Methods for reducing electrical losses at the gaas/inp interface of bonded multijunction solar cells
A solar cell and bonding technology, applied in circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve problems that do not involve the electrical properties of the interface, and achieve the effect of low diffusion coefficient
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] 1) Bonding layer design and MOCVD epitaxial growth
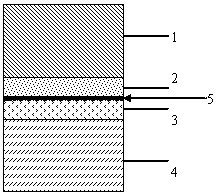
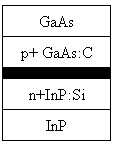
[0054] The (001) crystal plane n-type InP substrate and p-type GaAs substrate are used, and the doping concentration is 2×10 18 cm -3 , the thickness is 325um. C is used as the p-type dopant. The heavily doped p+GaAs bonding contact layer has a thickness of 40nm and a concentration of 2×10 19 cm -3 . Si is used as the n-type dopant. The thickness of the heavily doped n+InP bonding contact layer is 30nm, and the doping concentration is 7×10 18 cm -3 .
[0055] The bonding contact layer is grown on the GaAs and InP substrates by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth method. Using trimethylgallium and trimethylindium as gallium source and indium source respectively, using AsH 3 and PH 3 as a source of arsenic and phosphorus, respectively. The doping source of C is carbon tetrachloride, and the doping source of Si is silane.
[0056] After epitaxial growth such as MOCVD epitaxial gr...
Embodiment 2~5
[0068] Except having changed the bonding temperature in a bonding process to 500, 450, 400, and 350 degreeC respectively, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and obtained samples A2-A5.
Embodiment 6~9
[0070] Except having changed the bonding pressure in the bonding process to 0.5, 2, 12, and 20 MPa, respectively, it carried out similarly to Example 1, and obtained samples A6-A9.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com