, and the imaging device of the present invention is controlled by the data acquisition card. The laser intensity, the deflection angle of the two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, the displacement of the piezoelectric film base, the shutter control of the detector, etc., realize the synchronous action of the two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, the piezoelectric film base, and the shutter control of the detector.
[0052] The main control computer 16 sends a control signal command to the sample stage control device 15 to control the three-dimensional movement of the sample stage.
[0053] The laser emitting device mainly includes a laser 1, a si...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Take a single-color fluorescent sample labeled with a single-color fluorescent protein as an example.
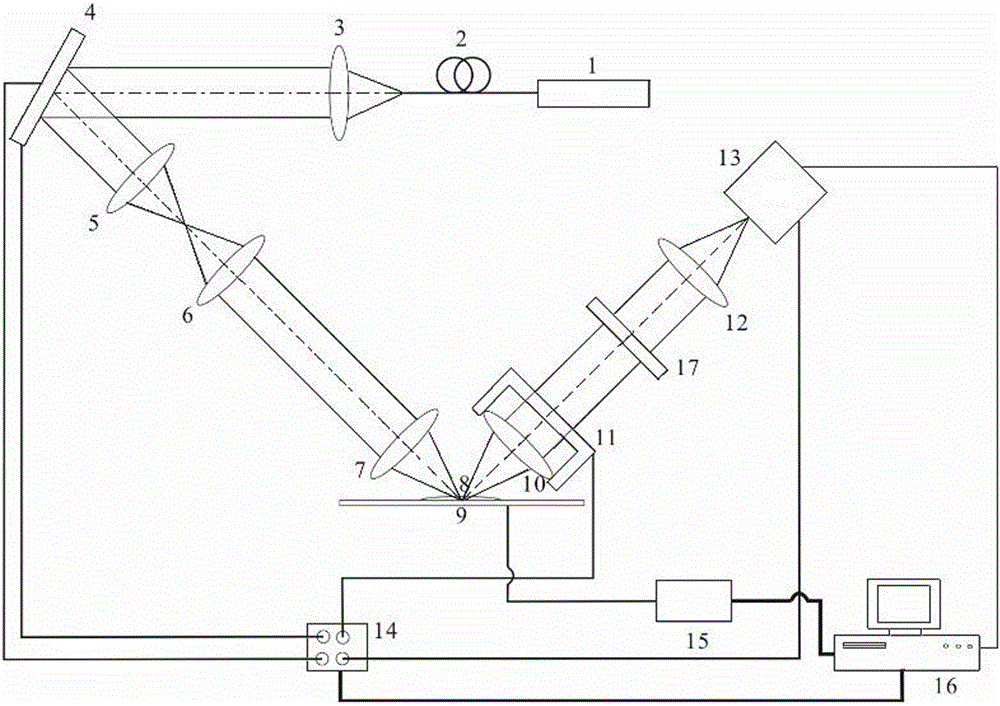
[0062] The difference from embodiment 1 to the non-fluorescent sample scanning imaging microscope system is that: when scanning and imaging monochromatic fluorescent samples, a filter 17 is installed between the second microscope objective lens 10 and the field lens 12, see figure 2 . The filter 17 allows the fluorescence excited by the scanning laser beam on the fluorescent sample to pass through, eliminates the reflected light and scattered light generated by the scanning laser beam, and only makes the excited fluorescence in the scanning area of the fluorescent sample image on the detection surface of the CCD detector. The structures of other imaging microscope systems are the same as those in Example 1. When laser scanning is performed on fluorescent samples, the emitted laser wavelength is the absorption wavelength corresponding to the fluorescent protein lab...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Take a dual-color fluorescent sample labeled with a dual-color fluorescent protein as an example.
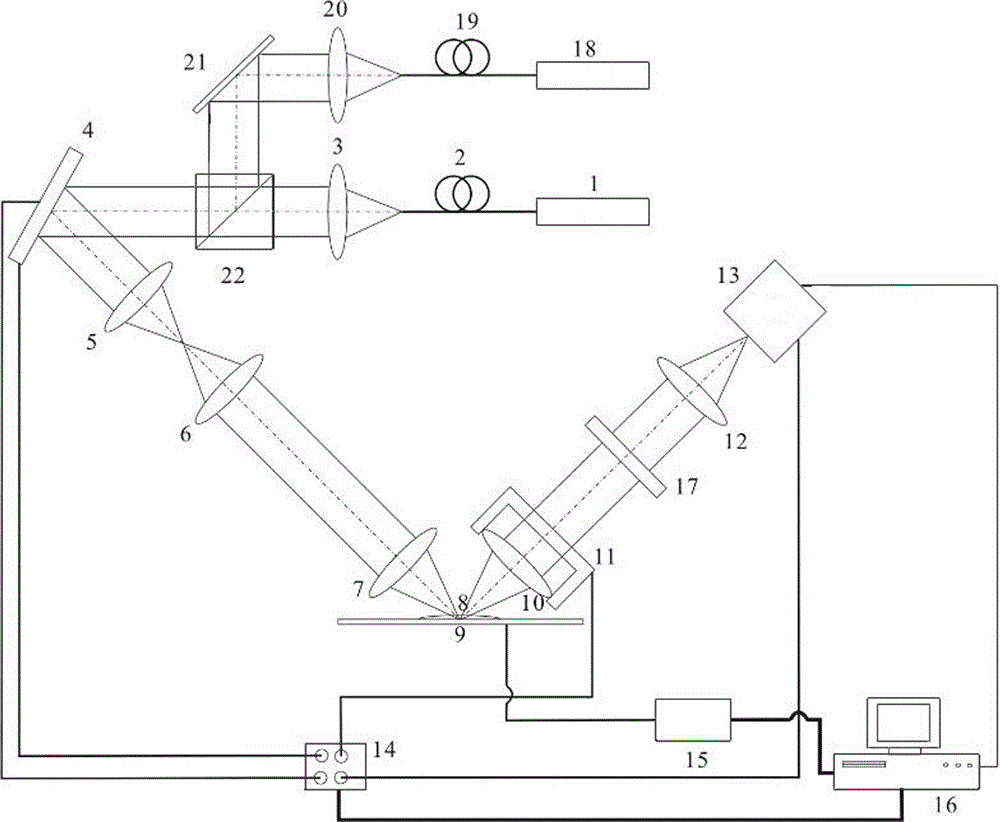
[0065] On the basis of the scanning imaging microscope system for monochromatic fluorescent samples in Example 2, a group of laser emitting devices is added to form two groups of first laser emitting devices and second laser emitting devices arranged in parallel, see image 3 .
[0066] The first laser emitting device comprises laser device 18, single-mode fiber 19, collimating lens 20 and reflector 21 successively, and described second laser generating device comprises laser device 1, single-mode fiber 2, collimating lens 3 and polarization beam splitter successively 22. The laser beam emitted by the laser 18 of the first laser emitting device is coupled by the single-mode optical fiber 19 and then collimated by the collimating lens 20 to form a collimated laser beam, and then reflected by the mirror 21 to the polarization beam splitter 22, and then polarized After bein...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com