Method for evaporation-free preparation of zinc sulfate from brass slag material
A technology of brass slag and zinc sulfate, which is applied in the fields of metallurgy and chemical industry, can solve the problems of high energy consumption in the concentration and evaporation of zinc sulfate products, high energy consumption in the evaporation and concentration process, and the impact on the quality of zinc sulfate products, so as to achieve good metal selection high performance, low energy cost, and low supersaturation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
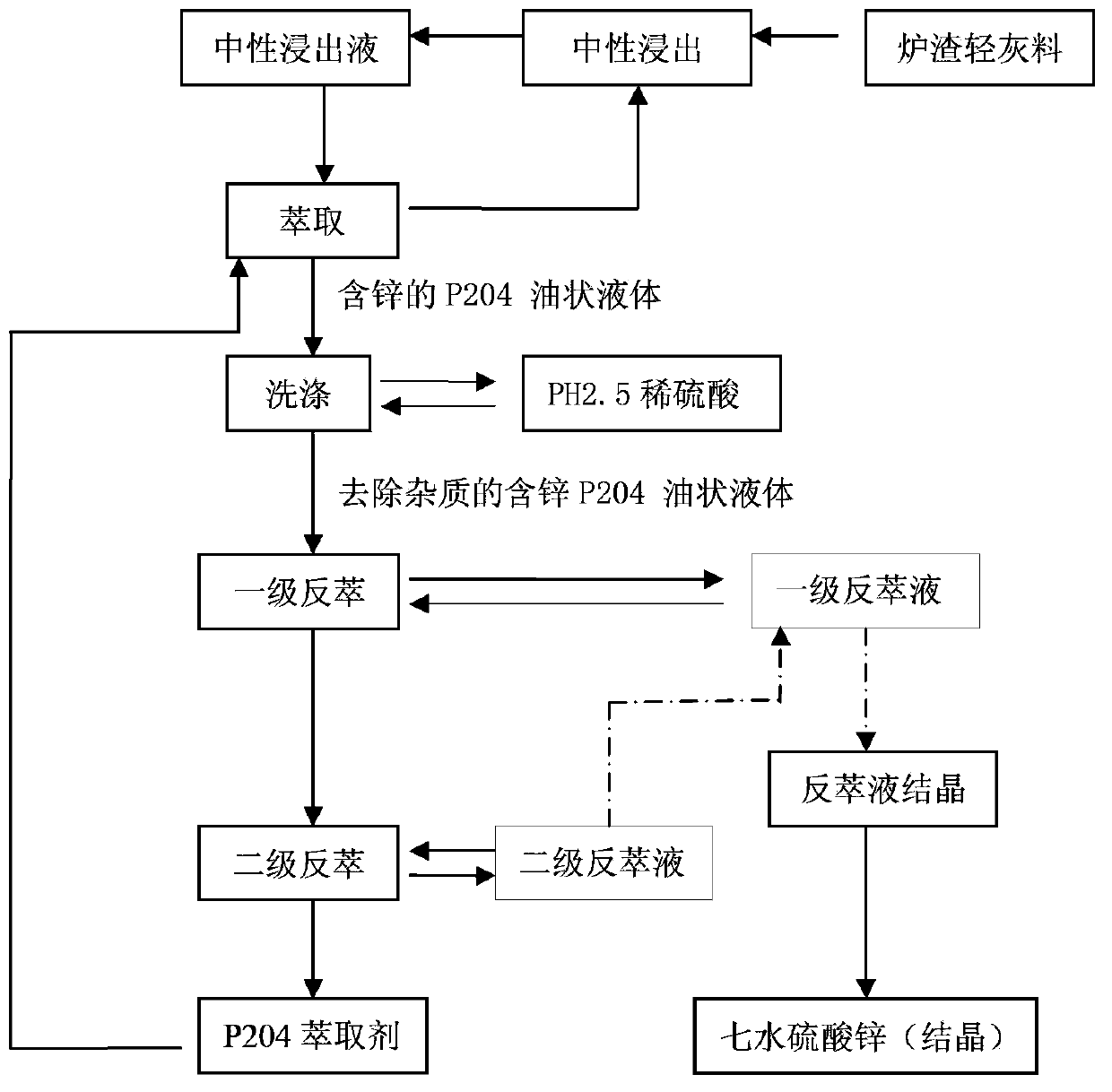
[0028] The raw material used in this example is 20Kg (dry weight) of light ash material after physical separation of brass slag. leach.
[0029] Next, extract the zinc in the neutral leaching solution with 30% P204 extractant (the diluent is kerosene), control the ratio of oil to water (O / A ratio) to 1:1, and separate the oil-water phase (water phase It can be recycled back to the leaching process, thereby replacing the input of sulfuric acid and water), and P204 (R 2 -Zn) oily liquid,
[0030] Chemical formula: 2(R-H)+Zn 2+ →(R 2 -Zn)+2H +
[0031] Then, the oily liquid containing 8g / L of zinc is washed with a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a pH value of 2.5 to remove a small amount of impurity elements entrained; at the same time, the washed oily liquid of zinc-containing P204 is subjected to primary dislocation with 400g / L of sulfuric acid. Flow stripping, the ratio of water to oil is 1:3, to obtain a primary stripping solution with a zinc content of 19.2g / L; repe...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The raw material used in this example is 24Kg (dry weight) of light ash material after physical separation of brass smelting slag. Sulfuric acid neutral leaching.
[0037] Next, extract the zinc in the neutral leaching solution with 30% P204 extractant (the diluent is kerosene), control the ratio of oil to water (O / A ratio) to 1:1, and separate the oil-water phase (water phase It can be recycled back to the leaching process, thereby replacing the input of sulfuric acid and water), and an oily liquid containing 8.2g / L of zinc is obtained.
[0038] Then, the oily liquid containing zinc 8.2g / L is washed with a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a pH value of 2.5 to remove a small amount of impurity elements entrained; at the same time, the washed zinc-containing P204 oily liquid is treated with 400g / L sulfuric acid for primary Cross-flow stripping, the ratio of water and oil is 1:3, to obtain a primary stripping solution with a zinc content of 19.7g / L; repeat stripping, w...
Embodiment 1、2
[0044] Embodiments 1 and 2 of the present invention: low energy consumption, high production efficiency, simple process, clean site, zinc sulfate crystals in granular form, bright white in color.
[0045] Comparative example: the energy consumption is obviously too high, and the production time is longer; the amount of acid and water used is increased, and the site environment is poor; the crystal of zinc sulfate is dusty, easy to absorb moisture and agglomerate, and appears light green or light yellow green.
[0046] Composition comparison:
[0047] The chemical compositions of the zinc sulfate crystals prepared in Examples 1, 2 and Comparative Example are shown in Table 1 after detection.
[0048] Table 1: Chemical composition of zinc sulfate heptahydrate
[0049] name
[0050] It can be drawn that the quality of the zinc sulfate prepared by the crystallization stripping method of the present invention is better than the zinc sulfate produced by the concentrated d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com