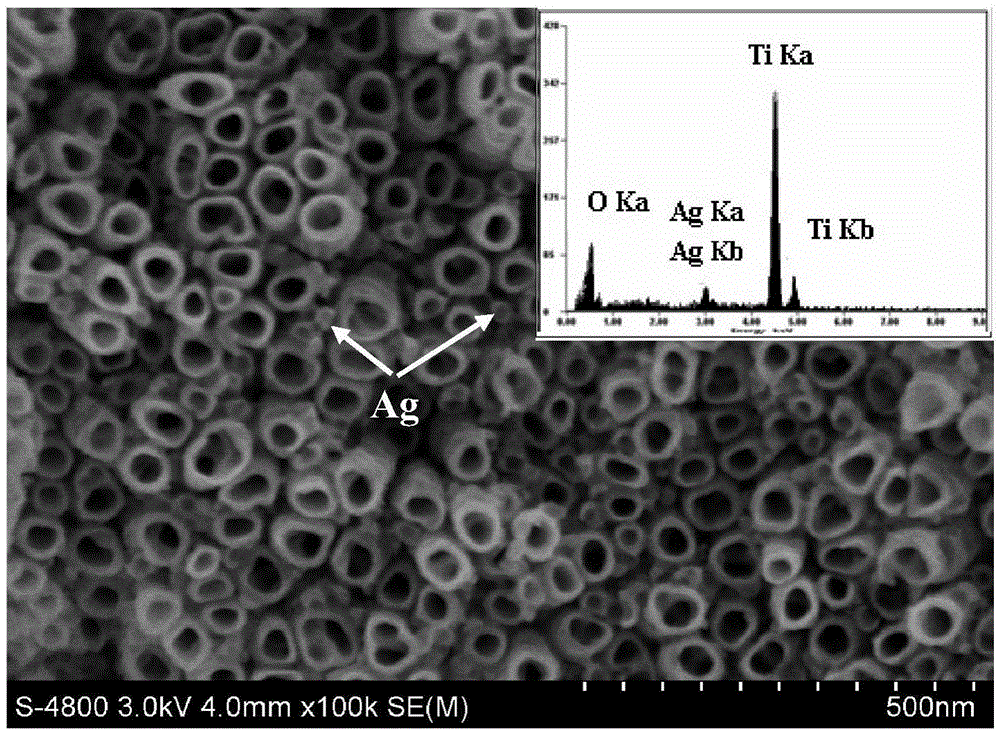
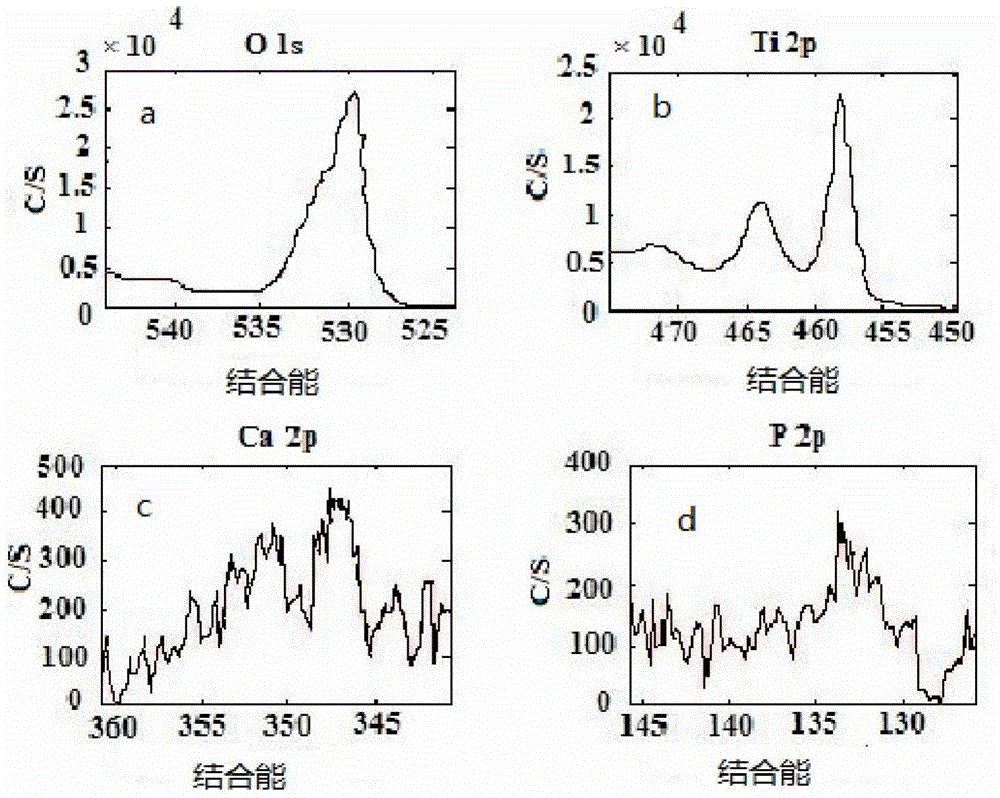
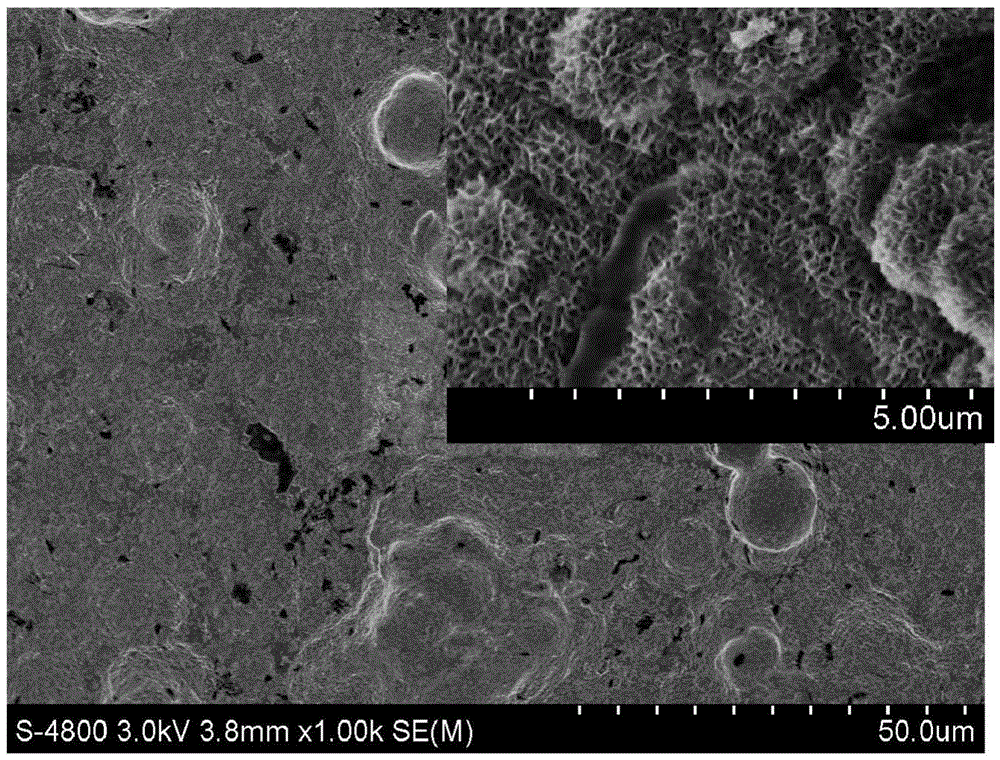
Preparation method of calcium-phosphorus-silver nanotube array loaded on medical titanium surface
A silver nanotube, calcium and phosphorus technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, to achieve the effects of large economic benefits, improved antibacterial properties, and good biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Weigh 0.05 mol of NaF powder, dissolve it in 500 ml of simulated body fluid (SBF), stir evenly with magnetic force to obtain NaF electrolyte with a concentration of 0.1M. Then weigh 0.01mol of AgNO 3 Dissolve the powder in 100ml deionized water and stir it evenly to obtain AgNO with a concentration of 0.1M 3 electrolyte. Medical pure titanium sheet (model: TA1, size 10mm×10mm×1mm, the same as the following examples) is polished with sandpaper, then cleaned with acetone, ethanol and deionized water, and then placed in 0.1M NaF electrolyte as an anode In this case, plate-shaped graphite (the size of graphite is 40mm×40mm×5mm, the same as in the following examples) is used as the cathode, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 40mm. Anodizing treatment is carried out by WYK-150 DC power supply device, and its process parameters are room temperature, 10V, 1h. After the treatment, the titanium sheet was taken out from the electrolyte, rinsed with deionized ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Weigh 0.02 mol of NaF powder, dissolve it in 100 ml of simulated body fluid (SBF), and stir evenly with a magnetic force to obtain a NaF electrolyte with a concentration of 0.2M. Then weigh 0.001mol of AgNO 3 Dissolve the powder in 100ml deionized water, and stir evenly with a magnetic force to obtain AgNO with a concentration of 0.01M 3 electrolyte. The medical pure titanium sheet is anodized by WYK-150 DC power supply unit. The electrode type, position, anodic oxidation temperature and experimental procedures are all the same as those described in Example 1, except that the oxidation voltage used in the NaF electrolyte is 10V, and the oxidation time is 2h. 3 The oxidation voltage in the electrolyte is 5V, and the oxidation time is 3min. After the finally obtained titanium sheet samples were rinsed with deionized water, they were left to dry in the air.
[0032] Carry out the performance detection in embodiment 1, find that the nanotube array of uniform distributio...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Weigh 0.1 mol of NaF powder, dissolve it in 100 ml of simulated body fluid (SBF), stir evenly with magnetic force to obtain NaF electrolyte with a concentration of 1M. Then weigh 0.05mol of AgNO 3 Dissolve the powder in 100ml deionized water and stir it evenly to obtain AgNO with a concentration of 0.5M 3 electrolyte. The medical pure titanium sheet is anodized by WYK-150 DC power supply unit. Electrode type, position, anodic oxidation temperature and experimental procedure are all described in Example 1, the difference is that the distance between cathode and anode is 50mm, the oxidation voltage used in NaF electrolyte is 30V, and the oxidation time is 30min. AgNO 3 The oxidation voltage selected in the electrolyte is 10V, and the oxidation time is 1min. After the finally obtained titanium sheet samples were rinsed with deionized water, they were left to dry in the air.
[0035] Carry out the performance test in embodiment 1, find that the nanotube array is formed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com