Bacterial strain for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids and screening method thereof
A technology of unsaturated fatty acid and screening method, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fungi, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve industrialized production, large variation, etc., to save screening costs and grow vigorously. , to avoid random effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Low temperature culture for primary screening
[0041] The nine soil samples (see Table 1) from the three regions are labeled as A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3, C1, C2, and C3, respectively. Weigh 1g of soil sample each, add it into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask filled with 100mL sterile water and glass beads, shake for 15min, and take 150μL suspension (dilution equivalent to 10 -2 ) on a PDA plate (three plates for each sample), and cultured at 5°C and 28°C, respectively.
[0042] Table 1 Basic conditions of collected soil
[0043]
[0044] The culture results are shown in Table 2. Under the low temperature condition of 5°C, the cultured microorganisms grow very slowly, and it takes about 7 days to grow enough colonies, most of which are moist bacterial colonies and a few filamentous fungal colonies; After 2 days of culture, more colonies appeared on the plates. After comparison, it can be seen that the culture at low temperature at 5°C inhibits the growth of many m...
Embodiment 2
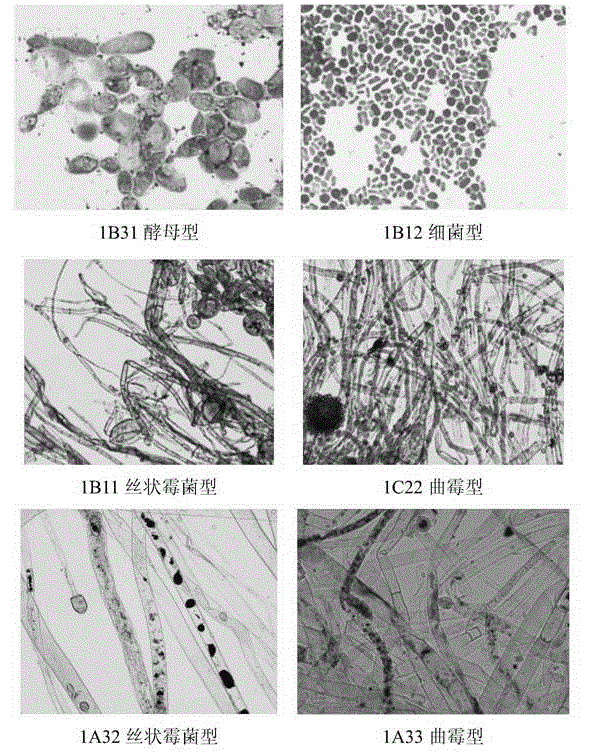
[0048] Example 2 Sudan black staining microscopic examination for re-screening
[0049] 80 colonies were selected from the plate grown at low temperature for Sudan black staining, and the oil particles in the bacteria were observed under a microscope. The specific dyeing method is as follows:
[0050] 1) Activation of bacteria: transplant 80 selected colonies to a fresh PDA medium slant for purification, isolation and numbering, and culture at 28°C for three days;
[0051] 2) Smear: Drop a small drop of distilled water in the center of a clean glass slide, use an inoculation loop to aseptically pick a little bacterial lawn from the slant culture in the water drop, mix it and paint it into a film;
[0052] 3) drying: natural drying at room temperature;
[0053] 4) Fixing: Hold one end of the glass slide with the bacteria-coated side facing up, and pass through the alcohol flame 2-3 times;
[0054] 5) Staining: place the smear in a horizontal position, add Sudan black dyeing ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Embodiment 3 liquid fermentation culture
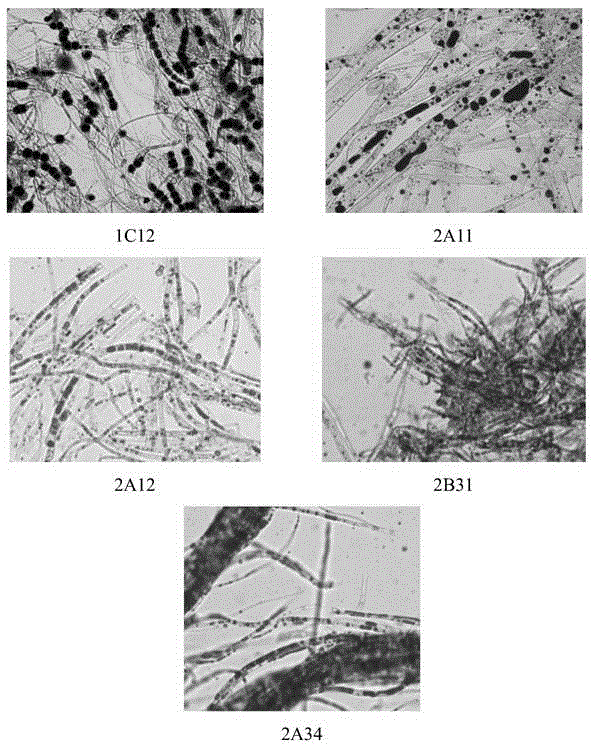
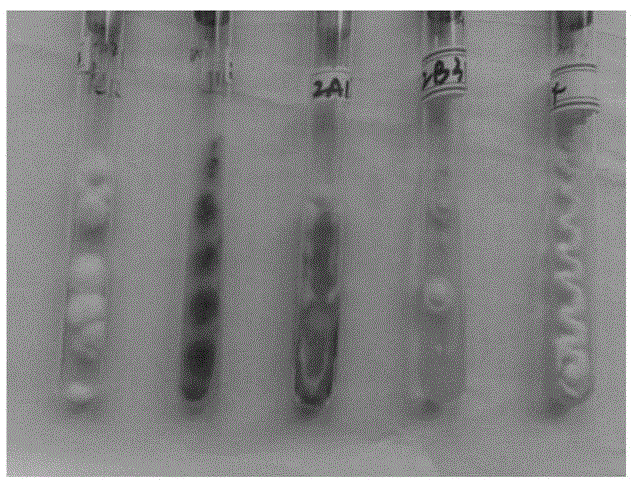
[0063] Seed liquid culture: Inoculate five strains of 1C12, 2A11, 2A12, 2B31, and 2A34 obtained through screening into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed medium, and culture them on a shaker at 30°C for 3 days at 150r / min as a fermentation medium. Use strains.
[0064] Shake flask fermentation culture: After breaking up the bacteria for fermentation with a disperser, inoculate 10% of the inoculum into a 1L Erlenmeyer flask with a baffle (the liquid volume is 200ml), at 30°C, 150r / min shaker culture 120h.
[0065] Determination of biomass: After the whole fermentation liquid was broken up by a disperser, it was filtered by suction and washed 3 times with distilled water. The bacteria were collected in a 9cm plate, freeze-dried and weighed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com