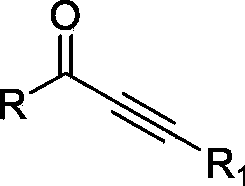
Method for preparing acetylenic ketone through oxidizing propargyl alcohol
A technology for preparing propargyl alcohol and acetylenic ketone, which is applied in the field of catalytic oxidation, can solve problems such as troublesome post-processing and pollution, and achieve the effects of easy product, simple operation and mild reaction conditions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
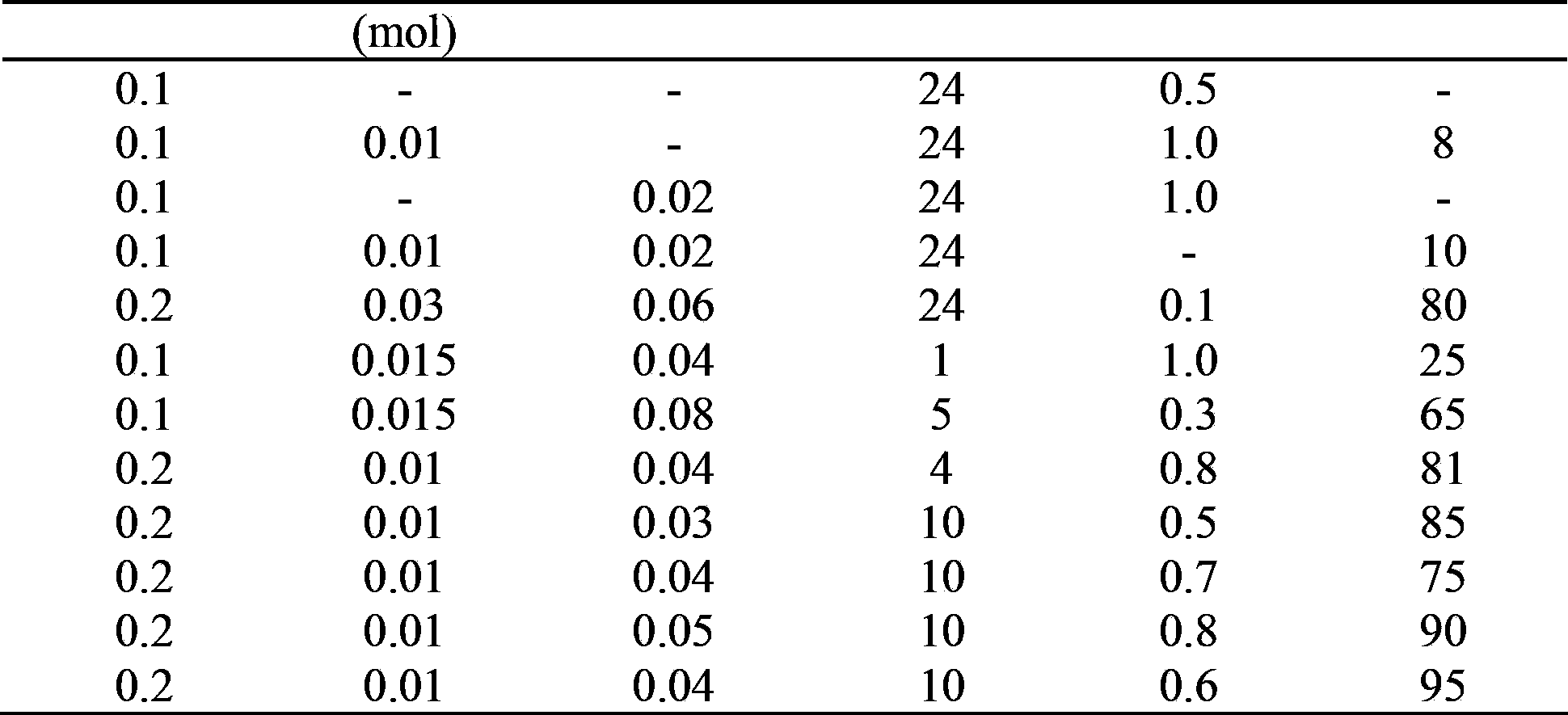
[0017] Embodiment 1, the investigation of reaction conditions
[0018] First, we investigated the reaction conditions by taking the oxidation of 1,3-diphenyl-2-propyn-1-ol to 1,3-diphenyl-2-yne-1-propanone as a model reaction.
[0019] The results are shown in Table 1.
[0020] The investigation of table 1 reaction condition
[0021]
[0022]
[0023] Note: The reaction temperature is 25°C, the substrate is 1,3-diphenyl-2-propyn-1-ol, and the organic solvent is dichloromethane (30ml). The product is 1,3-diphenyl-2-yne-1-propanone, light yellow solid, 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 )δ7.56-7.43(m,5H),7.72-7.62(m,3H),8.26-8.22(m,2H), 13 CNMR (100.6MHz, CDCl 3 )δ 86.8, 93.0, 119.9, 128.5, 128.6, 129.4, 130.7, 132.9, 134.0, 136.7, 177.8. IR(KBr,cm -1 ): 3063, 2955, 2921, 2851, 2198 (C≡C), 1727 (C=O).
[0024] It can be seen from Table 1 that DDQ, nitric acid, and oxygen play a vital role in the oxidation reaction and are indispensable. The oxygen pressure is high, the react...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2, the influence of different solvents on reaction
[0026] The influence of table 2 solvent on reaction
[0027]
[0028] Note: The reaction conditions are 0.1mol 1,3-diphenyl-2-propyn-1-ol oxidation, 0.01mol DDQ, 0.04mol98% nitric acid, 0.3Mpa O 2 ,25°C, 15h.
[0029] As can be seen from Table 2, when methylene dichloride, ethylene dichloride, chloroform and ethyl acetate were solvents, the yield of product 1,3-diphenyl-2-alkyne-1-propanone was higher, from the perspective of environmental protection and convenience Handling Considerations Dichloromethane and ethyl acetate are the preferred solvents.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3, 1-phenyl-2-propyn-1-alcohol oxidation
[0031]
[0032] Add 13.2g (100mmol) 1-phenyl-2-propyn-1-ol, 2.72g (9.8mmol) DDQ into 30mL of dichloromethane solvent, cool with an ice-water bath, and slowly add 1.15g ( 18mmol) of nitric acid, fed with 0.2MPa of oxygen, reacted at 25°C for 18h, slowly released the pressure, added NaOH aqueous solution to neutralize, extracted with dichloromethane, washed with water, dried, and evaporated the solvent. The resulting mixture was subjected to column separation to obtain 9.8 g (yield: 75%) of 1-phenyl-2-propyn-1-one. Melting point of yellow solid is 42.5-43.5°C; 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 )δ3.45(s,1H),7.49(t,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.63(t,J=7.4Hz,1H),8.16(d,J=7.4Hz,2H). 13 C NMR (100.6MHz, CDCl 3 ) δ80.2, 80.7, 128.7, 129.6, 134.5, 136.1, 177.3. IR(KBr,cm -1 ): 3311(-C≡H), 3045, 2109(C≡C), 1666(C=O).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com