Method for directly determining non-separated small nucleic acid in biological sample, and detection kit thereof
A biological sample, small nucleic acid technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve, complex processing, long analysis cycle, etc., and achieve the effect of wide linear range, good repeatability and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0077] Embodiment 1: PCSK9siRNA and liposome encapsulation
[0078] siRNA sequence:
[0079] Antisense strand: 5'UCCGAAUAAACUCCAGGCCUA3'
[0080] Sense strand: 5'UAGGCCUGGAGUUUAUUCGGA3'
[0081] According to the method of in vivo siRNA liposome delivery system provided by the supplier (Shanghai EMI (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), the siRNA was wrapped, and the wrapped double-stranded siRNA suspension was measured, and the wrapping rate was greater than 85%.
Embodiment 2
[0082] Embodiment 2: the processing that contains small nucleic acid plasma and tissue
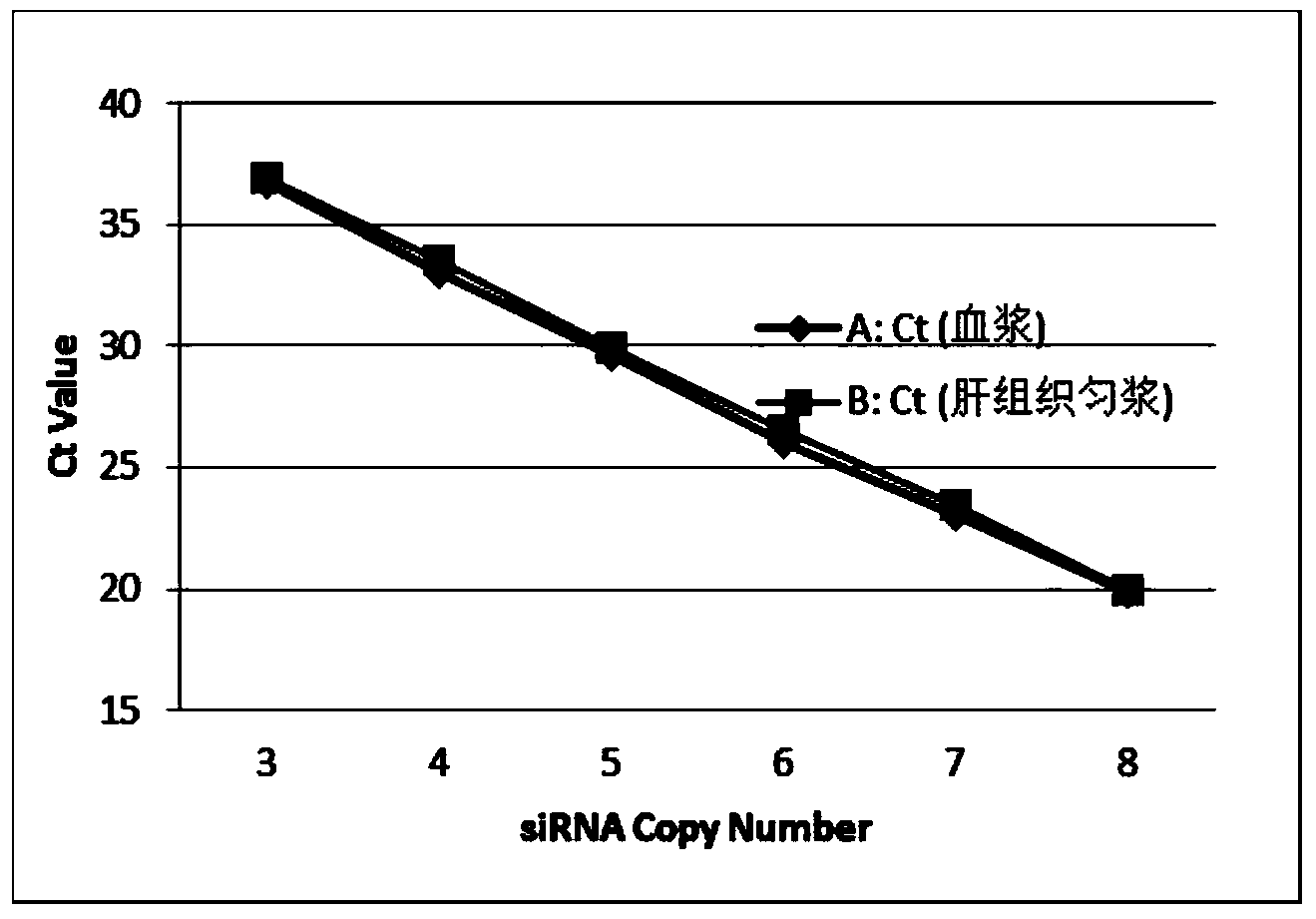
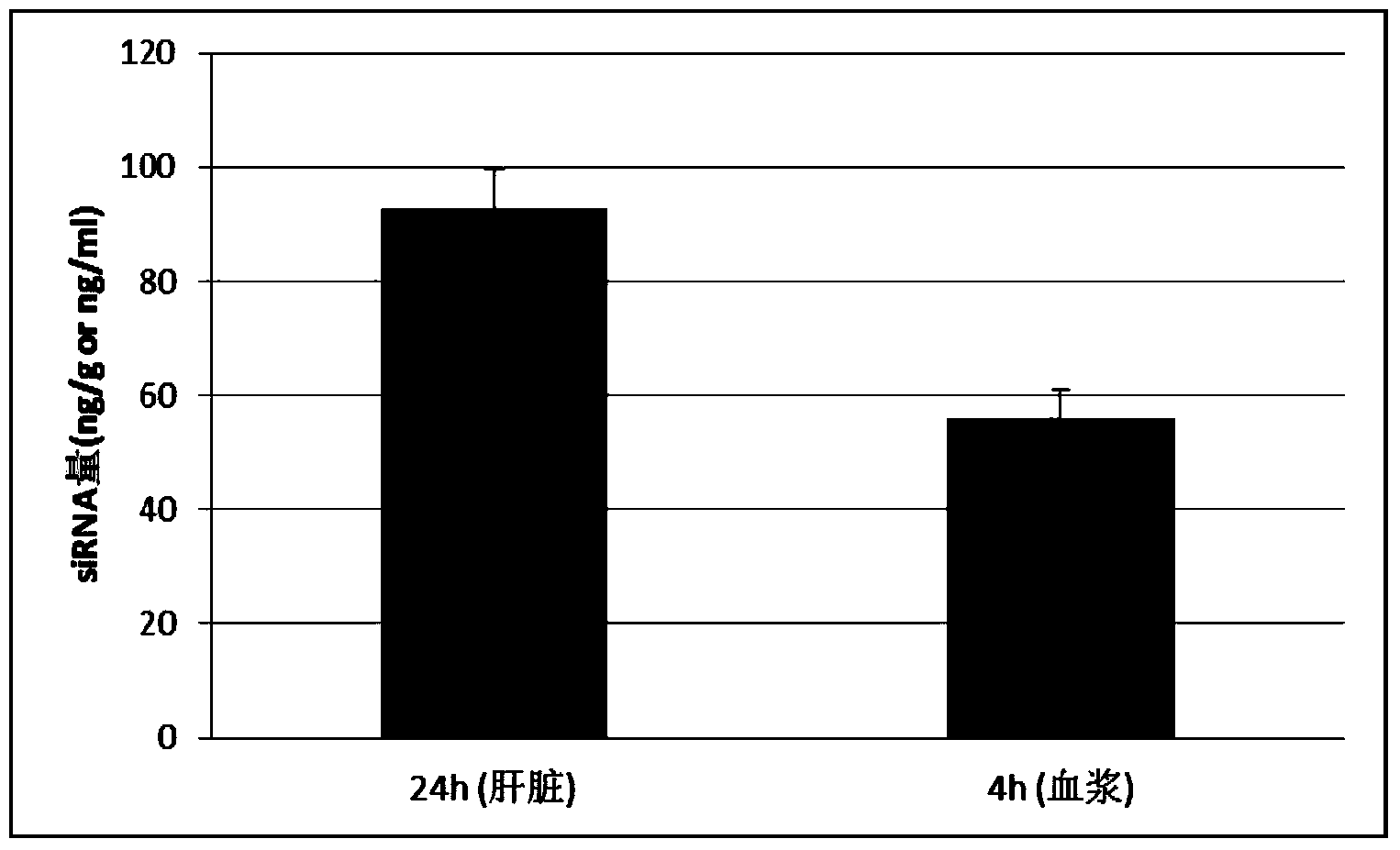
[0083] All procedures used in in vivo animal studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and performed in accordance with local government regulations. For CD1 mice, inject 0.2 ml of siRNA formulation at 1 mg / kg via the tail vein. After 24 hours, take blood, separate the plasma, and dilute the plasma with water containing 0.25% Triton X-100: add 2 microliters of plasma to 18 microliters of water containing 0.25% Triton X-100 and dilute it directly for quantitative RT-PCR Or quantitative PCR to measure the amount of small nucleic acids in plasma ( figure 1 ,2). Tissue processing: 100-500mg tissue samples were taken from animals injected with small nucleic acids. For tissue samples such as heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, etc., use tissue lysate (Qiagen: RLN or Lifetech: AM8540G) at 100 mg per ml of lysate, homogenize the tissue with a high-speed ti...
Embodiment 3
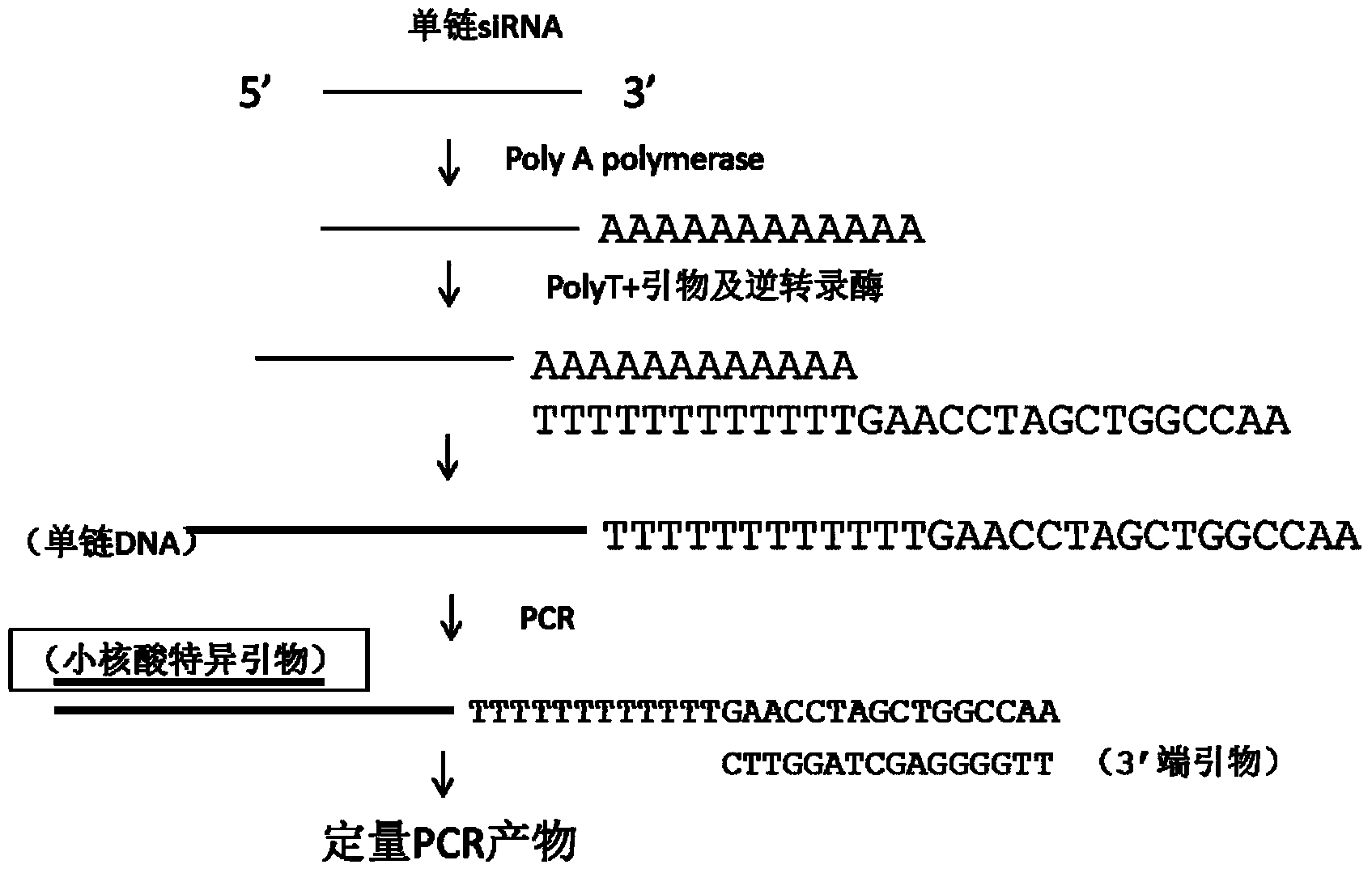
[0084] Embodiment 3: add Ploy A to the 3' end of small nucleic acid
[0085] If the small nucleic acid in the sample to be analyzed in Example 2 is ribonucleic acid (such as siRNA, miRNA), then a section of Poly A is added to the 3' end of the small nucleic acid with Poly A polymerase. Methods as below:
[0086] 1.25ul diluted plasma or tissue homogenate, then added in the following order:
[0087] 0.5ul 5X reaction solution
[0088] 0.25ul25mM MgCl 2
[0089] 0.1ul ATP
[0090] 0.05ul Poly A polymerase
[0091] 0.35ul water
[0092] Incubate at 37°C for 15 minutes.
[0093] The product should be: 5'TCCGAATAAACTCCAGGCCTAAAAAAAAAAAAAA...3'
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com