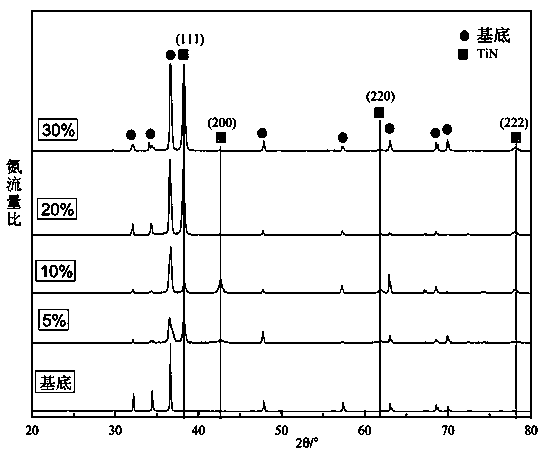
Method for improving bonding property of magnetron sputtering TiN coating on biomedical magnesium alloy surface
A biomedical and magnetron sputtering technology, which is applied in the direction of metal material coating process, coating, sputtering plating, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory bonding performance, insufficient continuity and integrity of surface coating, etc. Achieve the effect of reducing friction coefficient, improving bonding performance and simple operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) Surface pretreatment of biomedical magnesium alloys
[0026] Grind the Mg-1.87Nd-0.36Sr-0.31Zr biomedical magnesium alloy on the pre-grinding machine successively with water sandpaper of models 400#, 600#, 800#, 1000# until there are no obvious scratches on the surface of the magnesium alloy; Then the ground sample was polished on a polishing machine with a diamond polishing agent; the polished sample was placed in acetone and ethanol in turn for ultrasonic cleaning for 20 minutes, and finally dried with nitrogen for use.
[0027] (2) Installation of magnesium alloy substrate
[0028] Install the surface-pretreated magnesium alloy substrate on the tray that comes with the magnetron sputtering equipment, and fix it on the side with pins, which can not only prevent falling off, but also facilitate the complete coating of the entire surface of the substrate.
[0029] (3) Gradient bias Ti transition layer
[0030] Put the tray with the magnesium alloy substrate into t...
Embodiment 2
[0035] The operation methods of step (1) and step (2) are as shown in Example 1.
[0036] (3) Gradient bias Ti transition layer
[0037] Put the tray with the magnesium alloy substrate into the sputtering chamber, and the target material used for sputtering is metal Ti (diameter 80mm, thickness 5mm) with a purity of 99.8%. The Ti transition layer was deposited by a DC gradient bias method, that is, the gradient bias voltage was 0V / -10V / -30V / -50V, each bias condition was deposited for 2.5 minutes, and the total deposition time of the transition layer was 10 minutes. The distance between the target and the substrate during deposition is 60 mm, the substrate is cooled by water, and the background vacuum is 8×10 -4 Pa, working pressure 0.5 Pa, DC power 150 W, argon flow 30 ml min -1 (99.99% high-purity argon).
[0038] (4) TiN coating deposited by magnetron sputtering
[0039] Under the mixed conditions of nitrogen (99.99% high-purity nitrogen) and argon (99.99% high-purity a...
Embodiment 3
[0042] The operation methods of step (1) and step (2) are as shown in Example 1.
[0043] (3) Gradient bias Ti transition layer
[0044] Put the tray with the magnesium alloy substrate into the sputtering chamber, and the target material used for sputtering is metal Ti (diameter 80mm, thickness 5mm) with a purity of 99.8%. The Ti transition layer was deposited by DC gradient bias method, that is, the gradient bias voltage was -5V / -10V / -20V / -35V / -50V, each bias condition was deposited for 2 minutes, and the total deposition time of the transition layer was 10 minutes. The distance between the target and the substrate during deposition is 60 mm, the substrate is cooled by water, and the background vacuum is 7×10 -4 Pa, working pressure 0.5 Pa, DC power 150 W, argon flow 30 ml min -1 (99.99% high-purity argon).
[0045] (4) TiN coating deposited by magnetron sputtering
[0046] Under the mixed conditions of nitrogen (99.99% high-purity nitrogen) and argon (99.99% high-purity...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com