Material for efficiently removing basic nitrogen compounds in oils
A technology of nitrides and modified materials, which is applied in the petroleum industry, refined hydrocarbon oil, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems that there are no literatures to discuss the adsorption and application of nitrogen-containing compounds in graphite oxide, and achieve low price, easy regeneration, and source wide range of effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Oxidation treatment of original activated carbon AC: Mix 5 g of commercial activated carbon AC sample with 100 ml of ammonium persulfate sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 2 mol / L, and stir at 60 degrees for 3 hours. Separation by suction filtration, fully washed with deionized water to neutrality, and drying the sample in a 100-degree vacuum oven overnight to obtain oxidized activated carbon OAC with oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface;
Embodiment 2
[0041] Treatment of raw graphite GF: Add 69ml H2SO4 into the Erlenmeyer flask containing 3.0g graphite GF and 1.5g NaNO3 solid, stir evenly under cooling, slowly add 9.0g KMnO4 (make sure the temperature does not exceed 20 degrees), and continue stirring at room temperature for 1h. Then slowly add 140ml of deionized water, stir for 15min, add 420ml of deionized water again to dilute, add 30% H2O2 solution drop by drop until golden yellow appears in the solution, cool to room temperature, let stand overnight, discard the supernatant, and remove the lower layer The viscous liquid was dialyzed for 72 hours and then taken out, and then entered into the spray dryer with a peristaltic pump, at a rate of 2ml / min, and the temperature of the feed port was 120-140°C for spray drying to obtain oxidized modified graphite GO;
Embodiment 3
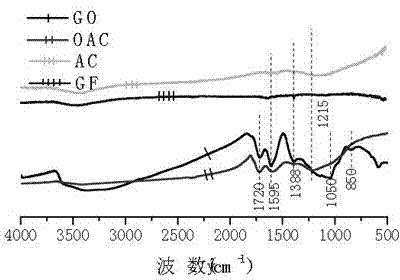
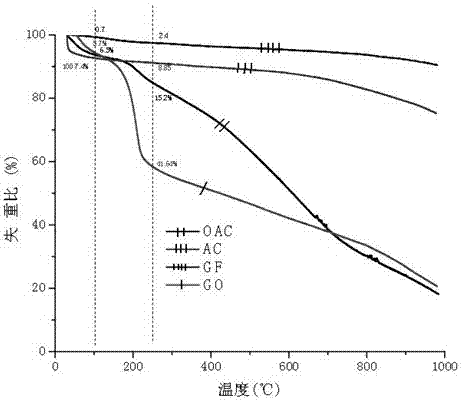
[0043] Characterization of the physical and chemical properties of the adsorption material: The elemental analysis data in Table 1 show that the oxygen content of the oxidized materials OAC and GO is significantly higher than that of the pre-oxidized materials AC and GF, and GO is slightly higher than that of OAC.
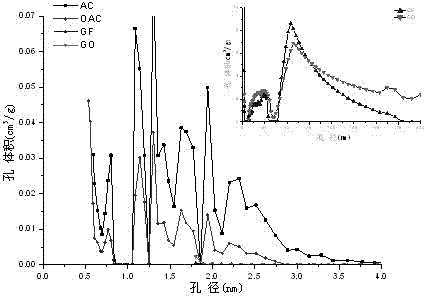
[0044] From the physical adsorption analysis data in Table 2, it can be seen that the BET specific surface area of AC and OAC is significantly higher than that of GF and GO. After oxidation, the BET specific surface area of OAC is significantly smaller than that of AC, mainly due to the well-developed pore structure in the AC material, which causes the collapse of the pore structure during the oxidation process. However, the BET specific surface area of GF is similar to that of GO, which is due to the underdeveloped mesopore structure of GF materials.
[0045] Table 1. Elemental analysis data for four adsorbent materials
[0046]
[0047] Table 2. Spe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com