Engineering bacteria based on extracellular Alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and implementation method thereof
A technology of furanosidase and engineering bacteria, applied in the field of biological genetic engineering, can solve the problems of insufficient development and utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Cultivation of Streptomyces griseus JSD-1
[0035] Streptomyces griseus was isolated from the rotting soil of Pujiang Town, Shanghai, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.5706; the strain was preserved in the Chinese Academy of Microbiology Research Center of General Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences on January 9, 2012 Office (Address: No. 3, No. 1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101)
[0036] The bacteria were inoculated in LB liquid medium, cultured at 32°C for 60 hours, the bacteria were collected by centrifugation and the genomic DNA of the bacteria was extracted.
[0037] The components of the LB liquid medium are: 10 g of peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 5 g of NaCl, 1 L of deionized water, and pH 6.8-7.2.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Cloning of Arabinofuranosidase (Sg-Abl) Gene of Streptomyces grisea
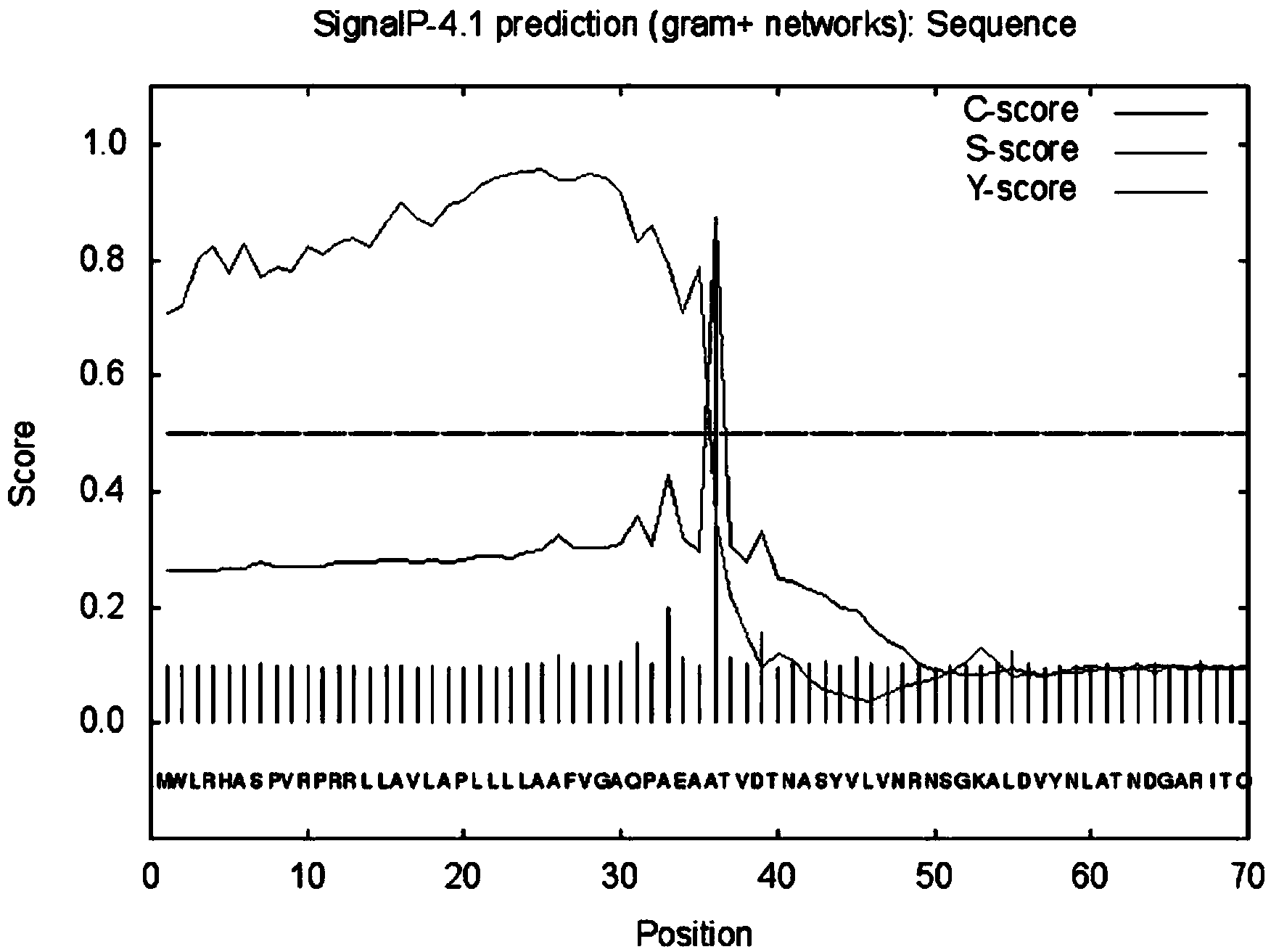
[0040] Through signal peptide sequence analysis of Streptomyces grisea arabinofuranosidase gene sequence (such as figure 1 ), the primers containing NdeI and EcoRI restriction sites were designed at both ends of the coding gene sequence of the mature protein as follows:
[0041] Forward primer Abl-NdeⅠ-F:
[0042] 5'-GGAATTCCATATGGCGACCGTGGACACGAACGCCTCGTAC-3'
[0043] Reverse primer Abl-EcoRI-R:
[0044] 5'-GGAATTCTCAGCGCCGCAGCGTCAGCAGACC-3'
[0045] Genomic DNA of Streptomyces grisea JSD-1 was used as a template, and PrimeSTAR GXL high-fidelity enzyme (TaKaRa) was used for amplification. The PCR amplification conditions were: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 3 min; deformation at 98°C for 10 s, extension at 68°C for 1 min; and final extension at 68°C for 3 min after 30 cycles.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Construction of Cloning Vector Containing Arabinofuranosidase (Sg-Abl) Gene
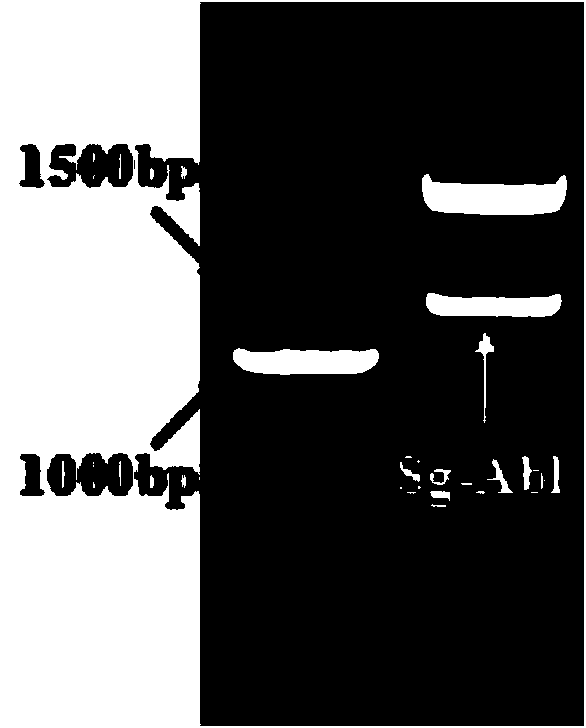
[0048] The PCR amplification product is carried out electrophoresis detection, and the result shows that the obtained fragment is about 1.4Kb (see figure 2 ); Then, after the PCR product was cut and recovered, the A-adding reaction was performed through the A-Tailing Kit (TaKaRa) and connected to pMD TM 19-T Vector (TaKaRa), then introduced into DH5α Escherichia coli competent cells.
[0049] Clones with corresponding resistance were picked and identified by colony PCR until positive clones were obtained. Pick positive clones, extract their plasmids by shaking bacteria and send them to Shanghai Sonny Biological Co., Ltd. for sequencing.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com